|
Isotope Analysis In Archaeology
Isotope analysis has many applications in archaeology, from dating sites and artefacts, determination of past diets and migration patterns and for environmental reconstruction. Information is determined by assessing the ratio of different isotopes of a particular element in a sample. The most widely studied and used isotopes in archaeology are carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, strontium and calcium. An isotope is an atom of an element with an abnormal number of neutrons, changing their atomic mass. Isotopes can be subdivided into stable and unstable or radioactive. Unstable isotopes decay at a predictable rate over time. The first stable isotope was discovered in 1913, and most were identified by the 1930s. Archaeology was relatively slow to adopt the study of isotopes. Whereas chemistry, biology and physics, saw a rapid uptake in applications of isotope analysis in the 1950s and 1960s, following the commercialisation of the mass spectrometer. It wasn't until the 1970s, with the publicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food web, to reconstruct past environmental and climatic conditions, to investigate human and animal diets, for food authentification, and a variety of other physical, geological, palaeontological and chemical processes. Stable isotope ratios are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio. Tissues affected Isotopic oxygen is incorporated into the body primarily through ingestion at which point it is used in the formation of, for archaeological purposes, bones and teeth. The oxygen is incorporated into the hydroxylcarbonic apatite of bone and tooth enamel. Bone is continually remodelled throughout the lifetime of an individual. Although the rate of tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronological Dating
Chronological dating, or simply dating, is the process of attributing to an object or event a date in the past, allowing such object or event to be located in a previously established chronology. This usually requires what is commonly known as a "dating method". Several dating methods exist, depending on different criteria and techniques, and some very well known examples of disciplines using such techniques are, for example, history, archaeology, geology, paleontology, astronomy and even forensic science, since in the latter it is sometimes necessary to investigate the moment in the past during which the death of a cadaver occurred. These methods are typically identified as absolute, which involves a specified date or date range, or relative, which refers to dating which places artifacts or events on a timeline relative to other events and/or artifacts. Other markers can help place an artifact or event in a chronology, such as nearby writings and stratigraphic markers. Absolute an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Decay Of Carbon-14
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: from nearly instantaneous to far longer than the age of the universe. The decaying nucleus is called the parent ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. Etymology Because it was produced from halite, rock salt according to the methods of Johann Rudolph Glauber, hydrochloric acid was historically called by European alchemists ''spirits of salt'' or ''acidum salis'' (salt acid). Both names are still used, especially in other languages, such as , , , , , , , , , , (''ensan''), zh, 盐酸 (''yánsuān''), and (''yeomsan''). Gaseous HCl was called ''marine acid air''. The name ''muriatic acid'' has the same origin (''muriatic'' means "pertaining to brine or salt", hence ''muriate'' means hydrochloride), and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
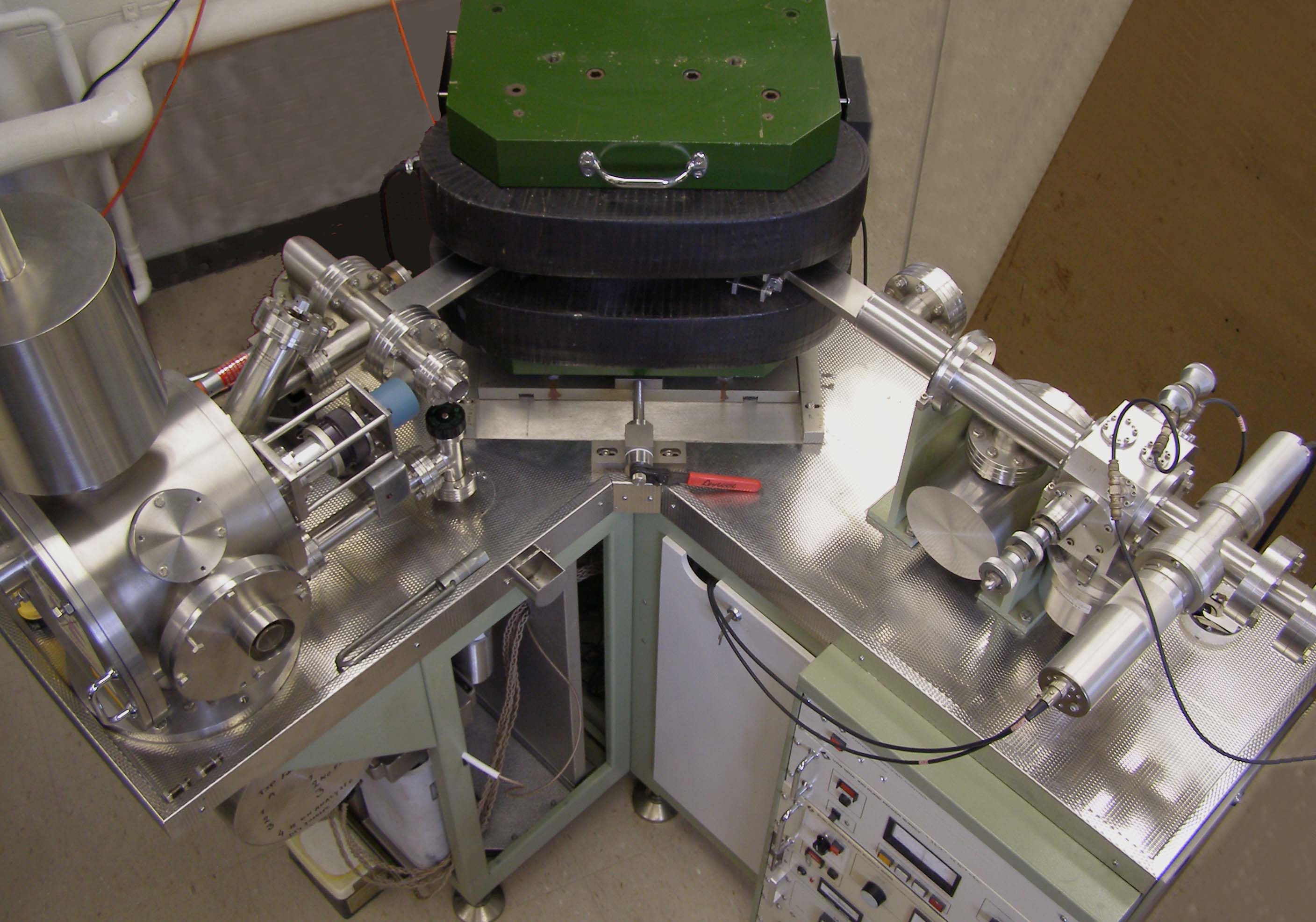
Mass Spectrometer Schematics
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh less than it d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Science
Archaeological science consists of the application of scientific techniques to the analysis of archaeological materials and sites. It is related to methodologies of archaeology. Martinón-Torres and Killick distinguish ‘scientific archaeology’ (as an epistemology) from ‘archaeological science’ (the application of specific techniques to archaeological materials). Martinón-Torres and Killick claim that ‘archaeological science’ has promoted the development of high-level theory in archaeology. However, Smith rejects both concepts of archaeological science because neither emphasize falsification or a search for causality. In the United Kingdom, the Natural and Environmental Research Council provides funding for archaeometry separate from the funding provided for archaeology. Types of archaeological science Archaeological science can be divided into the following areas: * physical and chemical dating methods which provide archaeologists with absolute and relative c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methods In Archaeology
Method (, methodos, from μετά/meta "in pursuit or quest of" + ὁδός/hodos "a method, system; a way or manner" of doing, saying, etc.), literally means a pursuit of knowledge, investigation, mode of prosecuting such inquiry, or system. In recent centuries it more often means a prescribed process for completing a task. It may refer to: *Scientific method, a series of steps, or collection of methods, taken to acquire knowledge *Method (computer programming), a piece of code associated with a class or object to perform a task *Method (patent), under patent law, a protected series of steps or acts *Methodism, a Christian religious movement *Methodology, comparison or study and critique of individual methods that are used in a given discipline or field of inquiry *''Discourse on the Method'', a philosophical and mathematical treatise by René Descartes * ''Methods'' (journal), a scientific journal covering research on techniques in the experimental biological and medical sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |