|
Ivan Andreyevich Tolstoy
Ivan Andreevich Tolstoy () (1644–1713) was a Russian officer in the army of Tsar Peter I. Ivan Andreevich was a member of prominent Tolstoy family, son of Andrey Vasiliyevich Tolstoy and Solomonida Miloslavskaya, older brother of Pyotr Andreyevich Tolstoy, distant relation of Maria Miloslavskaya (first wife of tzar Aleksey Mikhailovich). The royal relations became very dangerous for brothers Tolstoys after Peter I took the power, as he hated his half-sister Sophia and distrusted all her Miloslavsky relatives. Despite this Peter respected the abilities of the Tolstoy brothers and allowed them to follow a military career: ''Ah head, head, were you not so clever I should have cut it off long ago'' - he actually said to Pyotr Tolstoy. In 1703 Ivan Tolstoy was appointed Governor of Azov - the fortress and naval base on the Black Sea that was critically important in the confrontation between Russia and Turkey, bands of Don Cossacks and Kondraty Bulavin uprising. In 1708 Bulavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter I Of Russia
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman and Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a significant portion of the eastern Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a tsardom to an empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernized, and based on radical Enlightenment. In December 1699, he introduced the Julian calendar, and in 1703, he introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kondraty Bulavin
The Bulavin Rebellion or Astrakhan Revolt (; Восстание Булавина, ''Vosstaniye Bulavina'') was a war which took place in the years 1707 and 1708 between the Don Cossacks and the Tsardom of Russia. Kondraty Bulavin, a democratically elected Ataman of the Don Cossacks, led the Cossack rebels. The conflict was triggered by a number of underlying tensions between the Moscow government under Peter I of Russia, the Cossacks, and Russian peasants fleeing from serfdom in Russia to gain freedom in the autonomous Don area. It started with the 1707 assassination of Prince , the leader of Imperial army's punitive expedition to the Don area, by Don Cossacks under Bulavin's command. The end of the rebellion came with Bulavin's death in 1708. Underlying causes A number of social grievances were prevalent in the peasant population of Russia in the years leading up to the Bulavin Rebellion. Peter the Great's radical reforms designed to "Westernize" old Muscovy in the 18th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1713 Deaths
Events January–March * January 17 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore leads the Carolina militia out of Albemarle County, North Carolina, in a second offensive against the Tuscarora. Heavy snows force the troops to take refuge in Fort Reading, on the Pamlico River. * February 1 – Skirmish at Bender, Moldova: Charles XII of Sweden is defeated by the Ottoman Empire. * February 4 – Tuscarora War: The Carolina militia under Colonel James Moore leaves Fort Reading, to continue the campaign against the Tuscarora. * February 25 – Frederick William I of Prussia begins his reign. * March 1 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore's Carolina militia lays siege to the Tuscaroran stronghold of Fort Neoheroka, located a few miles up Contentnea Creek from Fort Hancock. * March 20 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore's Carolina militia launches a major offensive against Fort Neoheroka. * March 23 – Tuscarora War: Fort Neoheroka falls to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1644 Births
It is one of eight years (CE) to contain each Roman numeral once (1000(M)+500(D)+100(C)+(-10(X)+50(L))+(-1(I)+5(V)) = 1644). Events January–March * January 22 – The Royalist Oxford Parliament is first assembled by King Charles I of England. * January 26 – First English Civil War: Battle of Nantwich – The Parliamentarians defeat the Royalists, allowing them to end the 6-week siege of the Cheshire town. * January 30 **Dutch explorer Abel Tasman departs from Batavia in the Dutch East Indies (modern-day Jakarta in Indonesia) on his second major expedition for the Dutch East India Company, to map the north coast of Australia. Tasman commands three ships, ''Limmen'', ''Zeemeeuw'' and ''Braek'', and returns to Batavia at the beginning of August with no major discoveries. ** Battle of Ochmatów: Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth forces under hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski secure a substantial victory over the horde of Crimean Tatars under Tug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherkassk
Starocherkasskaya (), formerly Cherkassk (), is a rural locality (a ''stanitsa'') in Aksaysky District of Rostov Oblast, Russia, with origins dating from the late 16th century. It is located on the right bank of the Don River approximately upstream from the major Russian port city of Rostov-on-Don. It is famous for having been the center of Don Cossack culture and politics for nearly two centuries as the capital of the Don Host Oblast. Due to regular spring floods that submerged the small city on several occasions, the Cossacks moved their capital to higher ground at Novocherkassk in 1805. In and around Starocherkasskaya there are over forty noteworthy historical and cultural sites including the Resurrection (Voskresensky) Cathedral, completed in 1719, and its famous gilded wooden iconostasis. History A Cossack fortress on the island of what was later called ''Monastyrsky'' on the Don river was probably built before 1570 although it is first mentioned in chronicles from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pruth Campaign
The Prut (also spelled in English as Pruth; , ) is a river in Eastern Europe. It is a left tributary of the Danube, and is long. Part of its course forms Romania's border with Moldova and Ukraine. Characteristics The Prut originates on the eastern slope of Mount Hoverla, in the Carpathian Mountains in Ukraine (Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast). At first, the river flows to the north. Near Yaremche it turns to the northeast, and near Kolomyia to the south-east. Having reached the border between Moldova and Romania, it turns even more to the south-east, and then to the south. It eventually joins the Danube near Giurgiulești, east of Galați and west of Reni. Between 1918 and 1939, the river was partly in Poland and partly in Greater Romania (Romanian: ''România Mare''). Prior to World War I, it served as a border between Romania and the Russian Empire. After World War II, the river once again denoted a border, this time between Romania and the Soviet Union. Nowadays, for a length of , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyodor Apraksin
Count Fyodor Matveyevich Apraksin (also ''Apraxin''; ; , Moscow) was one of the first Russian admirals, governed Estonia and Karelia from 1712 to 1723, was made general admiral (1708), presided over the Russian Admiralty from 1717 to 1728''GRE'' and commanded the Baltic Fleet from 1723. Early shipbuilding activities The Apraksin brothers were launched to prominence after the marriage of their sister Marfa to ''Tsar'' Feodor III of Russia in 1681. Fyodor entered the service of his brother-in-law at the age of 10 as a ''stolnik''. After Feodor's death he served the little ''tsar'' Peter in the same capacity. He took part in military amusements of the young ''tsar'' and helped to build a toy flotilla for him. The playfellowship of the two lads resulted in a lifelong friendship. In 1692 Apraksin was appointed governor of Arkhangelsk, the foremost trade port of Russia at that time, and built ships capable of weathering storms, to the great delight of the ''tsar''. While living th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
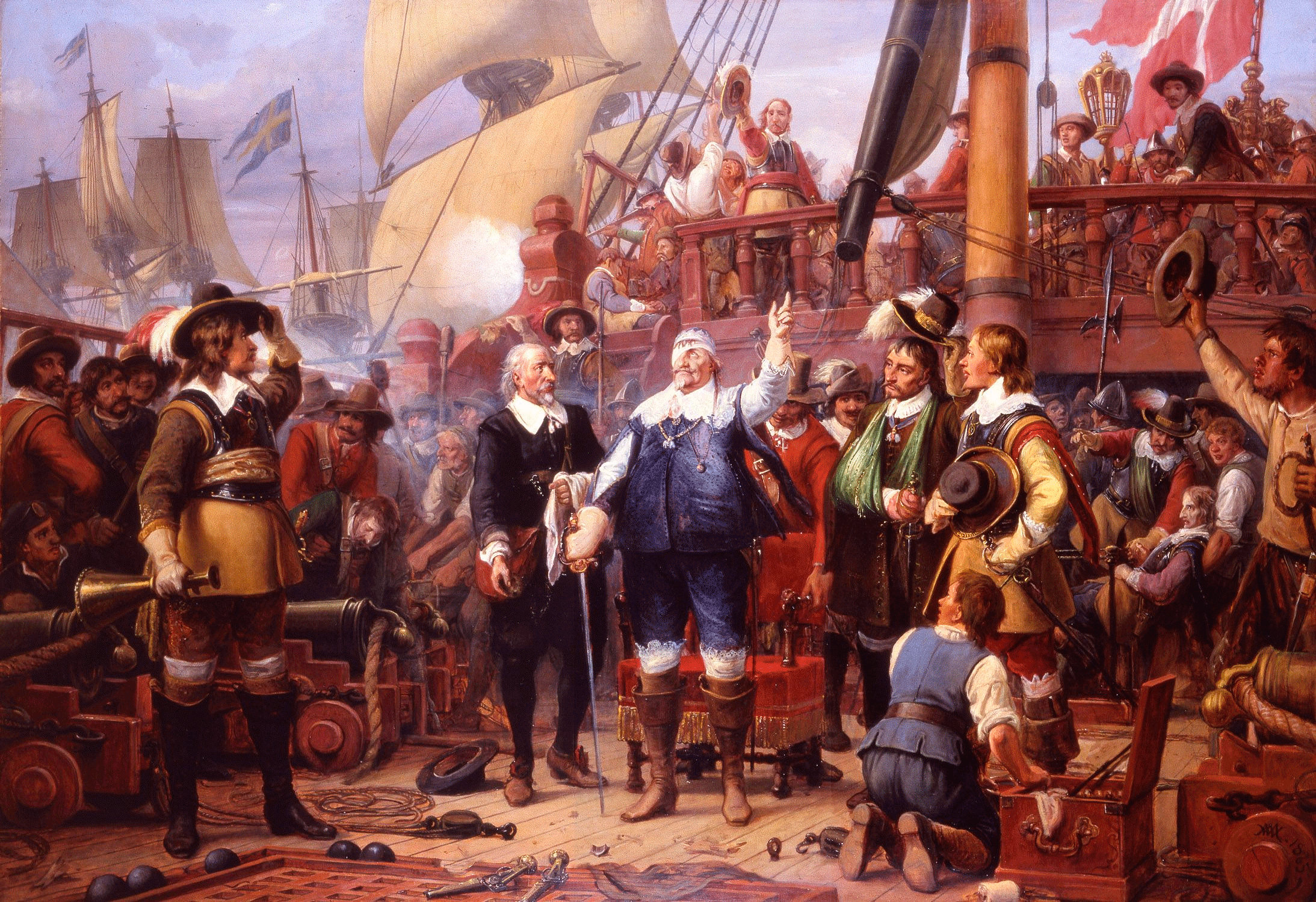
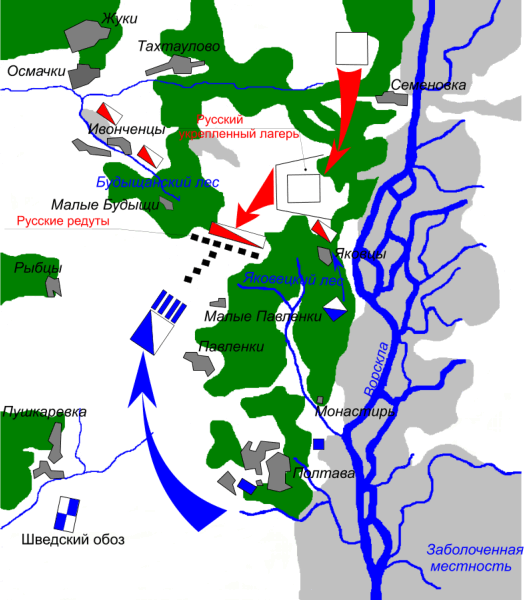
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava took place 8 July 1709, was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. The Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated the Swedish army commanded by Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle would lead to the Swedish Empire losing its status as a European great power and also marked the beginning of Russian supremacy in eastern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter, under , was the only one still fighting. Charles therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign was complicated by harsh weather conditions and by Russian scorched earth tactics and surprise attacks, which forced Charles to interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (, ) or Donians (, ), are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don River (Russia), Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (, ), which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic republic in present-day Southern Russia and parts of the Donbas region of Ukraine, from the end of the 16th century until 1918. As of 1992, by presidential decree of the Russian Federation, Cossacks can be enrolled on a special register. A number of Cossack communities have been reconstituted to further Cossack cultural traditions, including those of the Don Cossack Host. Don Cossacks have had a rich military tradition - they played an important part in the historical development of the Russian Empire and participated in most of its major wars. Etymology The name Cossack (; ) was widely used to characterise "free people" (compare Turkic languages, Turkic ''kazakhs, qazaq'', which means "free men") as opposed to others with different standi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
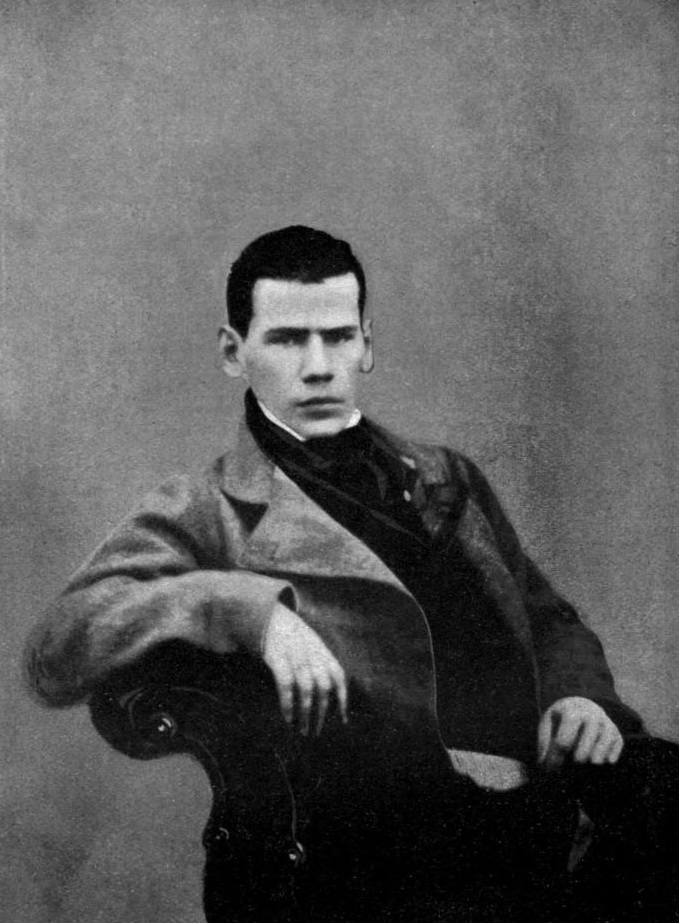
Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy Tolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; ,Throughout Tolstoy's whole life, his name was written as using pre-reform Russian orthography. ; ), usually referred to in English as Leo Tolstoy, was a Russian writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest and most influential authors of all time. Born to an aristocratic family, Tolstoy achieved acclaim in his twenties with his semi-autobiographical trilogy, ''Childhood'', '' Boyhood'' and ''Youth'' (1852–1856), and with ''Sevastopol Sketches'' (1855), based on his experiences in the Crimean War. His '' War and Peace'' (1869), '' Anna Karenina'' (1878), and ''Resurrection'' (1899), which is based on his youthful sins, are often cited as pinnacles of realist fiction and three of the greatest novels ever written. His ''oeuvre'' includes short stories such as " Alyosha the Pot" (1911) and " After the Ball" (1911) and novellas such as '' Family Happi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turkish people, Turks, while ethnic Kurds in Turkey, Kurds are the Minorities in Turkey, largest ethnic minority. Officially Secularism in Turkey, a secular state, Turkey has Islam in Turkey, a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city and economic center. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya. First inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic, present-day Turkey was home to List of ancient peoples of Anatolia, various ancient peoples. The Hattians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia (country), Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is Inflow (hydrology), supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper and Dniester. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea, not including the Sea of Azov, covers , has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |