|
Jack Parsons (other)
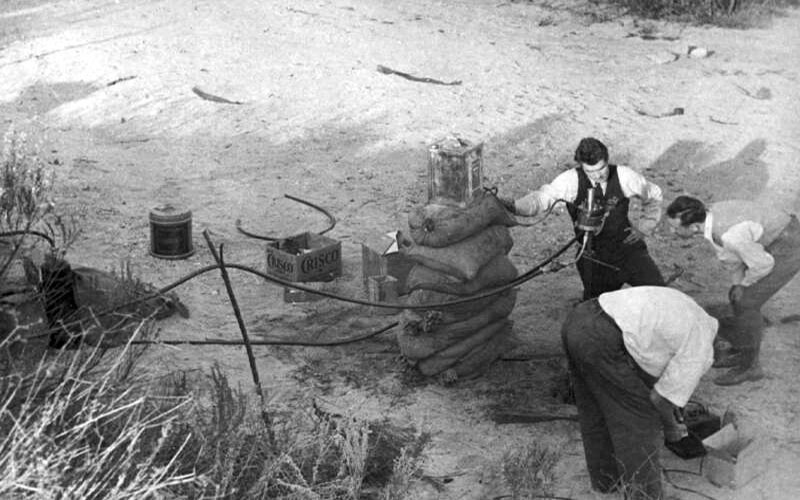
John Whiteside Parsons (born Marvel Whiteside Parsons; October 2, 1914 – June 17, 1952) was an American Aerospace engineering, rocket engineer, chemist, and Thelemite, Thelemite occultist. Parsons was one of the principal founders of both the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Aerojet. He invented the first rocket engine to use a Castability, castable, Composite material, composite rocket propellant, and pioneered the advancement of both Liquid-fuel rocket, liquid-fuel and Solid-fuel rocket, solid-fuel rockets. Parsons was raised in Pasadena, California. He began Amateur rocketry, amateur rocket experiments with school friend Edward Forman in 1928. Parsons was admitted to Stanford University but left before graduating due to financial hardship during the Great Depression. In 1934, Parsons, Forman, and Frank Malina formed the Caltech-affiliated Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory (GALCIT) Rocket Research Group, with support by GALCIT chairman Theodore von Kármán. The group w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasadena, California
Pasadena ( ) is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States, northeast of downtown Los Angeles. It is the most populous city and the primary cultural center of the San Gabriel Valley. Old Pasadena is the city's original commercial district. Its population was 138,699 at the 2020 census, making it the 45th-largest city in California and the ninth-largest in Los Angeles County. Pasadena was incorporated on June 19, 1886, 36 years after the city of Los Angeles but still one of the first in what is now Los Angeles County. Pasadena is home to many scientific, educational, and cultural institutions, including the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena City College, Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Fuller Theological Seminary, Theosophical Society, Parsons Corporation, Art Center College of Design, the Planetary Society, Pasadena Playhouse, the Ambassador Auditorium, the Norton Simon Museum, and the USC Pacific Asia Museum. Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms. Chemists carefully measure substance proportions, chemical reaction rates, and other chemical properties. In Commonwealth English, pharmacists are often called chemists. Chemists use their knowledge to learn the composition and properties of unfamiliar substances, as well as to reproduce and synthesize large quantities of useful naturally occurring substances and create new artificial substances and useful processes. Chemists may specialize in any number of Chemistry#Subdisciplines, subdisciplines of chemistry. Materials science, Materials scientists and metallurgists sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Malina
Frank Joseph Malina (October 2, 1912 — November 9, 1981) was an American aeronautical engineer and painter, known for his pioneering work in early rocketry. Early life Malina was born in Brenham, Texas. His father came from Moravia. Frank's formal education began with a degree in mechanical engineering from Texas A&M University in 1934. The same year he received a scholarship to study mechanical engineering at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), where he obtained his doctoral degree in 1940. In 1935, while a graduate student at Caltech, Malina persuaded Professor of Aeronautics Theodore von Kármán to allow him to pursue studies into rocketry and rocket propulsion. The formal goal was development of a sounding rocket. Malina and five associates (including Jack Parsons and Qian Xuesen) became known at Caltech as the "Suicide Squad" because of their dangerous experiments (and failures) when testing rocket motor designs. Malina's group was forced to move their o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and business failures around the world. The economic contagion began in 1929 in the United States, the largest economy in the world, with the devastating Wall Street stock market crash of October 1929 often considered the beginning of the Depression. Among the countries with the most unemployed were the U.S., the United Kingdom, and Weimar Republic, Germany. The Depression was preceded by a period of industrial growth and social development known as the "Roaring Twenties". Much of the profit generated by the boom was invested in speculation, such as on the stock market, contributing to growing Wealth inequality in the United States, wealth inequality. Banks were subject to laissez-faire, minimal regulation, resulting in loose lending and wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Forman
Edward Seymour Forman (December 3, 1912 – February 12, 1973) was an American engineer and inventor known for his pioneering work in early rocketry in the United States. Forman, along with his collaborators in Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology (GALCIT), demonstrated the first practical jet-assisted take-off (JATO) of an aircraft in the United States. Forman was among the GALCIT innovators that went on to found Aerojet General Corporation, the largest rocket technology manufacturer in the 1940s,Theodore von Kármán with Lee Edson (1967) ''The Wind and Beyond'', Little, Brown and Company and the GALCIT Rocket Research Group itself became the precursor of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Early life and education Forman was born in Gillespie, Illinois, the youngest of four brothers. The family moved to Pasadena, California and Forman attended Washington Junior High School, where he met Jack Parsons, who would become his lifelong collabora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Rocketry
An amateur () is generally considered a person who pursues an avocation independent from their source of income. Amateurs and their pursuits are also described as popular, informal, self-taught, user-generated, DIY, and hobbyist. History Historically, the amateur was considered to be the ideal balance between pure intent, open mind, and the interest or passion for a subject. That ideology spanned many different fields of interest. It may have its roots in the ancient Greek philosophy of amateur athletes competing in the Olympics. The ancient Greek citizens spent most of their time in other pursuits, but competed according to their natural talents and abilities. The "gentleman amateur" was a phenomenon among the gentry of Great Britain from the 17th century until the 20th century. With the start of the Age of Reason, with people thinking more about how the world works around them, (see science in the Age of Enlightenment), things like the cabinets of curiosities, and the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-fuel Rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses Rocket propellant#Solid chemical propellants, solid propellants (fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder. The inception of gunpowder rockets in warfare can be credited to the ancient Chinese, and in the 13th century, the Mongols played a pivotal role in facilitating their westward adoption. All rockets used some form of solid or powdered propellant until the 20th century, when liquid-propellant rockets offered more efficient and controllable alternatives. Because of their simplicity and reliability, solid rockets are still used today in military armaments worldwide, model rockets, solid rocket boosters and on larger applications. Since solid-fuel rockets can remain in storage for an extended period without much propellant degradation, and since they almost always launch reliably, they have been frequently used in military applications such as missiles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-fuel Rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket uses a rocket engine burning liquid propellants. (Alternate approaches use gaseous or solid propellants.) Liquids are desirable propellants because they have reasonably high density and their combustion products have high specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low. Types Liquid rockets can be monopropellant rockets using a single type of propellant, or bipropellant rockets using two types of propellant. Tripropellant rockets using three types of propellant are rare. Liquid oxidizer propellants are also used in hybrid rockets, with some of the advantages of a solid rocket. Bipropellant liquid rockets use a liquid fuel such as liquid hydrogen or RP-1, and a liquid oxidizer such as liquid oxygen. The engine may be a cryogenic rocket engine, where the fuel and oxidizer, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are gases which have been liquefied at very low temperatures. Most designs of liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsylvania, United States. Founded in 1855 as Farmers' High School of Pennsylvania, Penn State was named the state's first land-grant university eight years later, in 1863. Its primary campus, known as Penn State University Park, is located in State College, Pennsylvania, State College and College Township, Pennsylvania, College Township. Penn State enrolls more than 89,000 students, of which more than 74,000 are undergraduates and more than 14,000 are postgraduates. In addition to its land-grant designation, the university is a National Sea Grant College Program, sea-grant, National Space Grant College and Fellowship Program, space-grant, and one of only six Sun Grant Association, sun-grant universities. It is Carnegie Classification of Instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Flight Research Center
The NASA Neil A. Armstrong Flight Research Center (AFRC) is an aeronautical research center operated by NASA. Its primary campus is located inside Edwards Air Force Base in California and is considered NASA's premier site for aeronautical research. AFRC operates some of the most advanced aircraft in the world and is known for many aviation firsts, including supporting the first crewed airplane to exceed the speed of sound in level flight (Bell X-1), highest speed by a crewed, powered aircraft (North American X-15), the first pure digital fly-by-wire aircraft (F-8 DFBW), and many others. AFRC operated a second site next to Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, known as Building 703, once the former Rockwell International/North American Aviation production facility. There, AFRC housed and operated several of NASA's Science Mission Directorate aircraft including SOFIA (Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy), a DC-8 Flying Laboratory, a Gulfstream C-20A UAVSAR and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Propellant
Rocket propellant is used as reaction mass ejected from a rocket engine to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines. Overview Rockets create thrust by expelling mass rear-ward, at high velocity. The thrust produced can be calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate of the propellants by their exhaust velocity relative to the rocket (specific impulse). A rocket can be thought of as being accelerated by the pressure of the combusting gases against the combustion chamber and nozzle, not by "pushing" against the air behind or below it. Rocket engines perform best in outer space because of the lack of air pressure on the outside of the engine. In space it is also possible to fit a longer nozzle without suffering from flow separation. Most chemical propellants release energy through redox chemistry, more specifically combustion. As such, both an oxidizing agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
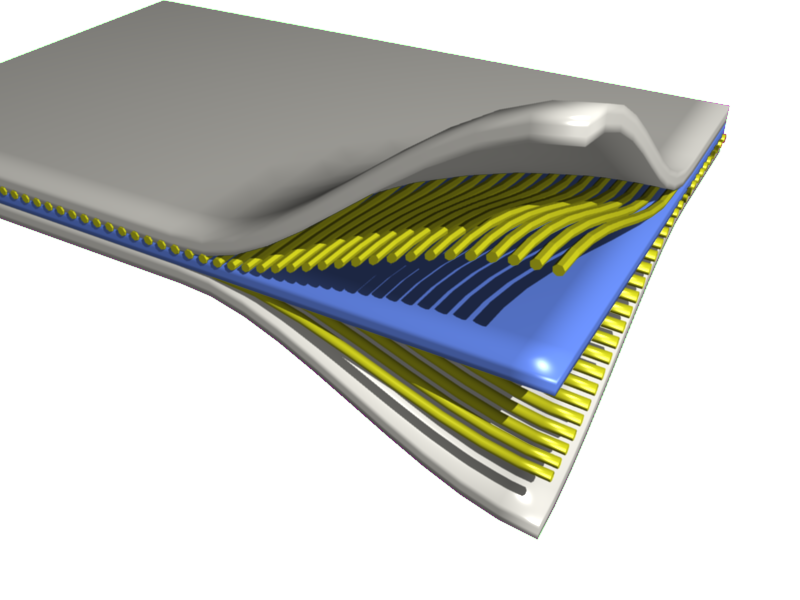
Composite Material
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called ''composite laminates''. Typical engineered composite materials are made up of a binding agent forming the ''matrix'' and a Filler (materials), filler material (particulates or fibres) giving ''substance'', e.g.: * Concrete, reinforced concrete and masonry with cement, lime or Mortar (masonry), mortar (which is itself a composite material) as a binder * Composite wood such as glulam and plywood with wood glue as a binder * Reinforced plastics, such as fiberglass and fibre-rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |