|
Itzgründisch Dialect
Itzgründisch is an East Franconian German, East Franconian dialect, which is spoken in the eponymous Itz Valley (German: ''Itzgrund'') and its tributaries of Grümpen, Effelder, Röthen/Röden, Lauter, Füllbach and Rodach, the valleys of the Neubrunn, Lower Franconia, Neubrunn, Biber and the upper Werra and in the valley of Steinach. In the small language area, which extends from the Itzgrund in Upper Franconia to the southern side of the Thuringian Highlands, East Franconian German, East Franconian still exists in the original form. Because of the remoteness of the area, this isolated by the end of the 19th century and later during the division of Germany, this language has kept many linguistic features to this day. Scientific study of the Itzgründisch dialect was made for the first time, in the middle of the 19th century, by the linguist August Schleicher. Geographical Distribution The zone of the Itzgründisch dialect includes south of the Rennsteig ridge in the distric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
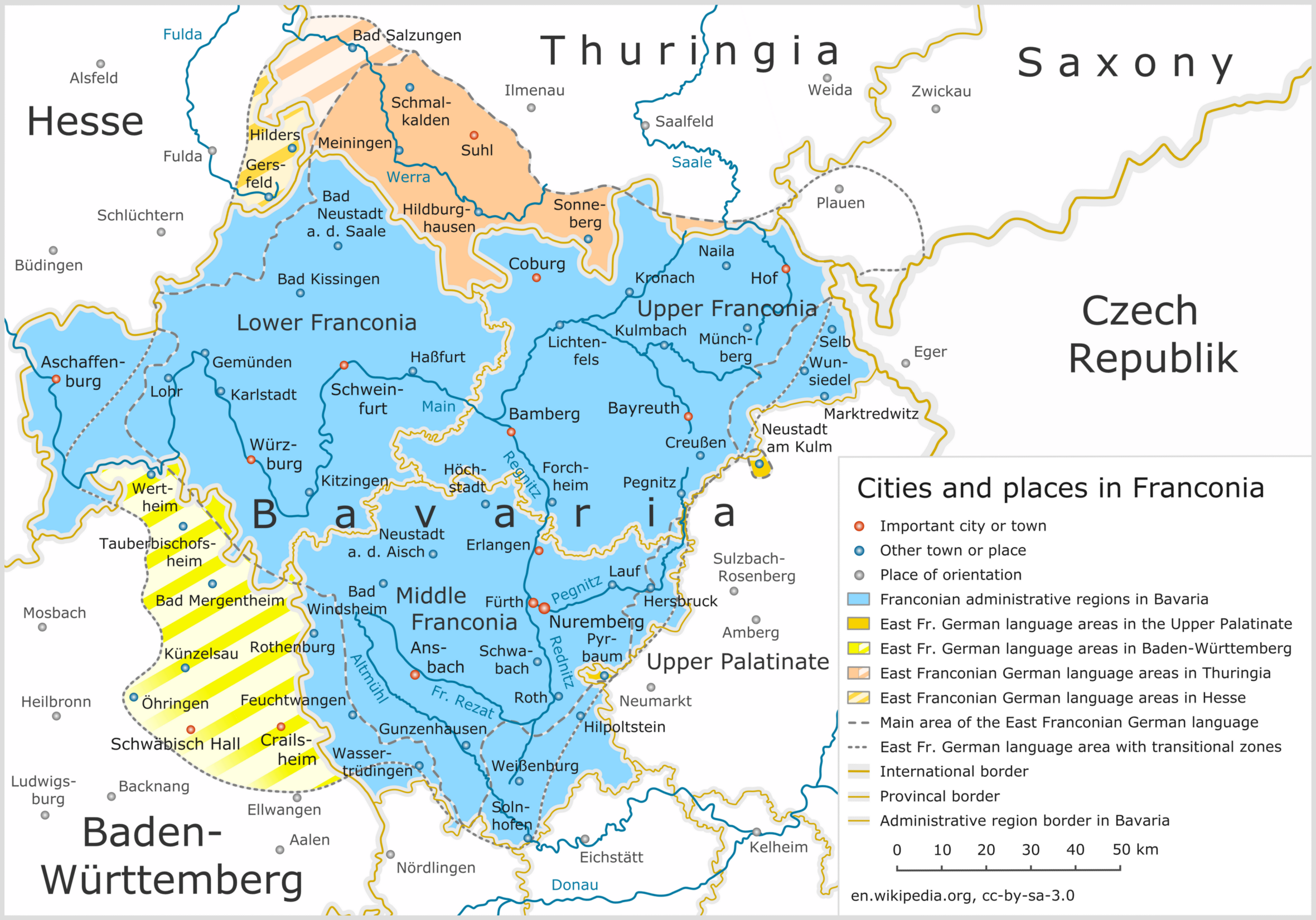
East Franconian German
East Franconian ( ), usually referred to as Franconian (' ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). Until the wholesale expulsion of Germans from Bohemia, the dialect was also spoken around Saaz (today: Žatec). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rennsteig
The () is a ridge walk as well as a historical boundary path in the Thuringian Forest, Thuringian Highland and Franconian Forest in Central Germany. The long-distance trail runs for about from and the valley in the northwest to and the river in the southeast. The is also the watershed between the river systems of the , Elbe and Rhine. The catchment areas of all three river systems meet at the ("Three Rivers Rock") near . Route The runs along the ridge of the Thuringian Central Uplands (') from northwest to southeast mostly at heights of around 500 to 970 metres. It starts in the town quarter of by the River (196 m above NHN) and ends in by the River (414 m above NHN). In 2003 the was re-surveyed by the Thuringian State Office for Survey and Geoinformation; they reported that it had a total length of . The marking along the trail is very good, usually indicated by a white 'R' (called '). Along the there are small, open shelters about every 5 to 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauscha
Lauscha is a town in the district of Sonneberg, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated 13 km north of Sonneberg, and 24 km southwest of Saalfeld. Lauscha is known for its glassblowing, especially for Christmas tree decorations like baubles. Geography Lauscha is located in the Thuringian Highland. The town is nestled into the steep valley of a tributary of the river Steinach just below the ridge of the mountain chain, the well-known Rennsteig. The main train station in Lauscha is 611 m above sea level, and the Pappenheimer Berg, the highest mountain within the town limits, rises to 835 m above sea level. History From 1680 to 1920, Lauscha was part of Saxe-Meiningen, from 1920 to 1952 of the State of Thuringia, from 1952 to 1990 of the Bezirk Suhl of East Germany and since 1990 again of Thuringia. Neighbouring towns Immediate neighbours are the following towns and villages: *Neuhaus am Rennweg *Lichte * Piesau * Oberland am Rennsteig * Steinach * Steinheid * Ernstth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
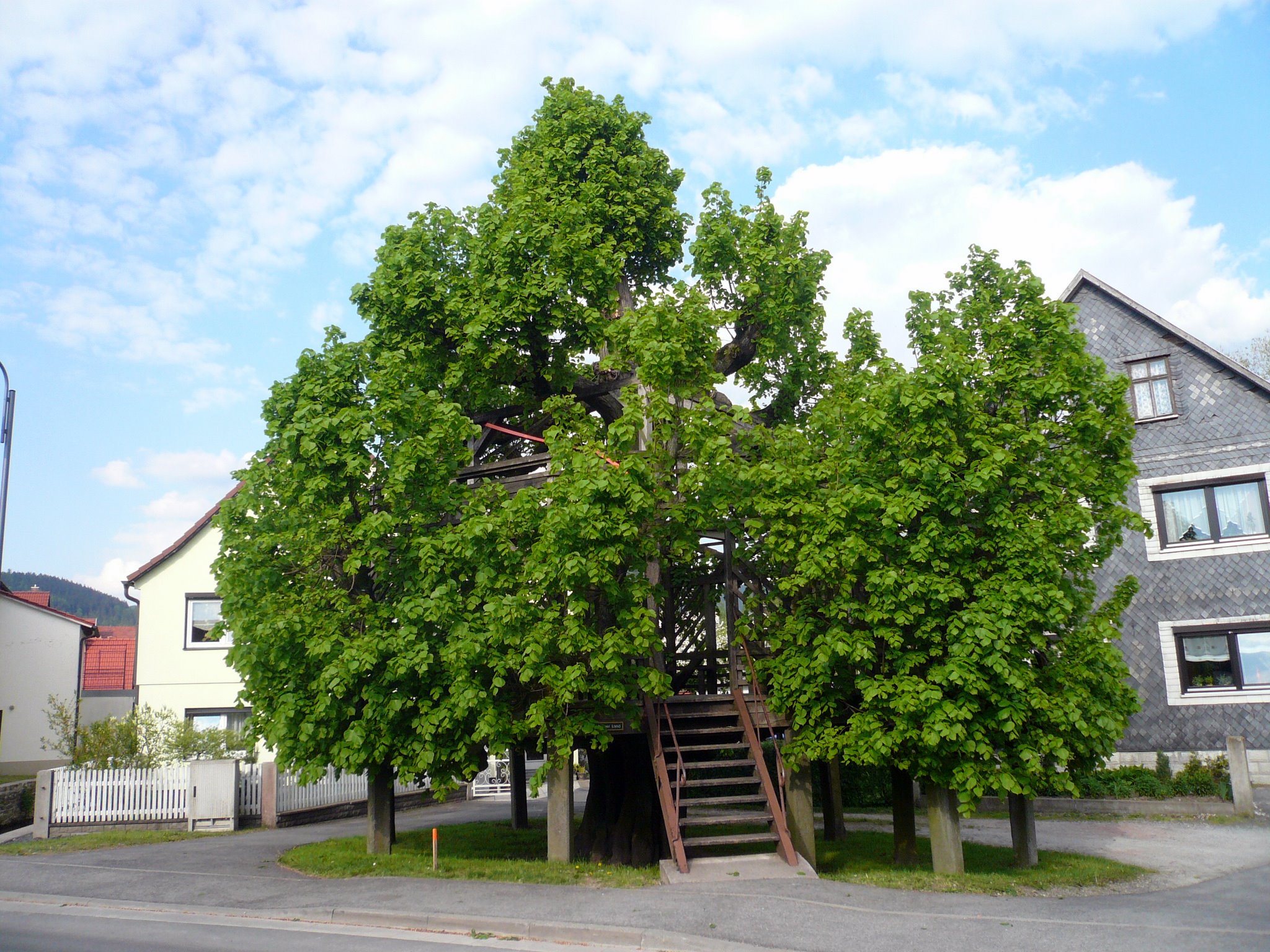
Sachsenbrunn
Sachsenbrunn is a village and a former municipality in the district of Hildburghausen, in Thuringia, Germany. It includes the community of Stelzen. Since 1 January 2019, it is part of the town Eisfeld. Culture A notable cultural item in the village of Sachsenbrunn is its Tanzlinde, a lime tree ''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Great Britain and Irelan ... that has had a dancing platform built around it. It is one of the best preserved examples of this in Germany. References Former municipalities in Thuringia Hildburghausen (district) {{Hildburghausen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringian
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon spoken mainly in the state of Saxony, therefore both are also regarded as one Thuringian-Upper Saxon dialect group. Thuringian dialects are among the Central German dialects with the highest number of speakers. History Thuringian emerged during the medieval German '' Ostsiedlung'' migration from about 1100, when settlers from Franconia ( Main Franconia), Bavaria, Saxony, and Flanders settled in the areas east of the Saale River previously inhabited by Polabian Slavs. Characteristics The Thuringian dialect is characterized by a rounding of the vowels, the weakening of consonants of Standard German (the lenition of the consonants "p," "t," and "k"), a marked difference in the pronunciation of the "g" sound (which is most common in the areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Franconian
High Franconian or Upper Franconian () is a part of High German consisting of East Franconian and South Franconian.Noble, Cecil A. M. (1983). ''Modern German Dialects.'' New York / Berne / Frankfort on the Main, Peter Lang, p. 119. It is spoken southeast of the Rhine Franconian area. It is spoken in Germany around Karlsruhe, Nuremberg, Erlangen, Fürth, Bamberg, Heilbronn, Meiningen and Würzburg and a small area in France. High Franconian is transitional between Upper German and Central German but usually regarded as Upper German. It is disputed whether it makes sense to summarise East and South Franconian because both are different. References See also * Franconian languages Franconian or Frankish is a collective term traditionally used by linguists to refer to many West Germanic languages, some of which are spoken in what formed the historical core area of Francia during the Early Middle Ages. Linguistically, it ha ... Bavaria Central German languages Up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinersdorf
Heinersdorf () is a locality in the boroughs of Berlin, borough of Pankow in Berlin, Germany. It is located close to the Pankow (locality), centre of Pankow. History Heinersdorf was first mentioned in a 1319 document when it was sold by Waldemar, Margrave of Brandenburg-Stendal, Margrave Waldemar of Brandenburg to the Order of the Holy Ghost, Hospital of the Holy Ghost in Berlin. After that it changed owners several times. In 1920 it was incorporated into Greater Berlin Act, Greater Berlin and belonged to the former ''Pankow'' borough, until it merged with Karow (Berlin), Karow, Blankenburg (Berlin), Blankenburg and Berlin-Weissensee, Weissensee in 1985. These localities belonged to Pankow again after Berlin's 2001 administrative reform. The foundations of the fieldstone church were laid around 1300. The church features two stained glass windows from 1946 by Charles Crodel. Another landmark is the Heinersdorf water tower, which was erected in 1910. Originally part of a planne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian German, East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia district in Bavaria, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main (river), Main. Bamberg had 79,000 inhabitants in 2022. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. Cited as one of Germany's most beautiful towns, with medieval streets and buildings, the old town of Bamberg with around 2,400 Timber framing, timber houses has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1993. From the 10th century onwards, Bamberg became a key link with the West Slavs, Western Slavic peoples, notably those of Poland and Pomerania. It experienced a period of great prosperity from the 12th century onwards, during which time it was briefly the centre of the Holy Roman Empire. Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry II was buried in the old town, alongside his wife Cunigunde of Luxemburg, Kunigunde. The town' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seßlach
Seßlach () is a town in the district of Coburg, in northern Bavaria, Germany. It is situated 12 km southwest of Coburg and has a population close to 4,000. Seßlach is notable for its largely intact medieval town wall and overall historic appearance with few modern structures. Geography Location Seßlach is located in Upper Franconia. To the north, the municipal territory borders on Thuringia. To the west and south lies the district Haßberge. Subdivisions Seßlach consists of 17 '' Stadtteile'': (inhabitants as of July 2015) History The first written mention of the two settlements on the ''Kirchhügel'' (church hill) and the ''Geiersberg'' (vulture hill) comes from the year 800. The Abbess Emhild of the monastery Milz transferred the monasterial properties by this certificate to Fulda Abbey. In 1335, the emperor '' Ludwig der Bayer'' awarded Seßlach the status of town. This gave the residents the permission to fortify their settlement which they soon did. By 1343 th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Franconian
In historical and comparative linguistics, Low Franconian is a linguistic category used to classify a number of historical and contemporary West Germanic varieties closely related to, and including, the Dutch language. Most dialects and languages included within this category are spoken in the Netherlands, northern Belgium (Flanders), in the Nord department of France, in western Germany (Lower Rhine), as well as in Suriname, South Africa and Namibia. Terminology ''Low Franconian'' is a purely linguistic category and not used as a term of self-designation among any of the speakers of the Germanic dialects traditionally grouped within it. Within the field of historical philology, the terminology for the historical phases of Low Franconian is not analogous to the traditional Old High German / Middle High German and Old Low German / Middle Low German dichotomies, with the terms Old Dutch and Middle Dutch commonly being preferred to ''Old Low Franconian'' and ''Middle Low Franconi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Franconian
East Franconian ( ), usually referred to as Franconian (' ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). Until the wholesale expulsion of Germans from Bohemia, the dialect was also spoken around Saaz (today: Žatec). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg. East Franconian is one of the German dialects with the highest number of speakers. The scope of East Franconian is disputed, because it o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |