|
Israel Of Bamberg
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. It occupies the Palestinian territories of the West Bank in the east and the Gaza Strip in the south-west. Israel also has a small coastline on the Red Sea at its southernmost point, and part of the Dead Sea lies along its eastern border. Its proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, while Tel Aviv is the country's largest urban area and economic center. Israel is located in a region known as the Land of Israel, synonymous with the Palestine region, the Holy Land, and Canaan. In antiquity, it was home to the Canaanite civilisation followed by the kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Situated at a continental crossroad, the region experienced demographic changes under the rule of empires from the Romans to the Ottomans. European antisemitism in the late 19th century gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatikvah
Hatikvah (, ; ) is the national anthem of the Israel, State of Israel. Part of 19th-century Jewish literature, Jewish poetry, the theme of the Romantic poetry, Romantic composition reflects the 2,000-year-old desire of the Jews, Jewish people to return to the Land of Israel in order to History of the Jews and Judaism in the Land of Israel, reclaim it as a free and sovereign nation-state. The piece's lyrics are adapted from a work by Naftali Herz Imber, a Jewish poet from Zolochiv, Lviv Oblast#The Austro-Hungarian Imperial Period (1772–1918), Złoczów, Austrian Galicia. Imber wrote the first version of the poem in 1877, when he was hosted by a Jewish scholar in Iași. History Text The text of Hatikvah was written in 1878 by Naftali Herz Imber, a Jewish poet from Zolochiv, Lviv Oblast, Zolochiv (), a city nicknamed "The City of Poets", then in Austrian Poland, today in Ukraine. His words "Lashuv le'eretz avotenu" (to return to the land of our forefathers) expressed its aspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Hebrew
Modern Hebrew (, or ), also known as Israeli Hebrew or simply Hebrew, is the Standard language, standard form of the Hebrew language spoken today. It is the only surviving Canaanite language, as well as one of the List of languages by first written account, oldest languages still spoken as a native language, native language, on account of Hebrew being attested since the 2nd millennium BC. It uses the Hebrew Alphabet, an Abjad, abjad script written from right-to-left. The current standard was Codification (linguistics), codified as part of the revival of Hebrew in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and now serves as the Official language, sole official and national language of the State of Israel, where it is Languages of Israel, predominantly spoken by over 9 million people. Thus, Modern Hebrew is near universally regarded as the most successful instance of language revitalization in history. A Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Israel
The president of the State of Israel (, or ) is the head of state of Israel. The president is mostly, though not entirely, ceremonial; actual executive power is vested in the Cabinet of Israel, cabinet led by the Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister. The incumbent president is Isaac Herzog, who took office on 7 July 2021. Presidents are elected by the Knesset for a single seven-year term. Election The President of Israel is elected by an Majority, absolute majority in the Knesset, by secret ballot. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of votes in the first or second round of voting, the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated in each subsequent round, if needed until only two remain. From 1949 to 2000, the president was elected for a five-year term, and was allowed to serve up to two terms in office. Since 2000, the president serves a single seven-year term. Any Israeli resident citizen is eligible to run for president; as there is no minimum age of candid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unitary Parliamentary Republic
A unitary parliamentary republic is a type of unitary state with a republican form of government in which political authority is entrusted to the parliament by multiple constituencies throughout a country. In this system, voters elect members of parliament, who then make legislative decisions on behalf of their constituents. List of unitary parliamentary republics See also *Federal republic A federal republic is a federation of Federated state, states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means a country that is governed by elected re ... Notes References {{portalbar, politics Types of republics Unitary state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelis
Israelis (; ) are the Israeli citizenship law, citizens and nationals of the Israel, State of Israel. The country's populace is composed primarily of Israeli Jews, Jews and Arab citizens of Israel, Arabs, who respectively account for 75 percent and 20 percent of the national figure, followed by Demographics of Israel, other ethnic and religious minorities, who account for 5 percent. Early Culture of Israel, Israeli culture was largely defined by communities of the Jewish diaspora who had made ''aliyah'' to Mandatory Palestine, British Palestine from History of the Jews in Europe, Europe, History of the Jews under Muslim rule, Western Asia, and History of the Jews in North Africa (other), North Africa in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. Later Jewish immigration from Ethiopian Jews in Israel, Ethiopia, the 1990s post-Soviet aliyah, post-Soviet states, and the Americas introduced new cultural elements to Israeli society and have had a profound impact on modern Isra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Central Bureau Of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including population, society, economy, industry, education, and physical infrastructure. The CBS is headquartered in the Givat Shaul neighborhood of Jerusalem, with another branch in Tel Aviv. Overview The CBS is headed by the National Statistician (previously named Government Statistician), who is appointed on the recommendation of the prime minister. Professor Emeritus Danny Pfefferman of Hebrew University has served in that position and as Director of the CBS since 2013. The bureau's annual budget in 2011 was NIS 237 million. The work of the CBS follows internationally accepted standards which enable comparison of statistical information with other countries. It gathers current, monthly, quarterly and annually data on the national e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Israel
Religion in Israel is manifested primarily in Judaism, the ethnic religion of the Jews, Jewish people. The Israel, State of Israel declares itself as a "Jewish and democratic state" and is the only country in the world with a Jewish-majority population (see Jewish state). Other faiths in the country include Islam (predominantly Sunni Islam, Sunni), Christianity (mostly Melkite Greek Catholic Church, Melkite and Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, Orthodox) and the religion of the Druze, Druze people. Religion plays a central role in national and civil life, and almost all Israeli citizenship law, Israeli citizens are automatically registered as members of the state's Millet (Ottoman Empire)#Post-Ottoman use, 14 official religious communities, which exercise control over several matters of personal status, especially Marriage in Israel, marriage. These recognized communities are Orthodox Judaism (administered by the Chief Rabbinate of Israel, Chief Rabbinate), Islam, the Druze fait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In Israel
Christianity (; ; ) is the third largest religion in Israel, after Judaism and Islam. At the end of 2022, Christians made up 1.9% of the Israeli population, numbering approximately 185,000. 75.8% of the Christians in Israel are Arab Christians. Christians make up 6.9% of the Palestinian citizens of Israel, Arab-Israeli population. Ten Christian churches are formally recognized under Religion in Israel, Israel's confessional system, for the self-regulation and state recognition of status issues, such as Marriage in Israel, marriage and divorce: the Armenian Apostolic Church, the Armenian Catholic Church, the Chaldean Catholic Church, the Episcopal Church in Jerusalem and the Middle East, the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem, Greek Orthodox Church, the Latin Church, Latin Catholic Church, the Melkite Greek Catholic Church, the Syriac Catholic Church, the Syriac Maronite Church, and the Syriac Orthodox Church. However, the practice of religion is free, with no restrictions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Israel
, Muslims are the largest religious minority in Israel, accounting for 18.1% of the country's total population. Most of this figure is represented by the Arab citizens of Israel,Israel CIA Factbook who are the country's largest ethnic minority, but there is a notable non-Arab Muslim populace, such as that of the Circassians in Israel, Circassians. Upwards of 99% of Israel's Muslims are Sunni Islam, Sunnis and the remainder are Ahmadiyya in Israel, Ahmadis. Despite Shia Islam, Shias constituting the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, Islamic sect, there are no reliable sources attesting a Shia presence in Israel or the Israeli occupation of the West Bank, Israeli-occupied West Bank, which the Israeli government administers as the Judea and Samaria Area. There were only Shia villages in Palestine, seven Shia villages in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of Israel
The demographics of Israel, monitored by the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, encompass various attributes that define the nation's populace. Since Israeli Declaration of Independence, its establishment in 1948, Israel has witnessed significant changes in its demographics. Formed as a homeland for the Jewish people, Israel has attracted Aliyah, Jewish immigrants from Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics defines the population of Israel as including Jews living in all of the West Bank and Palestinians in East Jerusalem but excluding Palestinians anywhere in the rest of the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and foreign workers anywhere in Israel. As of December 2023, this calculation stands at approximately 9,842,000 of whom: *73.2% (about 7,208,000 people) are Israeli Jews, Jews, including about 503,000 living outside the self-defined borders of the State of Israel in the West Bank *21.1% (around 2,080,000 people) are Israeli citizens cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
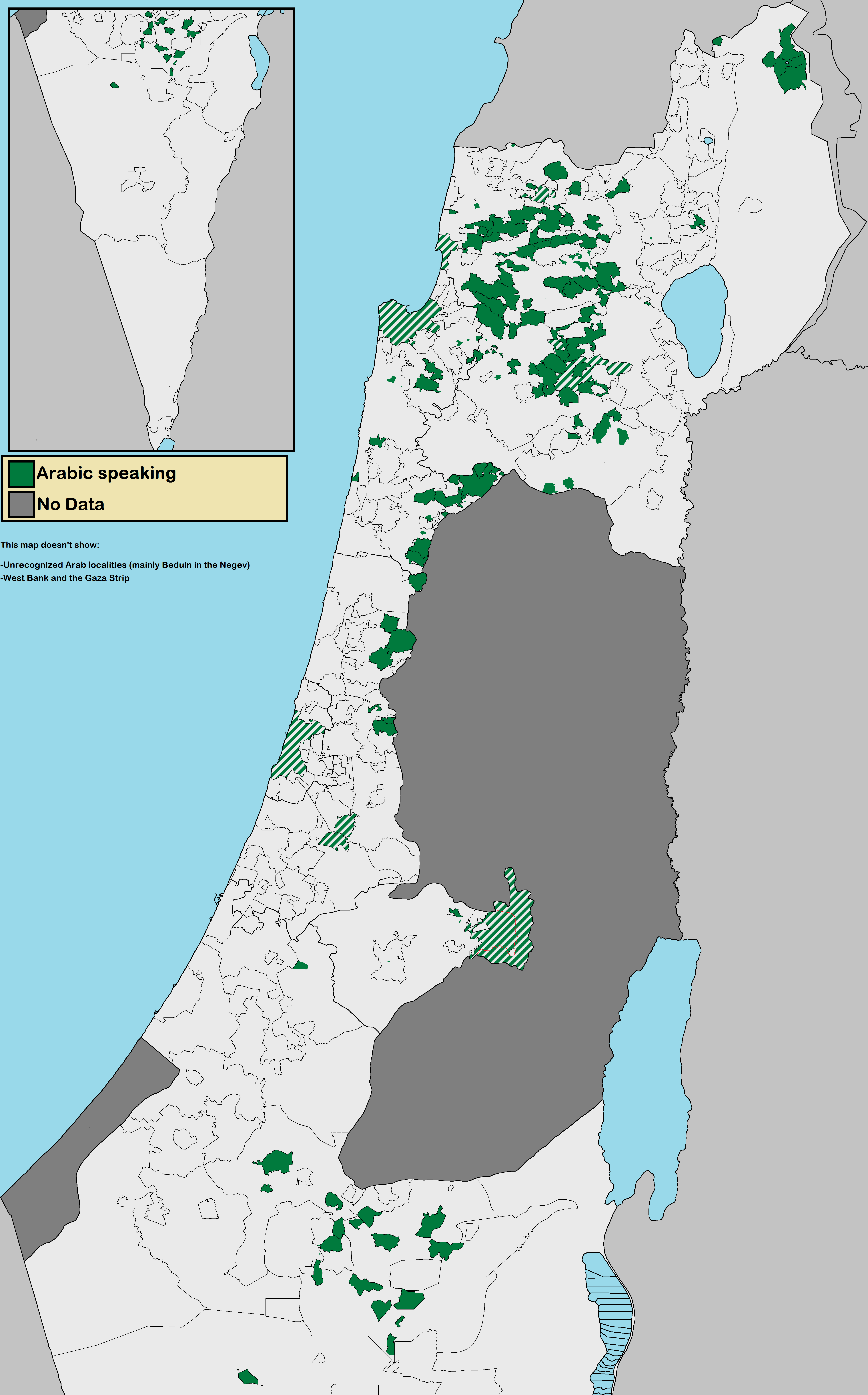
Arab Citizens Of Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel form the country's largest ethnic minority. Their community mainly consists of former Palestinian Citizenship Order 1925, Mandatory Palestine citizens (and their descendants) who continued to inhabit the territory that was acknowledged as Israeli by the 1949 Armistice Agreements. Notions of identity among Israel's Arab citizens are complex, encompassing civic, religious, and ethnic components. Some sources report that the majority of Arabs in Israel prefer to be identified as Palestinian citizens of Israel, while recent surveys indicate that most name "Israeli", "Israeli-Arab", or "Arab" as the most important components of their identity, reflecting a shift of "Israelization" among the community. In the wake of the 1948 Palestine war, the Israeli government Israeli citizenship law#Status of Palestinian Arabs, conferred Israeli citizenship upon all Palestinians who had 1948 Palestinian expulsion and flight, remained or were not expelled. However, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |