|
Iulia Campestris Babba
Iulia Campestris Babba is a Mauretanian city created as Roman colony around 30 BC by emperor Augustus. Its actual location is currently unknown, though its existence is confirmed by the literature. Characteristics Colonia Iulia Campestris Babba was one of the three colonias in Mauretania Tingitana (in northern Morocco) founded by emperor Augustus between 30 and 25 BC for veterans of the battle of Actium. Nearly 10,000 legionaries settled in Iulia Valentia Banasa, Iulia Constantia Zilil and Babba, according to historian Theodore Mommsen. The city of Babba in Mauritania Tingitana was probably situated on or near the river Lixus (El Haratel); and was made a colony in honor of Julius Caesar, as its name Iulia indicated. It was also called Campestris because away from the sea The city was populated by Roman colonists and their descendants and by romanised berbers. The exact location of Babba has been debated by many scholars, but one of the most probable possibilities is that Babba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
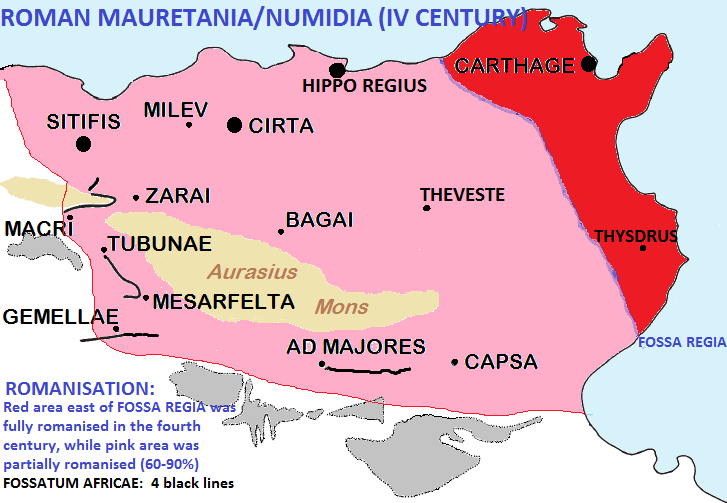
Mauretania Et Numidia
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It extended from central present-day Algeria to the Atlantic, encompassing northern present-day Morocco, and from the Mediterranean in the north to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, of Berber ancestry, were known to the Romans as the Mauri and the Masaesyli. In 25 BC, the kings of Mauretania became Roman vassals until about 44 AD, when the area was annexed to Rome and divided into two provinces: Mauretania Tingitana and Mauretania Caesariensis. Christianity spread there from the 3rd century onwards. After the Muslim Arabs subdued the region in the 7th century, Islam became the dominant religion. Moorish kingdom Mauretania existed as a tribal kingdom of the Berber Mauri people. In the early 1st century Strabo recorded ''Maûroi'' (Μαῦροι in Greek) as the native name of a people opposite the Iberian Peninsula. This appellation was adopted into Latin, whereas the Greek name for the tribe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Roads In Morocco, According To W
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible * Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Berber Cities
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system periodises ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chellah
The Chellah or Shalla ( or ; ), is a medieval fortified Muslim necropolis and ancient archeological site in Rabat, Morocco, located on the south (left) side of the Bou Regreg estuary. The earliest evidence of the site's occupation suggests that the Phoenicians established a trading emporium here in the first millennium BC. This was later the site of Sala Colonia, an ancient Roman colony in the province of Mauretania Tingitana, before it was abandoned in Late Antiquity. In the late 13th century the site began to be used as a dynastic necropolis for the Marinid dynasty. By the mid-14th century Marinid sultans had enclosed a part of the site with a new set of walls and built a religious complex inside it to accompany their mausoleums. In the 15th century the necropolis began to decline and it suffered damage over the centuries due to earthquakes and looting. Archeological excavations in the 20th century unearthed the remains of the ancient Roman town. Today the site is a tourist attra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abyla
Abyla was the pre-Roman name of Ad Septem Fratres (actual Ceuta of Spain). Ad Septem Fratres, usually shortened to ''Septem'' or ''Septa'', was a Roman Empire, Roman Roman colonia, colony in the Roman province, province of Mauretania Tingitana and a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine outpost in the exarchate of Exarchate of Africa, Africa. Its ruins are located within present-day Ceuta, an autonomous Spanish city in northwest Africa. Names The name Abyla is said to have been a Punic language, Punic name ("Lofty Mountain" or "Mountain of El (deity), God") for Jebel Musa (Morocco), Jebel Musa, the southern Pillars of Hercules, Pillar of Hercules. It appears in Ancient Greek, Greek variously as ''Abýla'' (), ''Abýlē'' (), ''Ablýx'' (), and ''Abílē Stḗlē'' (, "Pillar of Abyla") and in Latin as Mount Abyla (') or the Pillar of Abyla ('). The settlement below Jebel Musa was later renamed for the seven hills around the site, collectively referred to as the "Seven Brothers" (, ''He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman 'Coloniae' In Berber Africa
Roman colonies in North Africa are the cities—populated by Roman citizens—created in North Africa by the Roman Empire, mainly in the period between the reigns of Augustus and Trajan. Characteristics Since the second half of the first century BC and as a result of increasing communities of Roman citizens living in the North African centers, Rome started to create colonies in North Africa. The main reason was to control the area with Roman citizens, who had been legionaries in many cases. The second reason was to give land and urban properties to the Roman military troops who had fought for the Roman Empire and so decrease the demographic problem in the Italian peninsula. The third reason was to facilitate the Romanization of the area and so the integration of the local Berbers -through marriage and other relationships in the Roman Empire's social and cultural world. It is indicative that two of the main characteristics of the Roman world, Latin language and Christianity, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of the special member state territories and the European Union, special member state territories of the European Union. It was a regular municipalities in Spain, municipality belonging to the province of Cádiz prior to the passing of its Statute of Autonomy in March 1995, as provided by the Spanish Constitution, henceforth becoming an autonomous city. Ceuta, like Melilla and the Canary Islands, was classified as a free port before Spain joined the European Union. Its population is predominantly Christian and Islam in Spain, Muslim, with a small minority of Sephardic Jews and Sindhi Hindus, from Pakistan. Spanish language, Spanish is the official language, while Moroccan Darija, Darija Arabic is also widely spoken. Names The name Abyla has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingis
Tingis (Latin; ''Tíngis'') or Tingi ( Ancient Berber:), was the ancient name of Tangier in Morocco and an important Carthaginian, Moor, and Roman port on the Atlantic Ocean. It was eventually granted the status of a Roman colony and made the capital of the province of Mauretania Tingitana and, after Diocletian's reforms, the diocese of Hispania. Legends The Greeks claimed that Tingis had been named for a daughter of the titan Atlas, who was supposed to support the vault of heaven nearby. They claimed that the Berber legends comported with the stories of Hercules's labors, which carried him to North Africa and the North Atlantic to retrieve the golden apples of the Hesperides. Having killed her husband Antaeus and again condemned her father to eternally supporting the firmament, Hercules slept with Tinja and fathered the Berber hero Syphax. Syphax supposedly founded the port of Tingis and named it his mother's honor after her death.. The gigantic skeleton and tomb of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lixus (ancient City)
Lixus (Berber languages, Berber : ⵍⵓⴽⵓⵙ, Phoenician language, Phoenician: 𐤋𐤊𐤅𐤔) is an ancient city founded by Phoenicians (8th–7th century BC) before the city of Carthage. Its distinguishing feature is that it was continuously occupied from antiquity to the Islamic Era, and has ruins dating to the Phoenicia, Phoenician (8th–6th centuries BC), Punic people, Punic (5th–3rd centuries BC), Mauretanian (2nd century BC–AD 50), Roman Empire, Roman (AD 50–6th century AD) and Islamic (12th–15th centuries AD) periods. Tentative World Heritage Status Lixus was submitted to the World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage on July 1, 1995, by the Ministry of Culture of Morocco, on the basis of three World Heritage Site#Selection criteria, cultural selection criteria. In a 2019 press release, the Ministry of Culture stated that it was implementing a cultural and economic development strategy, with the intent on working towards Lixus being officially listed as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis, was a period in History of Rome, Roman history during which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressure of repeated Barbarian invasions into the Roman Empire of the 3rd century, foreign invasions, List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and Economic collapse, economic disintegration. At the height of the crisis, the Roman state split into three distinct and competing polities. The period is usually dated between the death of Severus Alexander (235) and accession of Diocletian (284). The crisis began in 235 with the assassination of Emperor Severus Alexander by his own troops. During the following years, the empire saw Barbarian invasions of the 3rd century, barbarian invasions and Human migration, migrations into Roman territory, civil wars, bagaudae, peasant rebellions and political instability, with multiple Roman usurper, usurpers competing for power. This led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |