|
Islamic–Jewish Relations
Religious ties between Muslims and the Jews, Jewish people have existed since the Muhammad's first revelation, founding of Islam in the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century; Muhammad's views on Jews were shaped by his extensive contact with the Jewish tribes of Arabia during his lifetime. Islam shares similar values, guidelines, and principles with the Judaism, Jewish religion, and also incorporates Jewish history as a part of its own.Dennis Prager, Prager, D; Joseph Telushkin, Telushkin, J. ''Why the Jews?: The Reason for Antisemitism''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1983. pp. 110–26. Muslims regard the Israelites, to whom Jews and Samaritans trace their ethnic ancestry, as an important religious concept; they are referenced around 43 times in the Quran, excluding individual prophets, and in many accounts of hadith. Similarly, Moses, the most important Prophets in Judaism, Jewish prophet, is also regarded by Muslims as an prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ( companions in Sunni Islam, Ahl al-Bayt in Shiite Islam). Each hadith is associated with a chain of narrators ()—a lineage of people who reportedly heard and repeated the hadith from which the source of the hadith can be traced. The authentication of hadith became a significant discipline, focusing on the ''isnad'' (chain of narrators) and '' matn'' (main text of the report). This process aimed to address contradictions and questionable statements within certain narrations. Beginning one or two centuries after Muhammad's death, Islamic scholars, known as muhaddiths, compiled hadith into distinct collections that survive in the historical works of writers from the second and third centuries of the Muslim era ( 700−1000 CE). For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halakha
''Halakha'' ( ; , ), also Romanization of Hebrew, transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Judaism, Jewish religious laws that are derived from the Torah, Written and Oral Torah. ''Halakha'' is based on biblical commandments (''Mitzvah, mitzvot''), subsequent Talmudic and Mitzvah#Rabbinic mitzvot, rabbinic laws, and the customs and traditions which were compiled in the many books such as the ''Shulchan Aruch'' or ''Mishneh Torah''. ''Halakha'' is often translated as "Jewish law", although a more literal translation might be "the way to behave" or "the way of walking". The word is derived from the Semitic root, root, which means "to behave" (also "to go" or "to walk"). ''Halakha'' not only guides religious practices and beliefs; it also guides numerous aspects of day-to-day life. Historically, widespread observance of the laws of the Torah is first in evidence beginning in the second century BCE, and some say that the first evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah scholars of the Middle Ages. In his time, he was also a preeminent astronomer and physician, serving as the personal physician of Saladin. He was born on Passover eve 1138 or 1135, and lived in Córdoba, Spain, Córdoba in al-Andalus (now in Spain) within the Almoravid dynasty, Almoravid Empire until his family was expelled for refusing to convert to Islam. Later, he lived in Morocco and Egypt and worked as a rabbi, physician and philosopher. During his lifetime, most Jews greeted Maimonides' writings on Halakha, Jewish law and Jewish ethics, ethics with acclaim and gratitude, even as far away as Iraq and Yemen. Yet, while Maimonides rose to become the revered head of the History of the Jews in Egypt, Jewish community in Egypt, his writings also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
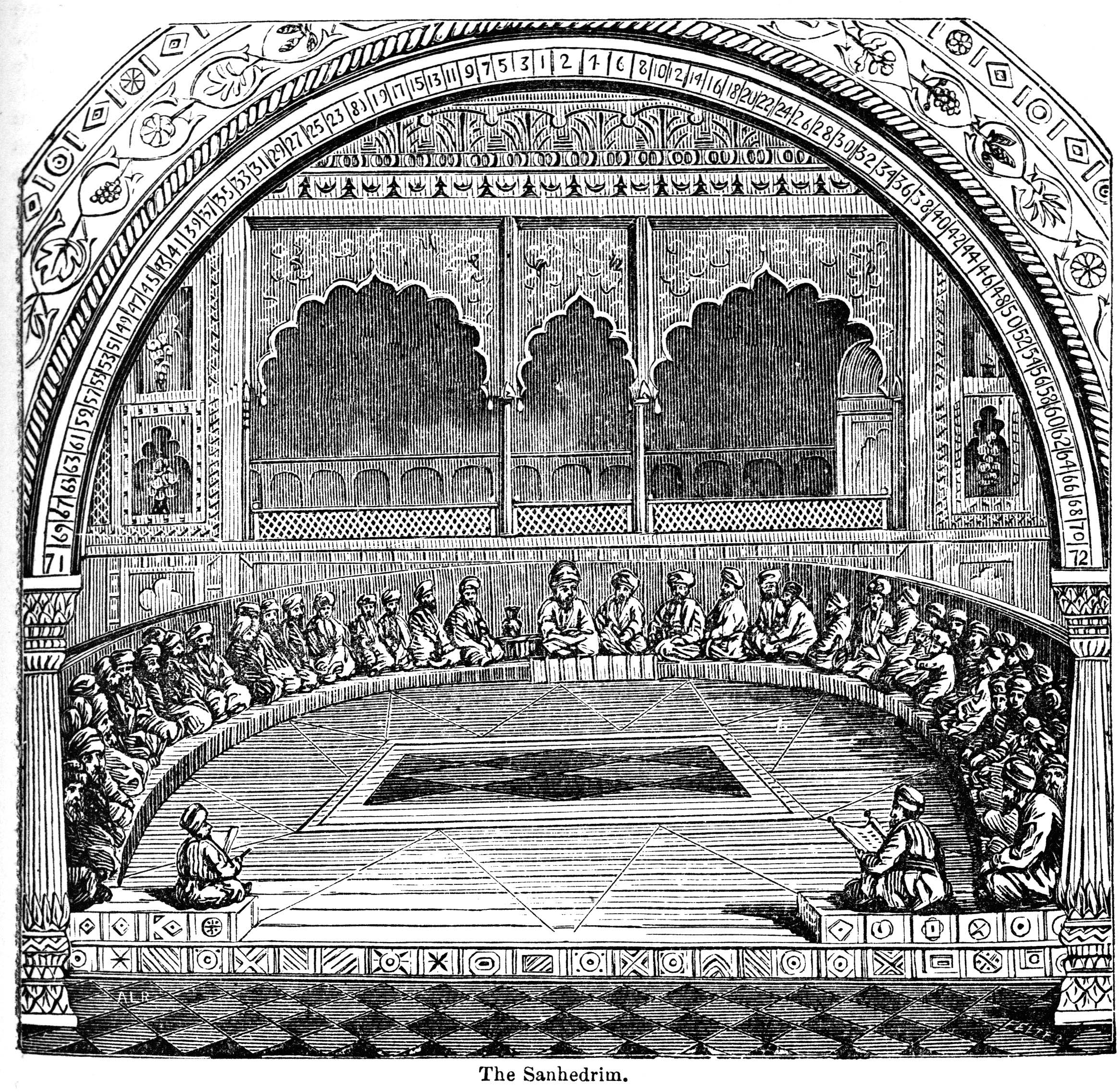
Rabbinic Authority
Rabbinic authority in Judaism relates to the theological and communal authority attributed to rabbis and their pronouncements in matters of Jewish law. The extent of rabbinic authority differs by various Jewish groups and denominations throughout history. The origins of rabbinic authority in Judaism is understood as originally linked to the High Court of ancient Israel and Judah, known as the Sanhedrin. Scholars understand that the extent of rabbinic authority, historically, would have related to areas of Jewish civil, criminal, and ritual law, while rabbinic positions that relate to non-legal matters, such as Jewish philosophy would have been viewed as non-binding.Turkel, E. (1993). The nature and limitations of rabbinic authority. Tradition: A Journal of Orthodox Jewish Thought, 27(4), 80-99. Rabbinic authority also distinguished the practice of Judaism by the Pharisees (i.e., Rabbinic Judaism) to the religious practice of the Sadducees and the Qumran sect. This concept is linke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torah In Islam
In Islam, the Torah ( ) is regarded as an Islamic holy book that was revealed by God to guide the Israelites. In the Quran, the word "Tawrat" appears eighteen times, particularly in passages mentioning the Jewish people or their history, including Jewish prophets who are also regarded as Islamic prophets and messengers, such as Moses. The Torah is held by Muslims in identification with other books of the Hebrew Bible and with Jewish writings and exegeses in the Talmud and Midrash. Quran The word Tawrat occurs eighteen times in the Quran and the name of Musa is mentioned 136 times in the Quran; nowhere in the Quran is it written that Moses alone was given the Tawrat, but on the contrary it is written in the Quran that the prophets governed with the Tawrat. As per Quran, the governing ayats containing an order of God is the Tawrat. The Law mentioned in the Quran (5:45): Similarly it is mentioned in Exodus: According to 7:157, Muhammad is written about in both the Inj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), although the term was used in pre-Islamic Arabia and continues to be used today by Arabic-speaking adherents of any of the Abrahamic religions, including God in Judaism, Judaism and God in Christianity, Christianity. It is thought to be derived by contraction from ''Arabic definite article, al-Ilah, ilāh'' (, ) and is linguistically related to God's names in other Semitic languages, such as Aramaic ( ) and Hebrew language, Hebrew ( ). The word "Allah" now conveys the superiority or sole existence of Monotheism, one God, but among the Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia#Role of Allah, pre-Islamic Arabs, Creator deity, Allah was a supreme deity and was worshipped alongside lesser deities in a Pantheon (religion), pantheon. Many Jews, Christians, and ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God In Abrahamic Religions
Monotheism—the belief that there is only one deity—is the focus of the Abrahamic religions, which like-mindedly conceive God as the all-powerful and all-knowing deity from whom Abraham received a divine revelation, according to their respective narratives. The most prominent Abrahamic religions are Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. They—alongside Samaritanism, Druzism, the Baháʼí Faith, and Rastafari—all share a common foundation in worshipping Abraham's God, who is called ''Yahweh'' in Hebrew and ''Allah'' in Arabic. Likewise, the Abrahamic religions share similar features distinguishing them from other categories of religions: *all of their theological traditions are, to some extent, influenced by the depiction of the God of Israel in the Hebrew Bible; *all of them trace their roots to Abraham as a common genealogical and spiritual patriarch. In the Abrahamic tradition, God is one, eternal, omnipotent, omniscient, and the creator of the universe. God ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Holy Books
Islamic holy books are certain religious scriptures that are viewed by Muslims as having valid divine significance, in that they were authored by God (Allah) through a variety of prophets and messengers, including those who predate the Quran. Among the group of religious texts considered to be valid revelations, the three that are mentioned by name in the Quran are the Tawrat (Arabic for Torah), received by prophets and messengers amongst the Israelites; the Zabur (Psalms), received by David; and the Injeel (Arabic for the Gospel), received by Jesus. Additionally, the Quran mentions God's revealing of the Scrolls of Abraham and the Scrolls of Moses. Muslims hold the Quran, as it was revealed to Muhammad, to be God's final revelation to mankind, and therefore a completion and confirmation of previous scriptures, such as the Bible. Despite the primacy that Muslims place upon the Quran in this context, belief in the validity of earlier Abrahamic scriptures is one of the six Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
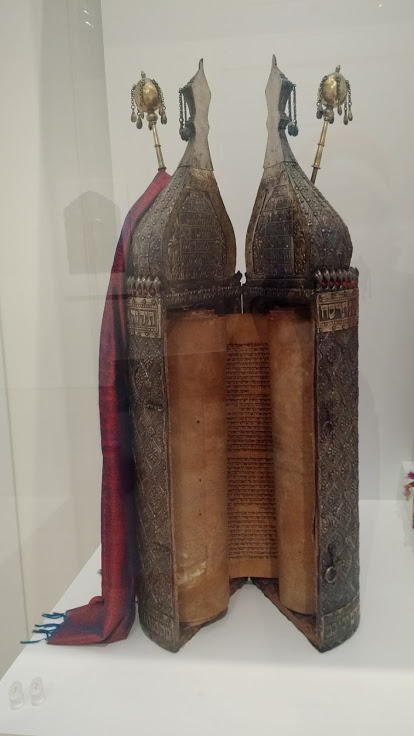
Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () or the Five Books of Moses. In Rabbinical Jewish tradition it is also known as the Written Torah (, ). If meant for liturgic purposes, it takes the form of a Torah scroll ( '' Sefer Torah''). If in bound book form, it is called '' Chumash'', and is usually printed with the rabbinic commentaries (). In rabbinic literature, the word ''Torah'' denotes both the five books ( "Torah that is written") and the Oral Torah (, "Torah that is spoken"). It has also been used, however, to designate the entire Hebrew Bible. The Oral Torah consists of interpretations and amplifications which according to rabbinic tradition have been handed down from generation to generation and are now embodied in the Talmud and Midrash. Rabbinic tradition's underst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moses In Islam
Moses ( , ) is a prominent Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet and messenger of God in Islam, God and is the most frequently mentioned individual in the Quran, with #Quranic references, his name being mentioned 136 times and his life being narrated and recounted more than that of any other prophet.Annabel Keeler, "Moses from a Muslim Perspective", in: Solomon, Norman; Harries, Richard; Winter, Tim (eds.)''Abraham's Muslims in conversation'', T&T Clark Publ. (2005), pp. 55–66. Apart from the Quran, Moses is also described and praised in the Hadith literature as well. He is one of the most important prophets and messengers within Islam. According to the Quran, Moses was born to an Israelite family. In his childhood, he is put in a basket which flows towards the Nile, and is eventually discovered by Pharaoh's (Fir'awn) wife (not named in the Quran but called Asiya in Hadith), who takes Moses as her adopted son. After reaching adulthood, Moses then resides in Midian, befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |