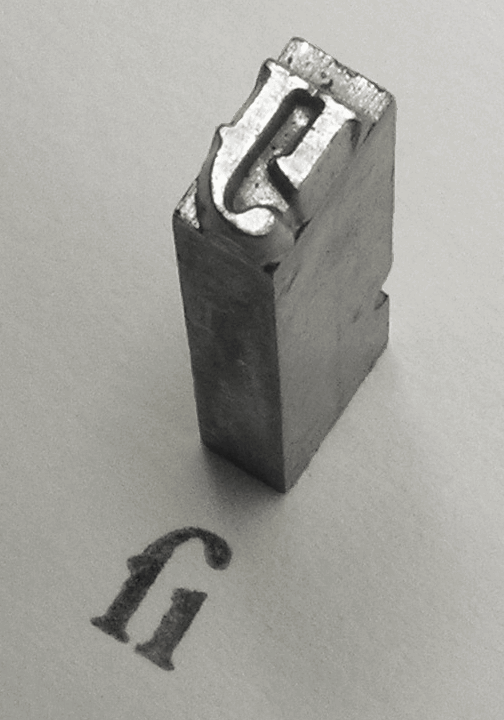|
Italics
In typography, italic type is a cursive font based on a stylised form of calligraphic handwriting. Along with blackletter and roman type, it served as one of the major typefaces in the history of Western typography. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, italics normally slant slightly to the right, ''like so''. Different glyph shapes from roman type are usually usedanother influence from calligraphyand upper-case letters may have Swash (typography), swashes, flourishes inspired by ornate calligraphy. Historically, italics were a distinct style of type used entirely separately from roman type, but they have come to be used in conjunction—most fonts now come with a roman type and an oblique type, oblique version (generally called "italic" though often not true italics). In this usage, italics are a way to emphasise key points in a printed text, to identify many types of creative works, to cite foreign words or phrases, or, when quoting a speaker, a way to show which w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oblique Type
Oblique type is a form of type that slants slightly to the right, used for the same purposes as italic type. Unlike italic type, however, it does not use different glyph shapes; it uses the same glyphs as roman type, except slanted. Oblique and italic type are technical terms to distinguish between the two ways of creating slanted font styles; oblique designs may be labelled italic by companies selling fonts or by computer programs. Oblique designs may also be called slanted or sloped roman styles. Oblique fonts, as supplied by a font designer, may be simply slanted, but this is often not the case: many have slight corrections made to them to give curves more consistent widths, so they retain the proportions of counter (typography), counters and the thick-and-thin quality of strokes from the regular design. Type designers have described oblique type as less organic and calligraphic than italics, which in some situations may be preferred. Contemporary type designer Jeremy Tankard s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design. For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regular"), "" and ""; each of these exists in a variety of sizes. In the digital description of fonts ( computer fonts), the terms "font" and "typeface" are often used interchangeably. For example, when used in computers, each style is stored in a separate digital font file. In both traditional typesetting and computing, the word "font" refers to the delivery mechanism of an instance of the typeface. In traditional typesetting, the font would be made from metal or wood type: to compose a page may require multiple fonts from the typeface or even multiple typefaces. Spelling and etymology The word ''font'' (US) or ''fount'' (traditional UK, CAN; in any case pronounced ) derives from Middle French ''fonte'', meaning "cast iron". The term re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
History Of Western Typography
Modern typographers view typography as a craft with a very long History of printing, history tracing its origins back to the first punches and dies used to make Seal (emblem), seals and coinage currency in Ancient history, ancient times. The basic elements of typography are at least as old as civilization and the earliest writing systems—a series of key developments that were eventually drawn together into one systematic craft. While woodblock printing and movable type had History of typography in East Asia, precedents in East Asia, typography in the Western world developed after the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the mid-15th century. The initial Global spread of the printing press, spread of printing throughout Germany and Italy led to the enduring legacy and continued use of blackletter, Roman type, roman, and italic types. Medieval design roots Typography, type-founding, and typeface design began as closely related crafts in mid-15th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Swash (typography)
A swash is a typographical flourish, such as an exaggerated serif, terminal, tail, entry stroke, etc., on a glyph. The use of swash characters dates back to at least the 16th century, as they can be seen in Ludovico Vicentino degli Arrighi's ''La Operina,'' which is dated 1522. As with italic type in general, they were inspired by the conventions of period handwriting. Arrighi's designs influenced designers in Italy and particularly in France. Typefaces with swashes Most typefaces with swashes are serif fonts, among which (if present) they are often found solely in italics. Advanced digital fonts often supply two italic designs: one with swashes and a more restrained standard italic. Among old-style typefaces, some releases of Caslon, such as Adobe Caslon, and Garamond, including Adobe Garamond Pro and EB Garamond, have swash designs. Old-style typefaces which include swashes but do not follow a specific historical model include Minion by Robert Slimbach and Nexus by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Typeface
A typeface (or font family) is a design of Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers and other symbols, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., 24 point), weight (e.g., light, bold), slope (e.g., italic), width (e.g., condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font. There are list of typefaces, thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly. The art and craft of designing typefaces is called type design. Designers of typefaces are called type designers and are often employed by type foundry, type foundries. In desktop publishing, type designers are sometimes also called "font developers" or "font designers" (a typographer is someone who ''uses'' typefaces to design a page layout). Every typeface is a collection of glyphs, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Underline
An underscore or underline is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript as an instruction to the printer. Its use to add emphasis in modern finished documents is generally avoided. The (freestanding) underscore character, , also called a low line, or low dash, originally appeared on the typewriter so that underscores could be typed. To produce an underscored word, the word was typed, the typewriter carriage was moved back to the beginning of the word, and the word was overtyped with the underscore character. In modern usage, underscoring is achieved with a markup language, with the Unicode combining low line or as a standard facility of word processing software. The free-standing underscore character is used to indicate word boundaries in situations where spaces are not allowed, such as in computer filenames, email addresses, and in Internet U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aldus Manutius
Aldus Pius Manutius (; ; 6 February 1515) was an Italian printer and Renaissance humanism, humanist who founded the Aldine Press. Manutius devoted the later part of his life to publishing and disseminating rare texts. His interest in and preservation of Greek manuscripts mark him as an innovative publisher of his age dedicated to the editions he produced. Aldus Manutius introduced the small portable book format with his ''enchiridia'', which revolutionized personal reading and are the predecessor of the modern paperback book. He also helped to standardize use of punctuation including the comma and the semicolon. Manutius wanted to produce Greek language, Greek texts for his readers because he believed that works by Aristotle or Aristophanes in their original Greek form were pure and unadulterated by translation. Before Manutius, publishers rarely printed volumes in Greek, mainly due to the complexity of providing a standardized Greek typeface. Manutius published rare manuscripts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Handwriting
Handwriting in Italian schools (XXth - XXIst century) Handwriting is the personal and unique style of writing with a writing instrument, such as a pen or pencil in the hand. Handwriting includes both block and cursive styles and is separate from generic and formal handwriting script/style, calligraphy or typeface. Because each person's handwriting is unique and different, it can be used to verify a document's writer. The deterioration of a person's handwriting is also a symptom or result of several different diseases. The inability to produce clear and coherent handwriting is also known as dysgraphia. Uniqueness Each person has their own unique style of handwriting, whether it be everyday handwriting or their personal signature. Cultural environment and the characteristics of the written form of the first language that one learns to write are the primary influences on the development of one's own unique handwriting style.Sargur Srihari, Chen Huang and Harish Srinivasan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aldine Press
The Aldine Press was the printing office started by Aldus Manutius in 1494 in Venice, from which were issued the celebrated Aldine editions of the classics (Latin and Greek masterpieces, plus a few more modern works). The first book that was dated and printed under his name appeared in 1495. The Aldine Press is famous in the history of typography, among other things, for the introduction of italics. The press was the first to issue printed books in the small octavo size, similar to that of a modern paperback, and intended for portability and ease of reading. According to Curt F. Bühler, the press issued 132 books during twenty years of activity under Aldus Manutius. After Manutius' death in 1515, the press was continued by his wife Maria and her father Andrea Torresani (), until Manutius' son Paulus (1512–1574) took over. His grandson Aldus Manutius the Younger then ran the firm until his death in 1597. Today, the antique books printed by the Aldine Press in Venice are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Typography
Typography is the art and technique of Typesetting, arranging type to make written language legibility, legible, readability, readable and beauty, appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, Point (typography), point sizes, line lengths, line spacing, letter spacing, and Kerning, spaces between pairs of letters. The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is also the work of graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers, and symbols for publication, display, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Page From The Edition Of Virgil Printed By Aldus Manutius In 1501 (BnF, Réserve Des Livres Rares, RES P-YC-1265)
Page most commonly refers to: * Page (paper), one side of a leaf of paper, as in a book Page, PAGE, pages, or paging may also refer to: Roles * Page (assistance occupation), a professional occupation * Page (servant), traditionally a young male servant * Page (wedding attendant) People and fictional characters * Page (given name), a list of people * Page (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * Pages (surname) * H. A. Page, a pen name of Scottish author Alexander Hay Japp (1836–1905) Places Australia * Page, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra * Division of Page, New South Wales * Pages River, a tributary of the Hunter River catchment in New South Wales, Australia * The Pages, South Australia, two islands and a reef **The Pages Conservation Park, a protected area in South Australia United States * Page, Arizona, a city * Page, Indiana * Page, Minneapolis, Minnesota, a neighborhood * Page, Nebraska, a village * Page, North Dakota, a city * Page, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Francesco Griffo
Francesco Griffo (1450–1518), also called Francesco da Bologna, was a fifteenth-century Italian punchcutter. He worked for Aldus Manutius, designing the printer's more important humanist typefaces, including the first italic type. He cut Roman, Greek, Hebrew and the first italic type. Aldus gives Griffo credit in the introduction of the ''Virgil'' of 1501. However, as Manutius had achieved a monopoly on italic printing and Greek publishing with the permission of the Venetian government, he had a falling-out with Griffo. Griffo then went to work for Gershom Soncino, whose family were Hebrew printers. It was with Soncino that Griffo's second italic type was cut in 1503. In 1516 he returned to Bologna where he began print publishing. In 1518 Griffo was charged with the murder of his son-in-law, who had been beaten to death with an iron bar. This is his last appearance in the historical record. He is presumed to have been executed. Influence Griffo's typefaces have been very influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |