|
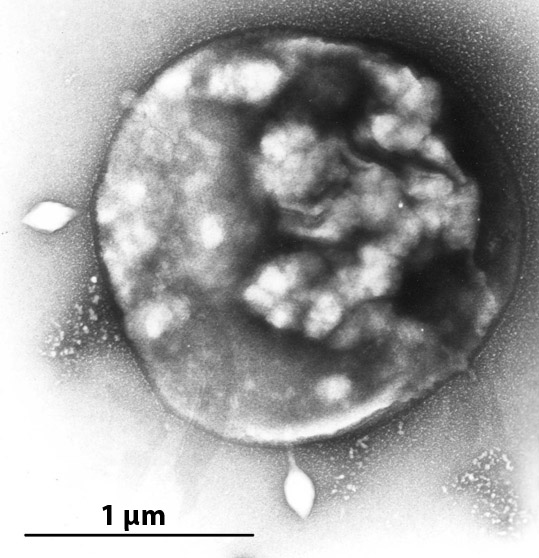
Itarudivirus
Acidianus rod-shaped virus 1 (ARV1), scientific name ''Itarudivurs ARV1'', is an archaeal virus An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as ac ... and the sole species in the genus ''Itarudivirus''. Its only known host is ''Acidianus'' sp. Acii26. References Archaeal viruses Ligamenvirales {{virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeal Virus
An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA). Much of the diversity observed in archaeal viruses is their morphology. Their complete bodies, called virions, come in many different forms, including being shaped like spindles or lemons, rods, bottles, droplets, and coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidianus Sp
''Acidianus'' is a genus of archaeans in the family Sulfolobaceae. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) See also * List of Archaea genera * List of bacterial genera named after mythological figures Several bacterial species are named after Greek or Roman mythical figures. The rules present for species named after a famous person do not apply, although some names are changed in the female nominative case, either by changing the ending to -a ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * * * Scientific books * External links''Acidianus'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Archaea genera Thermoproteota {{archaea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeal Viruses
An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA). Much of the diversity observed in archaeal viruses is their morphology. Their complete bodies, called virions, come in many different forms, including being shaped like spindles or lemons, rods, bottles, droplets, and coil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |