|
Ivane Mkhargrdzeli
Ivane I Zakarian (; ka, ივანე I მხარგრძელი, tr) was an Armenian prince, and a Court official of the Kingdom of Georgia holding the offices of '' Msakhurtukhutsesi'' (Majordomo) and ''Atabeg'' (Governor General) for Queen Tamar of Georgia during the early 13th centuries. He was a prince of the Zakarid dynasty, the son of Sargis Zakarian, and the younger brother and successor of Zakare II Zakarian. He was also ruler of feudal lands in the Kingdom of Georgia. Biography The brothers, Zakare and Ivane Zakarian, who were sons of Sargis, were the most successful representatives of the family, who were military commanders under Queen Tamar. Zakare and Ivane took Dvin in 1193 from the Seljuk Eldiguzids. They also took Sevan, Bjni, Amberd and Bargushat, and all the towns above the city of Ani, up to the bridge of Khodaafarin bridge. Around the year 1199, they took the city of Ani, and in 1201, Tamar gave Ani to them as a principality. Eventually, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harichavank
The Harichavank (; transliterated as ''Harijavank'' or ''Harichavank'') is a 7th century Armenian architecture, Armenian monastery located near the village of Harich, Armenia, Harich (Armenian: Հառիճ) in the Shirak Province of Armenia. The village is 3 km southeast of the town of Artik. History Harichavank is known as one of the most famous monastic centers in Armenia, and it was especially renowned for its school and scriptorium. Archaeological excavations of 1966 indicate that Harich was in existence during the 2nd century BC, and was one of the more well-known fortress towns in Armenia. The oldest part of this Armenian monastery is the Church of Gregory the Illuminator, St. Gregory the Enlightener (Սբ. Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ); it is a domed structure that is usually placed in the category of so-called "Mastara-style" churches (named after the fifth century church of Church of St. John, Mastara, St. Hovhannes in the village of Mastara, in the southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Tribes
Kurdish tribes are tribes of Kurds, Kurdish people, an ethnic group from the geo-cultural region of Kurdistan in West Asia, Western Asia. The tribes are socio-political and generally also a territorial unit based on descent and kinship, real or putative, with a characteristic internal structure. They are naturally divided into a number of sub-tribes, and each of these sub-tribes again are divided into smaller units: clans, lineages and households. Designation Each Kurdish tribe use different kinds of terms to designate "Tribe", "sub-tribe", "Clan", "lineage" and "household"; 'Ahiret, Tira, Hoz, il, Khel, Tayfa or Taifa, Zuma and Rama. These terms are used loosely and interchangeably despite the tribal structure and organization of all Kurdish tribes are almost the same. History Early record In the 9th century, it was reported by Ibn Khordadbeh, Ibn khurdubah that Kurdish tribes used the word Zūma to designate tribes (, ; ). The 9th century historian, Ya'qubi, recorded present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
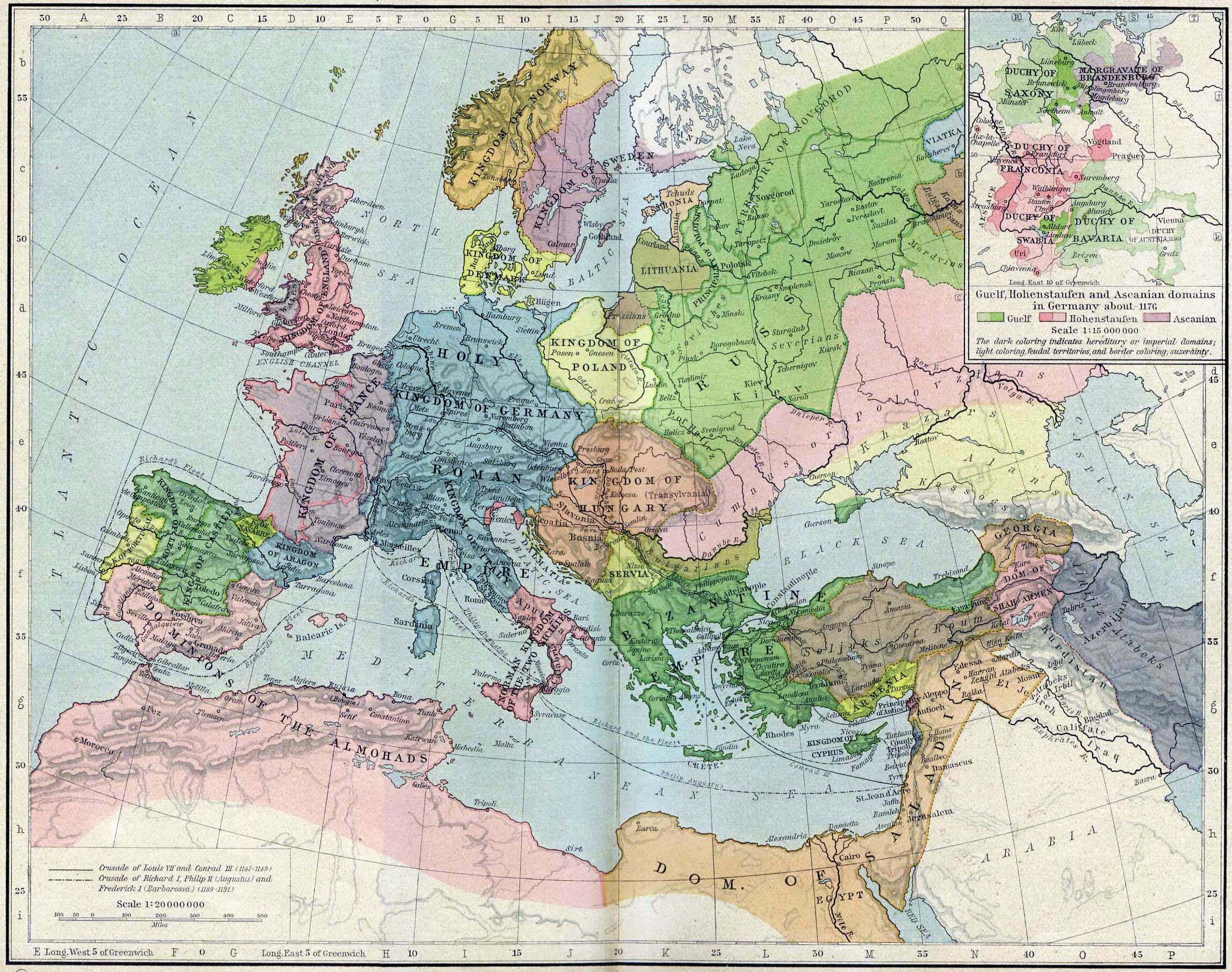
Zakarid Armenia
Zakarid Armenia () alternatively known as the Zakarid Period, describes a historical period in the Middle Ages during which the Armenian vassals of the Kingdom of Georgia were ruled by the Zakarid-Mkhargrzeli dynasty. The city of Ani was the capital of the princedom. The Zakarids were vassals to the Bagrationi dynasty in Georgia, but frequently acted independently and at times titled themselves as kings. In 1236, they fell under the rule of the Mongol Empire as a vassal state with local autonomy. During the reign of George V and Bagrat V, the Zakarid territories once again reverted to the Kingdom of Georgia. The Zakarid dynasty continued to rule Ani until around 1350, when it was conquered and ravaged by the Chobanids. Inception Armenian historians of the 13th century Kirakos Gandzaketsi and Vardan the Great reported that Ivane's great grandfather "broke away from the Kurdish tribe of Babir", and established himself in northern Armenia. He then became a vassal and a possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khodaafarin Bridges
Khudafarin Bridges or Khoda Afarin Bridges (, , ), are two arch bridges located at the border of Azerbaijan and Iran connecting the northern and southern banks of the Aras River. History Communication between the Caucasus and the historical Iranian region of Azerbaijan has long been hampered by the Aras River. Therefore, bridges have been built over it since ancient times. The Khudafarin bridge is strategically important and is considered one of the historical main points of contact between the Caucasus and the Iranian Azerbaijan. This bridge has also been called the "Khosrow Bridge" and "Aras Bridge" in chronicles. The bridge is first attested in the first half of the 14th century, in the '' Nuzhat al-Qulub'' by the Iranian geographer Hamdallah Mustawfi. The origin of the bridge's name has been the subject of several stories, most of which are mixed with mythology. According to the 18th-century Iranian historian Mohammad Kazem Marvi, the bridge is known as "Khudafarin" ("God c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bjni
Bjni (), is a village in the Kotayk Province of Armenia. It is situated in a valley between canyon walls and a small river. The village is one of the prominent centers of education and culture of ancient and medieval Armenia. It is the birthplace of the 11th-century scholar Grigor Magistros. History The first recorded mention of the village was by the 5th- to 6th-century chronicler and historian Ghazar Parpetsi. In the 11th century, the lands of Bjni were passed to the Pahlavuni family and played a significant role in Armenian life during the Bagratuni dynasty. Around this time, King Hovhannes-Smbat made the decision that the lands should become an Episcopal settlement. In 1066, the election for the Patriarch took place in Bjni. At the beginning of the 13th century, the lands were passed on to the Zakharyan family. A century later in the years 1387-1388 the Turko-Mongol conqueror Timur Lenk destroyed the village of Bjni. The French traveler Jean Chardin visited the village in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eldiguzids
The Ildegizids, EldiguzidsC.E. Bosworth, "Ildenizids or Eldiguzids", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Edited by P.J. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs et al., Encyclopædia of Islam, 2nd Edition., 12 vols. with indexes, etc., Leiden: E. J. Brill, 1960–2005. Vol 3. pp 1110-111. Excerpt 1: "Ildenizids or Eldiguzids, a line of Atabegs of Turkish slave commanders who governed most of northwestern Persia, including Arran, most of Azarbaijan, and Djibal, during the second half of the 6th/12th century and the early decades of the 7th/13th century". Excerpt 2: "The Turkish Ildenizids shared to the full in the Perso-Islamic civilization" or Ildenizids, also known as Atabegs of Azerbaijan ( ''Atabakan-e Āzarbayjan)'' were an Atabegate of the Seljuk Empire, and a Sunni Muslim Turkic dynastyBritannica. ArticleEldegüzid dynasty Eldegüzid dynasty, also spelled Ildigüzid, Ildegüzid, Ildegizid, or Ildenizid, (1137–1225), Iranian atabeg dynasty of Turkis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. The empire spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia in the north to the Persian Gulf in the south, and it spanned the time period 1037–1308, though Seljuk rule beyond the Anatolian peninsula ended in 1194. The Seljuk Empire was founded in 1037 by Tughril (990–1063) and his brother Chaghri Beg, Chaghri (989–1060), both of whom co-ruled over its territories; there are indications that the Seljuk leadership otherwise functioned as a triumvirate and thus included Seljuk dynasty, Musa Yabghu, the uncle of the aforementioned two. During the formative phase of the empire, the Seljuks first advanced from their original homelands near the Aral Sea into Greater Kho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvin (ancient City)
Dvin ( or ; , ''Doúbios'' or Τίβιον, ''Tíbion''; , Dabīl or Doubil) was a large commercial city and the capital of early medieval Armenia. It was situated north of the previous ancient capital of Armenia, the city of Artaxata, along the banks of the Metsamor River, 35 km to the south of modern Yerevan Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev .... It is claimed it was one of the largest cities east of Constantinople prior to its destruction by the Mongols in the 13th century, but with an overall area of approximately 1 km2, it was far smaller than many of the great cities of Asia. It had an estimated population of 45,000 in 361, 47,000 in 622, and around 100,000 at its height in the 8th-9th centuries. Nyura Hakobyan proposed a peak population of 100,000 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia (), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a Middle Ages, medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in Anno Domini, AD. It reached Georgian Golden Age, its Golden Age of political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV of Georgia, David IV and Queen Tamar of Georgia, Tamar the Great from the 11th to 13th centuries. Georgia became one of the pre-eminent nations of the Eastern_Orthodoxy#Distribution, Christian East, and its pan-Caucasus, Caucasian empire and network of tributaries stretched from Eastern Europe to Anatolia and northern frontiers of History_of_Iran#Medieval_period, Iran, while Georgia also maintained religious possessions abroad, such as the Monastery of the Cross in Jerusalem and the Iviron, Monastery of Iviron in Greece. It is the principal historical precursor of present-day Georgia (country), Georgia. Lasting for several centuries, the kingdom fell to the Mongol invasions of Georgia, Mongol invasions in the 13th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakare II Zakarian
Zakaria Mkhargrdzeli (, ), was a Georgian prince and a Court official of the Kingdom of Georgia holding the office of '' amirspasalar'' (Commander-in-Chief) of the Georgian army for Queen Tamar of Georgia, during the late 12th and early 13th centuries. He was a member of the Mkargrdzeli dynasty, and ruler of feudal lands in the Kingdom of Georgia. Biography Zakare along with his father Sargis supported the rebellion of Prince Demna and the Orbelian family in 1177, however they soon sided with George III and fought for the monarchy against the insurgents. The rebellion was suppressed, and King George III elevated the Zakarid–Mkhargrdzeli family. Following the death of George III, Queen Tamar elevated Sargis Zakarian (Mkhargrdzeli)— a well-born valorous man, well-trained in battle — to the office of '' Amirspasalar'' ( Lord High Constable) and granted him possessions over Lori (which was deprived of from Kubasar). She gave presents to his elder son, Zakare, and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakarid Dynasty
The Zakarid dynasty, also Zakarids or Zakarians () were an Armenian noble dynasty, rulers of Zakarid Armenia (1201–1350) under the suzerainty of the Kingdom of Georgia, and from 1256 under the control of the Mongol Ilkhanate of Persia. Their dynastic name was formed in honour of Zakare, the famous servant of the Georgian King Tamar. They were also known by their Georgian nickname Mkhargrdzeli (, "Long-armed", in , ''Yerkaynbazuk''). A family legend says that this name was a reference to their Achaemenid ancestor Artaxerxes II the "Longarmed" (404–358 BC). According to Cyril Toumanoff / ''Encyclopædia Iranica'', they were an offshoot of the Armenian Pahlavuni family. The Zakarians considered themselves Armenians. During the 13th century, the Zakarids held the highest offices in the Georgian government, as ''Atabegs'' (Governor General) and ''Amirspasalars'' (Commander-in-Chief of the Army) of the Kingdom of Georgia. History The dynasty was of Armenian or Kurdish origin. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |