|
Iterated Limit
In multivariable calculus, an iterated limit is a limit of a sequence or a limit of a function in the form : \lim_ \lim_ a_ = \lim_ \left( \lim_ a_ \right), : \lim_ \lim_ f(x, y) = \lim_ \left( \lim_ f(x, y) \right), or other similar forms. An iterated limit is only defined for an expression whose value depends on at least two variables. To evaluate such a limit, one takes the limiting process as one of the two variables approaches some number, getting an expression whose value depends only on the other variable, and then one takes the limit as the other variable approaches some number. Types of iterated limits This section introduces definitions of iterated limits in two variables. These may generalize easily to multiple variables. Iterated limit of sequence For each n, m \in \mathbf, let a_ \in \mathbf be a real double sequence. Then there are two forms of iterated limits, namely : \lim_ \lim_ a_ \qquad \text \qquad \lim_ \lim_ a_. For example, let :a_ = \frac. Then : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multivariable Calculus
Multivariable calculus (also known as multivariate calculus) is the extension of calculus in one variable to calculus with functions of several variables: the differentiation and integration of functions involving multiple variables ('' multivariate''), rather than just one. Multivariable calculus may be thought of as an elementary part of calculus on Euclidean space. The special case of calculus in three dimensional space is often called ''vector calculus''. Introduction In single-variable calculus, operations like differentiation and integration are made to functions of a single variable. In multivariate calculus, it is required to generalize these to multiple variables, and the domain is therefore multi-dimensional. Care is therefore required in these generalizations, because of two key differences between 1D and higher dimensional spaces: # There are infinite ways to approach a single point in higher dimensions, as opposed to two (from the positive and negative direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uniform Convergence
In the mathematical field of analysis, uniform convergence is a mode of convergence of functions stronger than pointwise convergence. A sequence of functions (f_n) converges uniformly to a limiting function f on a set E as the function domain if, given any arbitrarily small positive number \varepsilon, a number N can be found such that each of the functions f_N, f_,f_,\ldots differs from f by no more than \varepsilon ''at every point'' x ''in'' E. Described in an informal way, if f_n converges to f uniformly, then how quickly the functions f_n approach f is "uniform" throughout E in the following sense: in order to guarantee that f_n(x) differs from f(x) by less than a chosen distance \varepsilon, we only need to make sure that n is larger than or equal to a certain N, which we can find without knowing the value of x\in E in advance. In other words, there exists a number N=N(\varepsilon) that could depend on \varepsilon but is ''independent of x'', such that choosing n\geq N wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Limit Of A Sequence
As the positive integer n becomes larger and larger, the value n\times \sin\left(\tfrac1\right) becomes arbitrarily close to 1. We say that "the limit of the sequence n \times \sin\left(\tfrac1\right) equals 1." In mathematics, the limit of a sequence is the value that the terms of a sequence "tend to", and is often denoted using the \lim symbol (e.g., \lim_a_n).Courant (1961), p. 29. If such a limit exists and is finite, the sequence is called convergent. A sequence that does not converge is said to be divergent. The limit of a sequence is said to be the fundamental notion on which the whole of mathematical analysis ultimately rests. Limits can be defined in any metric space, metric or topological space, but are usually first encountered in the real numbers. History The Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea is famous for formulating Zeno's paradoxes, paradoxes that involve limiting processes. Leucippus, Democritus, Antiphon (person), Antiphon, Eudoxus of Cnidus, Eudoxus, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Riemann Zeta Function
The Riemann zeta function or Euler–Riemann zeta function, denoted by the Greek letter (zeta), is a mathematical function of a complex variable defined as \zeta(s) = \sum_^\infty \frac = \frac + \frac + \frac + \cdots for and its analytic continuation elsewhere. The Riemann zeta function plays a pivotal role in analytic number theory and has applications in physics, probability theory, and applied statistics. Leonhard Euler first introduced and studied the function over the reals in the first half of the eighteenth century. Bernhard Riemann's 1859 article "On the Number of Primes Less Than a Given Magnitude" extended the Euler definition to a complex variable, proved its meromorphic continuation and functional equation, and established a relation between its zeros and the distribution of prime numbers. This paper also contained the Riemann hypothesis, a conjecture about the distribution of complex zeros of the Riemann zeta function that many mathematicians consider th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Weierstrass M-test
In mathematics, the Weierstrass M-test is a test for determining whether an infinite series of functions converges uniformly and absolutely. It applies to series whose terms are bounded functions with real or complex values, and is analogous to the comparison test for determining the convergence of series of real or complex numbers. It is named after the German mathematician Karl Weierstrass (1815–1897). Statement Weierstrass M-test. Suppose that (''f''''n'') is a sequence of real- or complex-valued functions defined on a set ''A'', and that there is a sequence of non-negative numbers (''M''''n'') satisfying the conditions * , f_n(x), \leq M_n for all n \geq 1 and all x \in A, and * \sum_^ M_n converges. Then the series :\sum_^ f_n (x) converges absolutely and uniformly on ''A''. A series satisfying the hypothesis is called '' normally convergent''. The result is often used in combination with the uniform limit theorem. Together they say that if, in addition to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations. Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", it has two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus. The former concerns instantaneous Rate of change (mathematics), rates of change, and the slopes of curves, while the latter concerns accumulation of quantities, and areas under or between curves. These two branches are related to each other by the fundamental theorem of calculus. They make use of the fundamental notions of convergence (mathematics), convergence of infinite sequences and Series (mathematics), infinite series to a well-defined limit (mathematics), limit. It is the "mathematical backbone" for dealing with problems where variables change with time or another reference variable. Infinitesimal calculus was formulated separately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
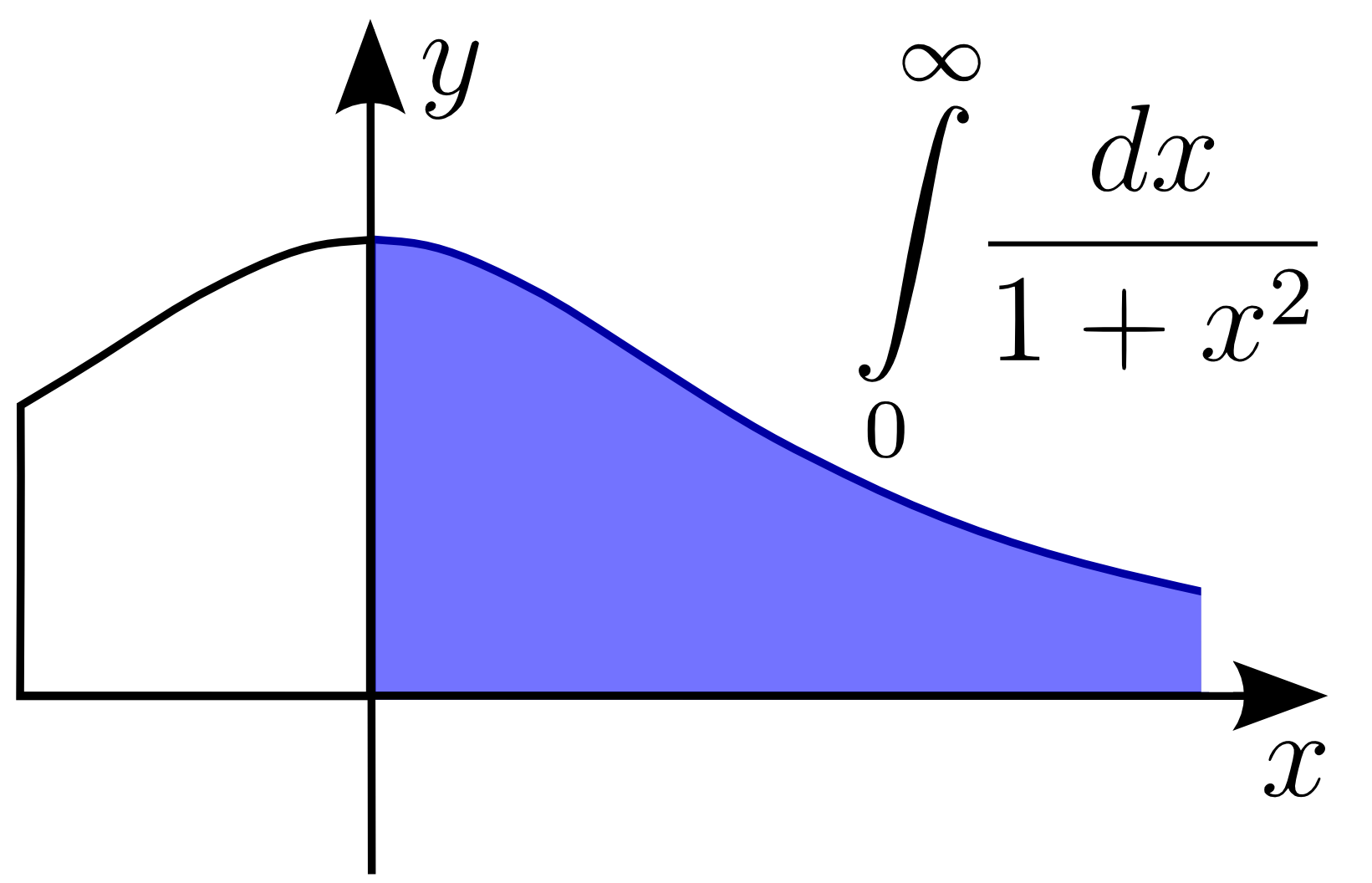
Improper Integral
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is an extension of the notion of a definite integral to cases that violate the usual assumptions for that kind of integral. In the context of Riemann integrals (or, equivalently, Darboux integrals), this typically involves unboundedness, either of the set over which the integral is taken or of the integrand (the function being integrated), or both. It may also involve bounded but not closed sets or bounded but not continuous functions. While an improper integral is typically written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, it actually represents a limit of a definite integral or a sum of such limits; thus improper integrals are said to converge or diverge. If a regular definite integral (which may retronymically be called a proper integral) is worked out as if it is improper, the same answer will result. In the simplest case of a real-valued function of a single variable integrated in the sense of Riemann (or Darbou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a small variation of the argument induces a small variation of the value of the function. This implies there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are the most general continuous functions, and their d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Limit Of A Sequence
As the positive integer n becomes larger and larger, the value n\times \sin\left(\tfrac1\right) becomes arbitrarily close to 1. We say that "the limit of the sequence n \times \sin\left(\tfrac1\right) equals 1." In mathematics, the limit of a sequence is the value that the terms of a sequence "tend to", and is often denoted using the \lim symbol (e.g., \lim_a_n).Courant (1961), p. 29. If such a limit exists and is finite, the sequence is called convergent. A sequence that does not converge is said to be divergent. The limit of a sequence is said to be the fundamental notion on which the whole of mathematical analysis ultimately rests. Limits can be defined in any metric space, metric or topological space, but are usually first encountered in the real numbers. History The Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea is famous for formulating Zeno's paradoxes, paradoxes that involve limiting processes. Leucippus, Democritus, Antiphon (person), Antiphon, Eudoxus of Cnidus, Eudoxus, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cauchy Criterion
The Cauchy convergence test is a method used to test infinite series for convergence. It relies on bounding sums of terms in the series. This convergence criterion is named after Augustin-Louis Cauchy who published it in his textbook '' Cours d'Analyse'' 1821. Statement A series \sum_^\infty a_i is convergent if and only if for every \varepsilon>0 there is a natural number N such that :, a_+a_+\cdots+a_, N and all p \geq 1. Explanation The test works because the space \R of real numbers and the space \C of complex numbers (with the metric given by the absolute value) are both complete. From here, the series is convergent if and only if the partial sums : s_n := \sum_^n a_i are a Cauchy sequence. Cauchy's convergence test can only be used in complete metric spaces (such as \R and \C), which are spaces where all Cauchy sequences converge. This is because we need only show that its elements become arbitrarily close to each other after a finite progression in the sequence to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infinite Sum
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, an addition of infinitely many terms, one after the other. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, mathematical analysis. Series are used in most areas of mathematics, even for studying finite structures in combinatorics through generating functions. The mathematical properties of infinite series make them widely applicable in other quantitative disciplines such as physics, computer science, statistics and finance. Among the Ancient Greeks, the idea that a potentially infinite summation could produce a finite result was considered paradoxical, most famously in Zeno's paradoxes. Nonetheless, infinite series were applied practically by Ancient Greek mathematicians including Archimedes, for instance in the quadrature of the parabola. The mathematical side of Zeno's paradoxes was resolved using the concept of a limit during the 17th century, especially through the early calculus of Isaac Newton. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |