|
Jackpot Nebula
The Jackpot Nebula is a large luminous Lyman-Alpha nebula located at a distance of z=2.041 with a size of 350 kpc. It has four quasars A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass rangi ... embedded within it and a overdensity of Lyman-Alpha emitting galaxies. The four quasars embedded within the Jackpot Nebula irradiate the nebula causing it to emitting light. References {{nebula-stub Nebulae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
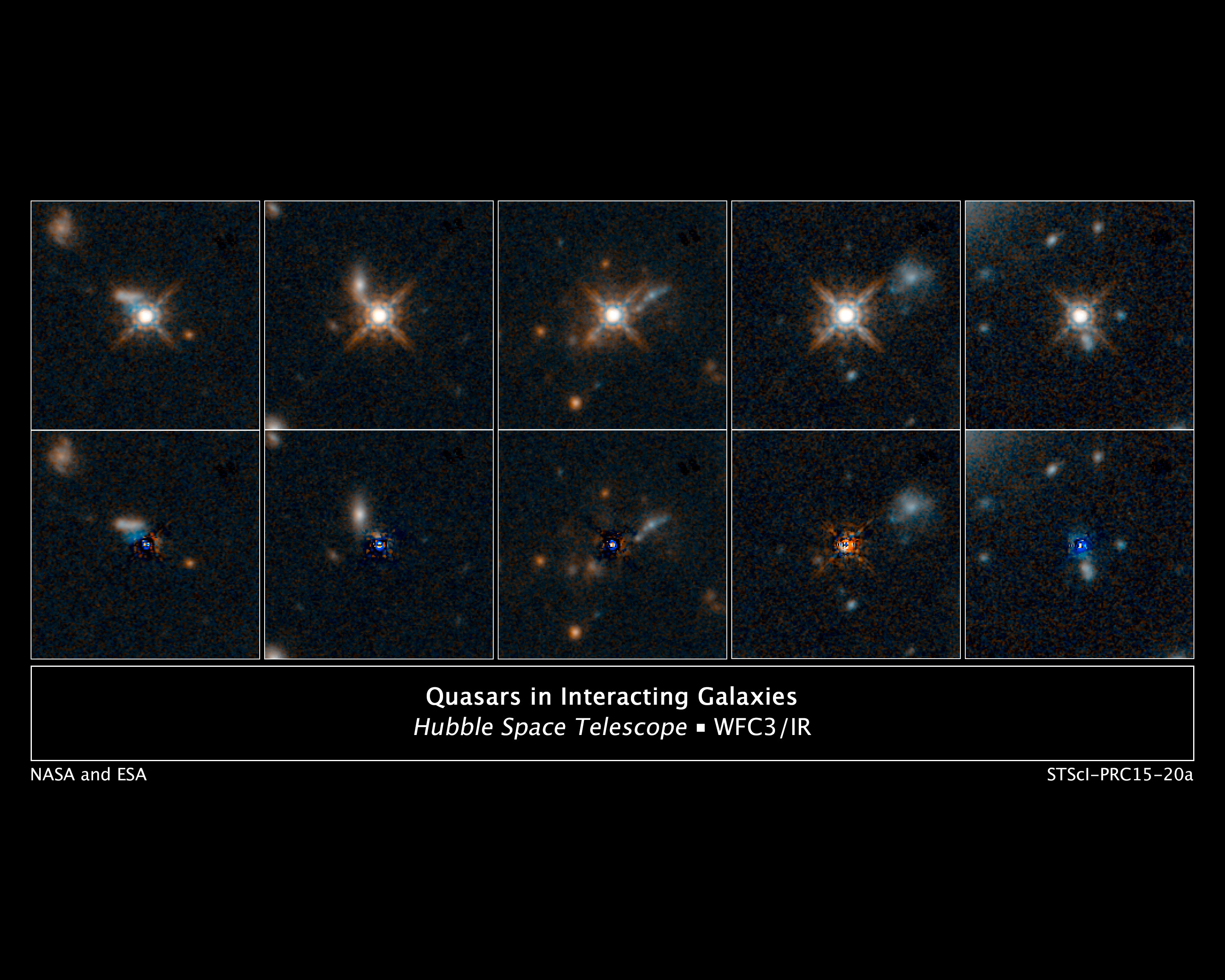
Quasars
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous Accretion disk, accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosity, luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Quasars are usually categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of Expansion of the universe, cosmological origin. The term originated as a Contraction (grammar), contraction of "quasi-stellar ''[star-like]'' radio source"—because they were first identified during the 1950s as sources of radio-wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasar
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous Accretion disk, accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosity, luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Quasars are usually categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of Expansion of the universe, cosmological origin. The term originated as a Contraction (grammar), contraction of "quasi-stellar ''[star-like]'' radio source"—because they were first identified during the 1950s as sources of radio-wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyman-alpha Emitter
A Lyman-alpha emitter (LAE) is a type of distant galaxy that emits Lyman-alpha radiation from neutral hydrogen. Most known LAEs are extremely distant, and because of the finite travel time of light they provide glimpses into the history of the universe. They are thought to be the progenitors of most modern Milky Way type galaxies. These galaxies can be found nowadays rather easily in narrow-band searches by an excess of their narrow-band flux at a wavelength which may be interpreted from their redshift : 1+z=\frac where z is the redshift, \lambda is the observed wavelength, and 1215.67 Å is the wavelength of Lyman-alpha emission. The Lyman-alpha line in most LAEs is thought to be caused by recombination of interstellar hydrogen that is ionized by an ongoing burst of star formation. Such Lyman alpha emission was first suggested as a signature of young galaxies by Bruce Partridge and P. J. E. Peebles in 1967. Experimental observations of the redshift of LAEs are importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |