|
Istakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', , i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. – d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel author and Islamic geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Arabic of the many Muslim territories he visited during the Abbasid era of the Islamic Golden Age. There is no consensus regarding his origin. Some sources describe him as Persian, while others state he was Arab. IV:222b-223b. The ''Encyclopedia Iranica'' states: "Biographical data are very meager. From his ''nesbas'' (attributive names) he appears to have been a native of Eṣṭaḵr in Fārs, but it is not known whether he was Persian". VIII(6):646-647 (I have used the updated online version). Istakhri's account of windmills is the earliest known. Istakhri met the celebrated traveller-geographer Ibn Hawqal, while travelling, and Ibn Hawqal incorporated the work of Istakhri in his book ''Kitab al-Surat al-Ard''. Works Istakhri's two surviving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
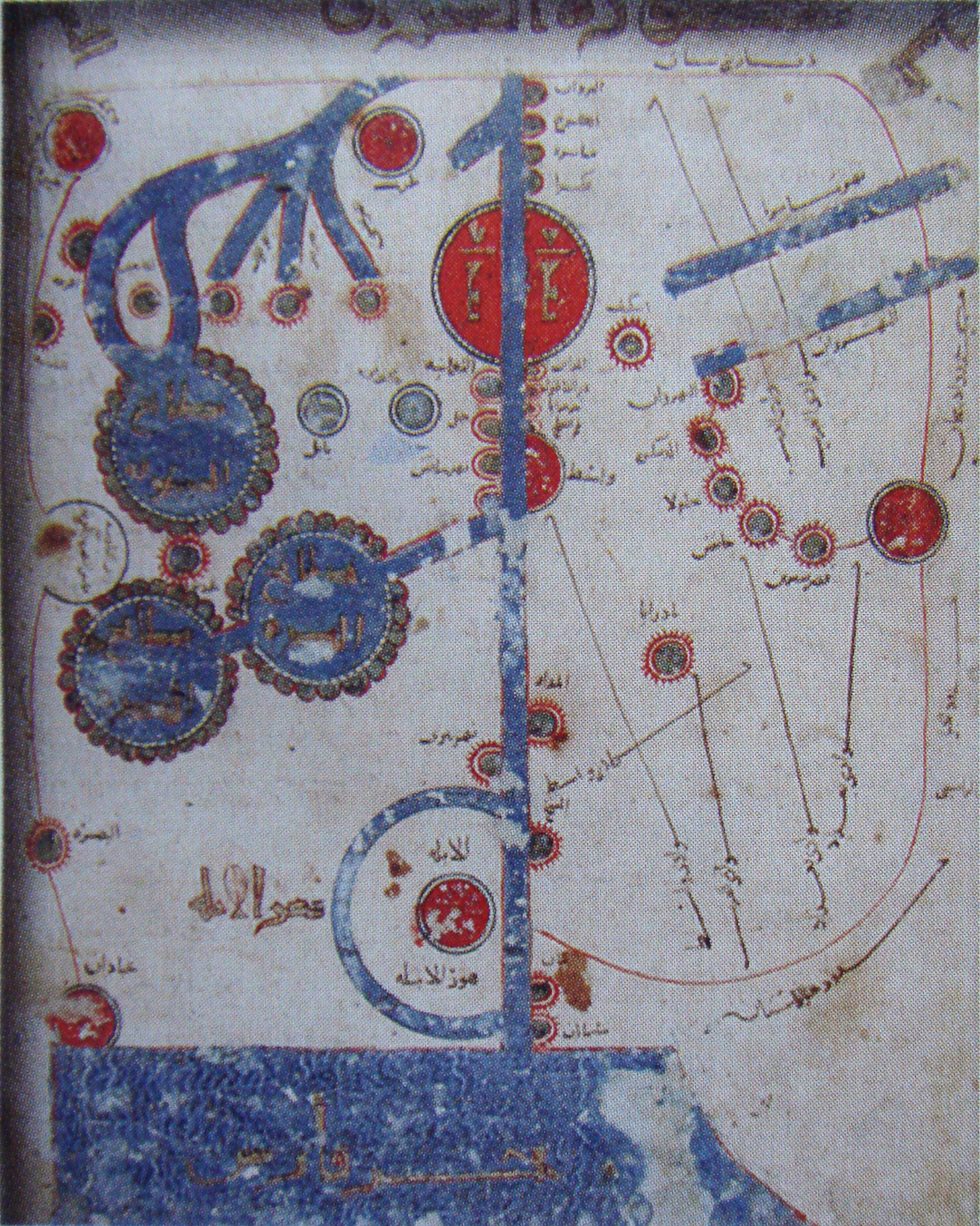
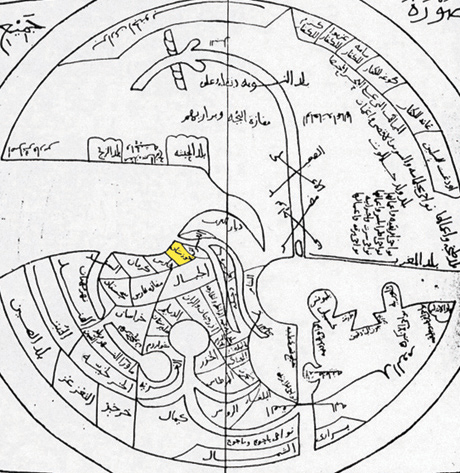
Book Of Roads And Kingdoms
The ''Book of Roads and Kingdoms'' (, ''Kitāb al-Masālik waʿl-Mamālik'') is a group of Islamic manuscripts composed from the Middle Ages to the early modern period. They emerged from the administrative tradition of listing pilgrim and post stages. Their text covers the cities, roads, topography, and peoples of the Muslim world, interspersed with personal anecdotes. A theoretical explanation of the "Inhabited Quarter" of the world, comparable to the ecumene, frames the world with classical concepts like the seven climes. The books include illustrations so geometric that they are barely recognizable as maps. These schematic maps do not attempt a mimetic depiction of physical boundaries. With little change in design, the treatises typically offer twenty regional maps and a disc-shaped map of the world surrounded by the Encircling Ocean. The maps have a flat quality, but the textual component implies a spherical Earth. Andalusi scholar Abi Bakr Zuhri explained, "Their objective i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography In Medieval Islam
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age (variously dated between the 8th century and 16th century). Muslim scholars made advances to the map-making traditions of earlier cultures, explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Islamic geography had three major fields: exploration and navigation, physical geography, and cartography and mathematical geography. Islamic geography reached its apex with Muhammad al-Idrisi in the 12th century. History 8th and 9th century Islamic geography began in the 8th century, influenced by Hellenistic geography, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Muslim scholars engaged in extensive exploration and navigation during the 9th-12th centuries, including journeys across the Muslim world, in addition to regions such as China, Southeast Asia an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Al-Jazira (caliphal province), Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled from AD 943 to 969.Ludwig W. Adamec (2009), ''Historical Dictionary of Islam'', p.137. Scarecrow Press. . His famous work, written in 977, is called ''Surat Al-Ard'' (; "The face of the Earth"). The date of his death, known from his writings, was after Anno Hegirae, AH 368/AD 978. Biography Details known of Ibn Hawqal's life are extrapolated from his book. He spent the last 30 years of his life traveling to remote parts of Asia and Africa, and writing about different things he saw during his journey. One journey brought him 20° south of the equator along the East African coast where he discovered large populations in regions the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek writers had deemed uninhabitable. Ṣūrat al-’Arḍ Ibn Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden University Libraries
Leiden University Libraries is the set of libraries of Leiden University, founded in 1575 in Leiden, Netherlands. A later edition entitled ''The bastion of liberty : a history of Leiden University'', was published in 2018. Full-text at archive.org. Holdings include some five million volumes, one million e-books, ninety thousand electronic journal, e-journals, two thousand current paper Academic journal, journals, and three thousand cuneiform tablets. The library manages large collections on Indonesia and the Caribbean, and curates seven entries in UNESCO's international and Dutch Memory of the World, Memory of the World Register. Joseph Justus Scaliger, who was a languages and history professor at Leiden from 1593 up to 1609, commented in Latin on the library: :"''Est hic magna commoditas bibliothecae ut studiosi possint studere''" ::—Josephus Justus Scaliger :"Here [at Leiden] is the great convenience of a library so that those who want to study [students], can study." His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istakhr
Istakhr (Middle Persian romanized: ''Stakhr'', ) was an ancient city in Fars province, north of Persepolis in southwestern Iran. It flourished as the capital of the Persian '' Frataraka'' governors and Kings of Persis from the third century BC to the early 3rd century AD. It reached its apex under the Sasanian Empire (224-651 AD), and was the hometown of the Sasanian dynasty. Istakhr briefly served as the first capital of the Sasanian Empire from 224 to 226 AD and then as principal city, region, and religious centre of the Sasanian province of Pars. During the Arab conquest of Iran, Istakhr was noted for its stiff resistance, which resulted in the death of many of its inhabitants. Istakhr remained a stronghold of Zoroastrianism long after the conquests, and remained relatively important in the early Islamic era. It went into gradual decline after the founding of nearby Shiraz, before being destroyed and abandoned under the Buyids. Cursorily explored by Ernst Herzfeld and a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Zayd Al-Balkhi
Abu Zayd Ahmed ibn Sahl Balkhi () was a Persian Muslim polymath: a geographer, mathematician, physician, psychologist and scientist. Born in 850 CE in Shamistiyan, in the province of Balkh, Greater Khorasan, he was a disciple of al-Kindi. He also founded the "Balkhī school" of terrestrial mapping in Baghdad. Al-Balkhi is believed to have been the first to diagnose that mental illness can have psychological and physiological causes and he was the first to typify four types of emotional disorders: fear and anxiety; anger and aggression; sadness and depression; and obsessions. Biography al-Balkhi was born in 850 CE in a small village called Shamisitiyan, in an area called Balkh which is now part of Afghanistan. As a young man, around the time of al-Kindi's death, al-Balkhi travelled to Iraq.Who was Abu Zayd al-Balkhi? Malik Badri, introduction to Sustenance of the Soul, Gutenberg Press At this time Islamic culture was making strong efforts to absorb the knowledge of previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Iranian Scientists
The following is a list of Iranian scientists, engineers, and scholars who lived from antiquity up until the beginning of the modern age. A * Abdul Qadir Gilani (12th century) theologian and philosopher * Abu al-Qasim Muqane'i (10th century) physician * Abu Dawood (c. 817–889), Islamic scholar * Abu Hanifa (699–767), Islamic scholar * Abu Said Gorgani (10th century) * 'Adud al-Dawla (936–983), scientific patron * Ahmad ibn Farrokh (12th century), physician * Ahmad ibn 'Imad al-Din (11th century), physician and chemist * Alavi Shirazi (1670–1747), royal physician in Mughal India * Amuli, Muhammad ibn Mahmud (c. 1300–1352), physician * Abū Ja'far al-Khāzin (900–971), mathematician and astronomer * Ansari, Khwaja Abdullah (1006–1088), Islamic scholar * Aqa-Kermani (18th century), physician * Aqsara'i (?–1379), physician * Abu Hafsa Yazid, physician * Arzani, Muqim (18th century), physician * Astarabadi (15th century), physician * Aufi, Muhammad (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of science, culture, arts, and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. By housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Maqdisi
Shams al-Din Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ahmad ibn Abi Bakr, commonly known by the ''Nisba (onomastics), nisba'' al-Maqdisi or al-Muqaddasī, was a medieval Arab geographer, author of ''The Best Divisions in the Knowledge of the Regions'' and ''Description of Syria (Including Palestine)''. Al-Maqdisi is one of the earliest known historical figures to self-identify as a Palestinians, Palestinian, having done so during one of his travels in Iran, Persia. Biography Sources Outside of his own work, there is little biographical information available about al-Maqdisi.Miquel 1993, p. 492. He is neither found in the voluminous biographies of Ibn Khallikan (d. 1282) nor were the aspects of his life mentioned in the works of his contemporaries.Al-Mukaddasi, ed. Le Strange 1886, piii/ref> Early life and education He was born in Jerusalem in and belonged to a middle-class family whose roots in the city's environs dated from the period approximate to the Muslim conquest of the Levant, 7t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalili Collection Of Islamic Art
The Nasser D. Khalili Collection of Islamic Art includes 26,000 objects documenting Islamic art over a period of almost 1400 years, from 700 AD to the end of the twentieth century. It is the largest of the Khalili Collections: eight collections assembled, conserved, published and exhibited by the British scholar, collector and philanthropist Nasser David Khalili, each of which is considered among the most important in its field. Khalili's collection is one of the most comprehensive Islamic art collections in the world and the largest in private hands. In addition to copies of the Quran, and rare and illustrated manuscripts, the collection includes album and miniature paintings, lacquer, ceramics, glass and rock crystal, metalwork, arms and armour, jewellery, carpets and textiles, over 15,000 coins, and architectural elements. The collection includes folios from manuscripts with Persian miniatures, including the Great Mongol ''Shahnameh'', the ''Shahnameh'' of Shah Tahmasp, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Masudi
al-Masʿūdī (full name , ), –956, was a historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus of the Arabs". A polymath and prolific author of over twenty works on theology, history (Islamic and universal), geography, natural science and philosophy, his celebrated magnum opus '' The Meadows of Gold'' () combines universal history with scientific geography, social commentary and biography. Birth, travels and literary output Apart from what al-Mas'udi writes of himself little is known. Born in Baghdad, he was descended from Abdullah Ibn Mas'ud, a companion of Islamic prophet Muhammad. It is believed that he was a member of Banu Hudhayl tribe of Arabs. Al-Masudi mentions a number of scholar associates he encountered during his journeys: Al-Masʿudi may have reached Sri Lanka and China although he is known to have met Abu Zayd al-Sirafi on the coast of the Persian Gulf and received information on China from him.[Mas‘udi. ''The Meadows of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |