|
Isoxsuprine
Isoxsuprine (used as isoxsuprine hydrochloride) is a drug used as a vasodilator in humans (under the trade name Duvadilan) and equines. Isoxsuprine is a β2 adrenoreceptor agonist that causes direct relaxation of uterine and vascular smooth muscle via β2 receptors. Use In humans Isoxsuprine is used in humans for treatment of premature labor, i.e. a tocolytic, and as a vasodilator for the treatment of cerebral vascular insufficiency, Raynaud's phenomenon, and other conditions. Isoxsuprine may increase the heart rate, cause changes in blood pressure, and irritate the GI tract. It should therefore be used with caution if combined with other drugs that affect blood pressure, such as sedatives and anesthetic drugs. In horses Isoxsuprine is most commonly used to treat hoof-related problems in the horse, most commonly for laminitis Laminitis is a disease of the feet of ungulates, found mostly in horses and cattle involving inflammation of the laminae. Clinical signs include fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
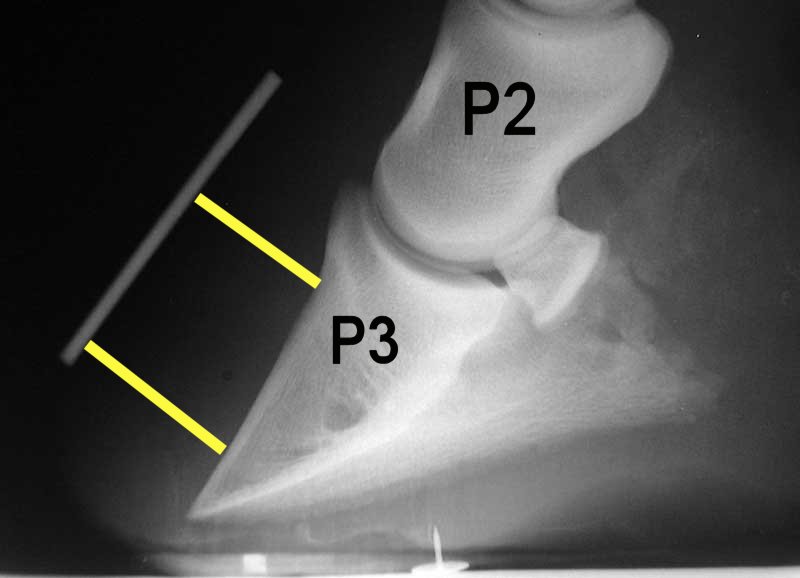
Navicular Disease
Navicular syndrome, often called navicular disease, is a syndrome of lameness problems in horses. It most commonly describes an inflammation or degeneration of the navicular bone and its surrounding tissues, usually on the front feet. It can lead to significant and even disabling lameness. Description of the navicular area Knowledge of equine forelimb anatomy is especially useful for understanding navicular syndrome. The navicular bone lies behind the coffin bone and under the small pastern bone (middle phalanx). The deep digital flexor (DDF) tendon runs down the back of the cannon and soft tissue in that area and under the navicular bone before attaching to the underside of the coffin bone. The DDF tendon flexes the coffin joint, and the navicular bone acts as a fulcrum that the DDF tendon runs over. The navicular bone is stabilized by the impar ligament distally at its attachment to the coffin bone (distal phalanx), and by the collateral ligaments of the navicular bone extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta2-adrenergic Agonist
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders. Bronchodilators are considered an important treatment regime for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and are usually used in combination with short acting medications and long acting medications in a combined inhaler. Mechanism of action Activation of β adrenergic receptors leads to relaxation of smooth muscle in the lung, and dilation and opening of the airways. β adrenergic receptors are coupled to a stimulatory G protein of adenylyl cyclase. This enzyme produces the second messenger cyclic adenosine monoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2 adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increases cAMP, and, via downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation. Robert Lefkowitz and Brian Kobilka's study of the beta-2 adrenergic receptor as a model system earned them the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for studies of G-protein-coupled receptors". The official symbol for the human gene encoding the β2 adrenoreceptor is ''ADRB2''. Gene The gene is intronless. Different polymorphic forms, point mutations, and/or downregulation of this gene are associated with nocturnal asthma, obesity and type 2 diabetes. Structure The 3D crystallographic structure (see figure and links to the right) of the β2-adrener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminitis
Laminitis is a disease of the feet of ungulates, found mostly in horses and cattle involving inflammation of the laminae. Clinical signs include foot tenderness progressing to inability to walk, increased digital pulses, and increased temperature in the hooves. Severe cases with outwardly visible clinical signs are known by the colloquial term ''#Rotation, sinking, and founder, founder'', and progression of the disease will lead to perforation of the coffin bone through the sole of the hoof or being unable to stand up, requiring Animal euthanasia, euthanasia. Laminae The bones of the hoof are suspended within the Anatomical terms of location#Other directional terms, axial hooves of ungulates by layers of modified skin cells, known as laminae or lamellae, which suspend the bony column from the hoof wall, contributing to shock absorption during locomotion. In horses, there are about 550–600 pairs of primary epidermis (zoology), epidermal laminae, each with 150–200 secondary la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-adrenergic Agonists
Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, causing widening of the airways and resulting in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents, each acting upon the Adrenergic receptor#β receptors, beta adrenoceptors. In general, pure beta-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of beta blockers: beta-adrenoreceptor agonist ligands mimic the actions of both epinephrine- and norepinephrine- signaling, in the heart and lungs, and in smooth muscle tissue; epinephrine expresses the higher affinity. The activation of β1, β2 and β3 activates the enzyme, Adenylyl cyclase, adenylate cyclase. This, in turn, leads to the activation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates target proteins, ultimately inducing smooth muscle relaxation and contraction of the cardiac tissue. Function Activation of β1 receptors induces positive inot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tocolytics
Tocolytics (also called anti-contraction medications or labor suppressants) are medications used to suppress premature labor (from Greek τόκος ''tókos'', "childbirth", and λύσις ''lúsis'', "loosening"). Preterm birth accounts for 70% of neonatal deaths. Therefore, tocolytic therapy is provided when delivery would result in premature birth, postponing delivery long enough for the administration of glucocorticoids (which accelerate fetal lung maturity) to be effective, as they may require one to two days to take effect. Commonly used tocolytic medications include Beta2-adrenergic agonist, β2 agonists, calcium channel blockers, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, NSAIDs, and magnesium sulfate. These can assist in delaying preterm delivery by suppressing uterine muscle contractions and their use is intended to reduce fetal Disease, morbidity and Mortality rate, mortality associated with preterm birth. The suppression of contractions is often only partial and tocolytics c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, conferring hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (ninth century CE), was that by adding salt to boiling win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Receptor Antagonists
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor ( NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for humans and animals; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Several synthetic opioids function additionally as NMDAR-antagonists, such as pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, dextropropoxyphene, tramadol, and ketobemidone. Some NMDA receptor antagonists, such as ketamine, dextromethorphan (DXM), phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are sometimes used as recreational drugs, for their dissociative, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant properties. When used recreationally, they are classified as dissociative drugs. Uses and effects NMDA receptor antagonists induce a state called dissociative anesthesia, marked by catalepsy, amnesia, and analgesia. Ketamine is a favored anesthetic for emergency patients with unknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Medications
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, known from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They originated in North America, before dispersing to every continent except Australia and Antarctica. They are thought to be a monophyletic grouping. Members of the subfamily are referred to as equines; the only extant equines are the horses, asses, and zebras of the genus ''Equus'', with two other genera ''Haringtonhippus'' and ''Hippidion'' becoming extinct at the beginning of the Holocene, around 11–12,000 years ago. The subfamily contains two tribes, the Equini and the Hipparionini, as well as two unplaced genera, ''Merychippus'' and ''Scaphohippus''. Members of the family ancestrally had three toes, while members of the tribe Equini from the Middle Miocene onwards developed monodactyl feet. Sister taxa * Anchitheriinae * Hyracotheriinae ''Hyracotherium'' ( ; " hyrax-like beast") is an extinct genus of small (about 60 cm in length) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diols
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry. The most common industrial diol is ethylene glycol. Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol and propylene-1,3-diol, or beta propylene glycol, . Synthesis of classes of diols Geminal diols A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. These species arise by hydration of the carbonyl compounds. The hydration is usually unfavorable, but a notable exception is formaldehyde which, in water, exists in equilibrium with methanediol H2C(OH)2. Another example is (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone. Many gem-diols undergo further condensation to give dimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |