|
Iwakiyama Ryūta
Iwakiyama Ryūta (born March 2, 1976, as Ryūta Tsushima in Aomori Prefecture, Japan), is a former sumo wrestler. A former amateur sumo champion, he turned professional in 2000 and reached the top division at the end of 2002. The highest rank he reached was ''komusubi.'' He was a runner-up in one tournament and earned two special prizes in his career. After his retirement in 2010 he became an elder of the Japan Sumo Association under the name Sekinoto. Early life and sumo background He was born in Hirosaki, Nakatsugaru District. After a successful start in amateur sumo at Aomori University, Tsushima worked as a member of staff at Aomori Yamada High School after graduating, not joining the professional sport until the age of 24 in July 2000. He was recruited by ex-''komusubi'' Ryōgoku, a former amateur champion himself, and joined his Sakaigawa stable (then known as Nakadachi stable). His ''shikona'' or fighting name came from Mount Iwaki, which is near his home town. Career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakaigawa Stable
is a stable of sumo wrestlers, part of the Dewanoumi group of stables. It was established in its modern form on 25 May 1998 by former ''komusubi'' Ryōgoku Kajinosuke IV, who branched off from Dewanoumi stable. It was originally called Nakadachi stable, but when Sakaigawa-''oyakata'' (the 50th ''yokozuna'' Sadanoyama) reached the Japan Sumo Association's mandatory retirement age in February 2003, he passed on the Sakaigawa name, and the stable was renamed. As of January 2023, it had 19 wrestlers, with four of them ranked in the two top professional divisions. The stable is known for its rigorous training. At the heart of the stable are written ten rules, these having been written by the master (former Ryōgoku) and Ōnaruto (former Yoshinotani) at the time of the stable's foundation. It has become traditional for wrestlers to recite them at the end of training. In July 2005, Satsuki, a ''sandanme'' wrestler encountered a fire in Aichi Prefecture during the Nagoya tournament, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandanme
Professional sumo as administered by the Japan Sumo Association is divided into six ranked divisions. Wrestlers are promoted and demoted within and between these divisions based on the merit of their win–loss records in official tournaments. For more information, see ''kachi-koshi'' and ''make-koshi''. Wrestlers are also ranked within each division. The higher a wrestler's rank within a division is, the general level of opponents he will have to face becomes stronger. According to tradition, each rank is further subdivided into East and West, with East being slightly more prestigious, and ranked slightly higher than its West counterpart. The divisions, ranked in order of hierarchy from highest to lowest, are as follows: ''Makuuchi'' , or , is the top division. It is fixed at 42 wrestlers who are ranked according to their performance in previous tournaments. At the top of the division are the four ranks of "titleholders", or "champions" called the ''san'yaku'', comprising '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Times
''The Japan Times'' is Japan's largest and oldest English-language daily newspaper. It is published by , a subsidiary of News2u Holdings, Inc. It is headquartered in the in Kioicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo. History ''The Japan Times'' was launched by on 22 March 1897, with the goal of giving Japanese people an opportunity to read and discuss news and current events in English language, English to help Japan participate in the international community. In 1906, Zumoto was asked by Japanese Resident-General of Korea Itō Hirobumi to lead the English-language newspaper ''The Seoul Press''. Zumoto closely tied the operations of the two newspapers, with subscriptions of ''The Seoul Press'' being sold in Japan by ''The Japan Times'', and vice versa for Korea. Both papers wrote critically of Korean culture and civilization, and advocated for Korea under Japanese rule, Japan's colonial control over the peninsula in order to civilize the Koreans. The newspaper was independent of government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Infarction
Cerebral infarction, also known as an ischemic stroke, is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain (cerebral infarct). In mid to high income countries, a stroke is the main reason for disability among people and the 2nd cause of death. It is caused by disrupted blood supply (ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply ( hypoxia). This is most commonly due to a thrombotic occlusion, or an embolic occlusion of major vessels which leads to a cerebral infarct . In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis. Classification There are various classification systems for cerebral infarcts, some of which are described below. * The Oxford Community Stroke Project classification (OCSP, also known as the Bamford or Oxford classification) relies primarily on the initial symptoms. Based on the extent of the symptoms, the stroke episode is classified as total anterior circulation infarct (TACI), partial anterior circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makuuchi
, or , is the top division of Professional sumo divisions, the six divisions of professional sumo. Its size is fixed at 42 wrestlers (''rikishi''), ordered into five ranks according to their ability as defined by their performance in previous tournaments. This is the only division that is featured on NHK's standard live coverage of sumo tournaments. The lower divisions are shown on their satellite coverage, with only the ''makuuchi'' broadcast having bilingual English commentary. ''Makuuchi'' literally means "inside the curtain", a reference to the early period of professional sumo, when there was a curtained-off area reserved for the top ranked wrestlers, to sit before appearing for their bouts. Wrestlers are considered for Promotion and relegation, promotion or demotion in rank before each grand tournament according to their performance in the one previous. Generally, a greater number of wins than losses (''kachi-koshi'') results in a promotion, and the reverse (''makekoshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kachi-koshi
The following words are terms used in sumo is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ... wrestling in Japan. A B C D E F G H I J K M N O R S T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yūshō
is the term for a championship in Japanese. This article focuses on championships in the sport of professional sumo. It is awarded in each of the six annual '' honbasho'' or official tournaments, to the wrestler who wins the most bouts. ''Yūshō'' are awarded in all six professional sumo divisions. The prize money for a top ''makuuchi'' division championship is currently 10 million yen, while for the lowest '' jonokuchi'' division the prize is 100,000 yen. A runner-up is referred to as a ''jun-yūshō.'' Perhaps surprisingly, considering that most of the interest in tournaments today revolves around who will win the ''yūshō'', the concept of a prize for a wrestler's individual performance is a relatively recent one. Legendary wrestlers such as Tanikaze and Raiden are credited today with winning many championships, but they are all unofficial and are really nothing more than a "best tournament record." The individual ''yūshō'' idea evolved gradually, from wrestlers sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanshō (Sumo)
Sanshō may refer to: * Sanshō (sumo) (), three special prizes awarded at official sumo tournaments *Sanshō (spice) (), name of a plant, ''Zanthoxylum piperitum'', also known as "Japanese pepper" or "Korean pepper" *, a 1954 film directed by Kenji Mizoguchi People with the given name Sanshō include: * Kawarazaki Sanshō (1838–1903), Japanese kabuki actor * Sansho Shinsui (1947–2017), Japanese film and television actor See also *''Acmella oleracea'', species of flowering herb sometimes called "Sanshō buttons" *Sichuan pepper, ''Zanthoxylum bungeanum'', not to be confused with the Japanese spice sanshō *Sanshou Sanda (), formerly Sanshou (), is the official China, Chinese kickboxing full-contact combat sport. In Chinese language, Chinese Language, "Sanda" originally referred to independent and separate training and combat techniques in contrast to "Ta ..., Chinese self-defense system and combat sport {{disambig, given name Japanese masculine given names Masculine gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinboshi
is a notation used in professional sumo is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ... wrestling to record a lower-ranked ('' maegashira'') wrestler's victory over a '' yokozuna''. It is believed that the term stems from the usage of the terms ''shiroboshi'' (lit: white star) to designate a bout victory, and ''kuroboshi'' (black star) to designate a bout defeat. Thus, a "gold star" designates it as a special victory. The word ''kinboshi'' first came into popular use in the Taishō period (1912–1926), and the system of monetarily awarding a ''maegashira'' who defeated a ''yokozuna'' in an official tournament began in January, 1930. A ''kinboshi'' victory increases the balance in the ''maegashiras '' mochikyūkin'' account by 10 yen. This balance is converted using a multip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
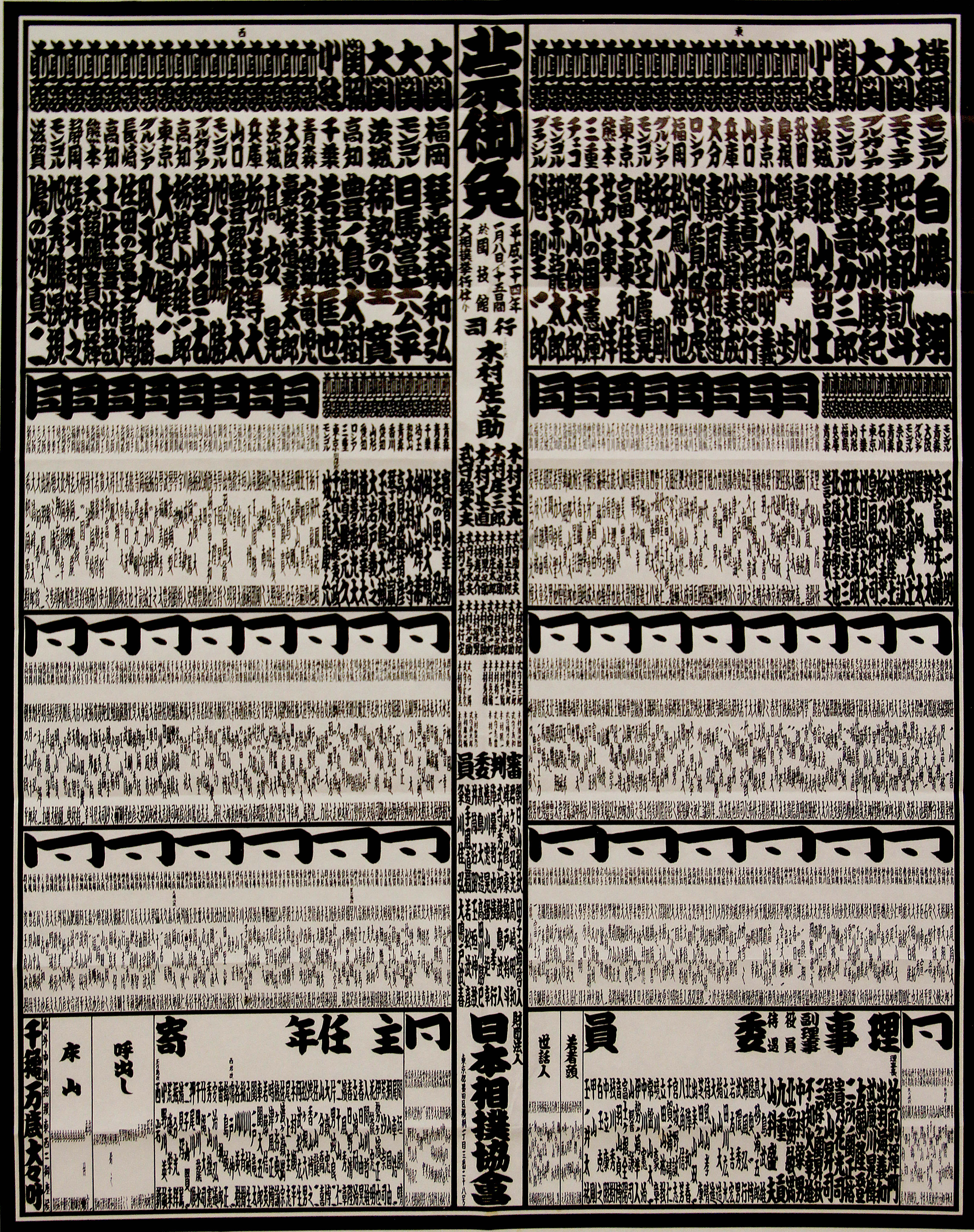
Banzuke
A , officially called is a document listing the rankings of professional sumo wrestlers published before each official tournament ('' honbasho''). The term can also refer to the rankings themselves. The document is normally released about two weeks before the tournament begins. On the ''banzuke'', wrestlers are divided into East, which is printed on the right, and West, which is printed on the left. Each wrestler's full ''shikona'' (ring name), hometown and rank is also listed. The top of the page starts with the highest ranked ''makuuchi'' wrestlers printed in the largest characters, down to the wrestlers in the lowest divisions which are written in much smaller characters. The names of '' gyōji'' (sumo referees), '' yobidashi'' (ushers/handymen), '' shimpan'' (judges), '' oyakata'' (elders of the Japan Sumo Association), and occasionally ''tokoyama'' (hairdressers) are also listed. While not as old as sumo itself, the form and production of this document can be traced as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumo May09 Iwakiyama
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by throwing, shoving or pushing him down). Sumo originated in Japan, the only country where it is practised professionally and where it is considered the national sport. It is considered a ''gendai budō'', which refers to modern Japanese martial arts, but the sport has a history spanning many centuries. Many ancient traditions have been preserved in sumo, and even today the sport includes many ritual elements, such as the use of salt purification, from Shinto. Life as a wrestler is highly regimented, with rules regulated by the Japan Sumo Association. Most sumo wrestlers are required to live in communal sumo training stables, known in Japanese as '' heya'', where all aspects of their daily livesfrom meals to their manner of dressare dictated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |