|
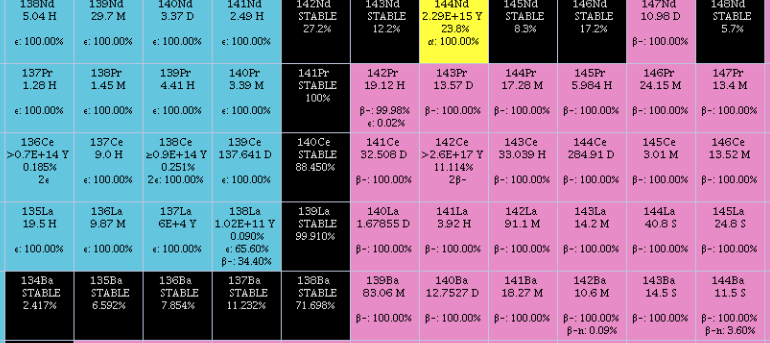
Isotopes Of Cerium
Naturally occurring cerium (58Ce) is composed of 4 stable isotopes: 136Ce, 138Ce, 140Ce, and 142Ce, with 140Ce being the most abundant (88.48% natural abundance) and the only one theoretically stable; 136Ce, 138Ce, and 142Ce are predicted to undergo double beta decay but this process has never been observed. There are 35 radioisotopes that have been characterized, with the most stable being 144Ce, with a half-life of 284.893 days; 139Ce, with a half-life of 137.640 days and 141Ce, with a half-life of 32.501 days. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 4 days and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 10 minutes. This element also has 10 meta states. The isotopes of cerium range in atomic weight from 119 u (119Ce) to 157 u (157Ce). List of isotopes , -id=Cerium-121 , rowspan=2, 121Ce , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 58 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 63 , rowspan=2, 120.94344(43)# , rowspan=2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure. Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium, lanthanum, and praseodymium. Its estimated abundance of elements in Earth's crust, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino. : : or when written as a nuclear reaction equation, ^_e + ^_p -> ^_n + ^_ ν_e Since this single emitted neutrino carries the entire decay energy, it has this single characteristic energy. Similarly, the momentum of the neutrino emission causes the daughter atom to recoil with a single characteristic momentum. The resulting daughter nuclide, if it is in an excited state, then transitions to its ground state. Usually, a gamma ray is emitted during this transition, but nuclear de-excitation may also take place by internal conversion. Following capture of an inner electron from the atom, an outer elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Cerium
Naturally occurring cerium (58Ce) is composed of 4 stable isotopes: 136Ce, 138Ce, 140Ce, and 142Ce, with 140Ce being the most abundant (88.48% natural abundance) and the only one theoretically stable; 136Ce, 138Ce, and 142Ce are predicted to undergo double beta decay but this process has never been observed. There are 35 radioisotopes that have been characterized, with the most stable being 144Ce, with a half-life of 284.893 days; 139Ce, with a half-life of 137.640 days and 141Ce, with a half-life of 32.501 days. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 4 days and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 10 minutes. This element also has 10 meta states. The isotopes of cerium range in atomic weight from 119 u (119Ce) to 157 u (157Ce). List of isotopes , -id=Cerium-121 , rowspan=2, 121Ce , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 58 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 63 , rowspan=2, 120.94344(43)# , rowspan=2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Barium
Naturally occurring barium (56Ba) is a mix of six stable isotopes and one very long-lived radioactive primordial isotope, barium-130, identified as being unstable by geochemical means (from analysis of the presence of its daughter xenon-130 in rocks) in 2001. This nuclide decays by double electron capture (absorbing two electrons and emitting two neutrinos), with a half-life of (0.5–2.7)×1021 years (about 1011 times the age of the universe). There are a total of thirty-three known radioisotopes in addition to 130Ba. The longest-lived of these is 133Ba, which has a half-life of 10.51 years. All other radioisotopes have half-lives shorter than two weeks. The longest-lived isomer is 133mBa, which has a half-life of 38.9 hours. The shorter-lived 137mBa (half-life 2.55 minutes) arises as the decay product of the common fission product caesium-137. Barium-114 is predicted to undergo cluster decay, emitting a nucleus of stable 12C to produce 102Sn. However this decay is not yet obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Lanthanum
Naturally occurring lanthanum (57La) is composed of one stable (139La) and one radioactive (138La) isotope, with the stable isotope, 139La, being the most abundant (99.91% natural abundance). There are 39 radioisotopes that have been characterized, with the most stable being 138La, with a half-life of 1.03×1011 years; 137La, with a half-life of 60,000 years and 140La, with a half-life of 1.6781 days. The remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than a day and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 1 minute. This element also has 12 nuclear isomers, the longest-lived of which is 132mLa, with a half-life of 24.3 minutes. Lighter isotopes mostly decay to isotopes of barium and heavy ones mostly decay to isotopes of cerium. 138La can decay to both. The isotopes of lanthanum range in atomic weight from 115.96 u (116La) to 154.96 u (155La). List of isotopes , -id=Lanthanum-116 , rowspan=2, 116La , rowspan=2 style="text-align:r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Praseodymium
Naturally occurring praseodymium (59Pr) is composed of one stable isotope, 141Pr. Thirty-eight radioisotopes have been characterized with the most stable being 143Pr, with a half-life of 13.57 days and 142Pr, with a half-life of 19.12 hours. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than six hours and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 33 seconds. This element also has 15 meta states with the most stable being 138mPr (t1/2 2.12 hours), 142mPr (t1/2 14.6 minutes) and 134mPr (t1/2 11 minutes). The isotopes of praseodymium range in atomic weight from (121Pr) to (159Pr). The primary decay mode before the stable isotope, 141Pr, is electron capture and the mode after is beta decay. The primary decay products before 141Pr are element 58 (cerium) isotopes and the primary products after are element 60 (neodymium) isotopes. List of isotopes , -id=Praseodymium-121 , 121Pr , style="text-align:right" , 59 , style="text-align:righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Physical Journal A
The ''European Physical Journal A: Hadrons and Nuclei'' is an academic journal, recognized by the European Physical Society, presenting new and original research results in a variety of formats, including Regular Articles, Reviews, Tools for Experiment and Theory/Scientific Notes and Letters. Topics covered include: ;Hadron Physics: *Structure and Dynamics of Hadrons *Baryon and Meson Spectroscopy *Hadronic and Electroweak Interactions of Hadrons *Nonperturbative Approaches to QCD *Phenomenological Approaches to Hadron Physics ;Nuclear Physics: *Nuclear Structure and Reactions *Structure and function of nanostructures *Few-Body and Many-Body Systems *Heavy-Ion Physics *Hypernuclei *Radioactive Beams *Nuclear Astrophysics History Prior to 1998, the journal was named ''Zeitschrift für Physik A Hadrons and Nuclei''. Thomas Walcher's term as Editor-in-Chief of EPJ A came to an end in 2006. In January 2007, Enzo de Sanctis started as new Editor-in-Chief and he was joined in July that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission Product
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release of heat energy (kinetic energy of the nuclei), and gamma rays. The two smaller nuclei are the ''fission products''. (See also Fission products (by element)). About 0.2% to 0.4% of fissions are ternary fissions, producing a third light nucleus such as helium-4 (90%) or tritium (7%). The fission products themselves are usually unstable and therefore radioactive. Due to being relatively neutron-rich for their atomic number, many of them quickly undergo beta decay. This releases additional energy in the form of beta particles, antineutrinos, and gamma rays. Thus, fission events normally result in beta and additional gamma radiation that begins immediately after, even though this radiation is not produced directly by the fission even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-life
Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay. Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to: Film * Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang * ''Half Life: A Parable for the Nuclear Age'', a 1985 Australian documentary film Literature * Half Life (Jackson novel), ''Half Life'' (Jackson novel), a 2006 novel by Shelley Jackson * Half-Life (Krach novel), ''Half-Life'' (Krach novel), a 2004 novel by Aaron Krach * Halflife (Michalowski novel), ''Halflife'' (Michalowski novel), a 2004 novel by Mark Michalowski * ''Rozpad połowiczny'' (), a 1988 award-winning dystopia novel by Edmund Wnuk-Lipiński Music *Half Life (3 album), ''Half Life'' (3 album) (2001) *Halflife (EP), ''Halflife'' (EP), an EP by Lacuna Coil and the title track *''Half-Life E.P.'', an EP by Local H * "Half Life", a song by 10 Years from ''The Autumn Effect'' * "Half Life", a song by Come from ''Near-Life Experience'' * "Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observationally Stable
Stable nuclides are isotopes of a chemical element whose nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The nuclei of such isotopes are not radioactive and unlike radionuclides do not spontaneously undergo radioactive decay. When these nuclides are referred to in relation to specific elements they are usually called that element's stable isotopes. The 80 elements with one or more stable isotopes comprise a total of 251 nuclides that have not been shown to decay using current equipment. Of these 80 elements, 26 have only one stable isotope and are called monoisotopic. The other 56 have more than one stable isotope. Tin has ten stable isotopes, the largest number of any element. Definition of stability, and naturally occurring nuclides Most naturally occurring nuclides are stable (about 251; see list at the end of this article), and about 35 more (total of 286) are known to be radioactive with long enou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomeric Transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer, 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). Some references recommend seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the nuclear isomer survives so long (at least years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as , , , , and multiple holmium isomers. Sometimes, the gamma decay from a metastable state is referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |