|
Islam In Armenia
Islam began to make inroads into the Armenian plateau during the seventh century. Arab, and later Kurdish, tribes began to settle in Armenia following the first Arab invasions and played a considerable role in the political and social history of Armenia. Ter-Ghewondyan, Aram (1976). ''The Arab Emirates in Bagratid Armenia''. Trans. Nina G. Garsoïan. Lisbon: Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation. With the Seljuk invasions of the eleventh and twelfth centuries, the Turkic element eventually superseded that of the Arab and Kurdish. With the establishment of the Iranian Safavid dynasty, Afsharid dynasty, Zand dynasty and Qajar dynasty, Armenia became an integral part of the Shia world, while still maintaining a relatively independent Christian identity. The pressures brought upon the imposition of foreign rule by a succession of Muslim states forced many lead Armenians in Anatolia and what is today Armenia to convert to Islam and assimilate into the Muslim community. Many Armenians wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speros Vryonis
Speros Vryonis Jr. (, July 18, 1928 – March 12, 2019) was an American historian of Greek descent and a specialist in Byzantine, Balkan, and Greek history. He was the author of a number of works on Byzantine and Greek-Turkish relations, including his seminal ''The Decline of Medieval Hellenism in Asia Minor'' (1971) and ''The Mechanism of Catastrophe'' (2005). Vryonis attained his Bachelor of Arts in ancient history and the classics from Southwestern College (now Rhodes College) in Memphis, Tennessee, in 1950. He received his Masters of Arts from Harvard University two years later and his Ph.D. from the same school in 1956. Vryonis carried out his post-doctoral research at Dumbarton Oaks before joining the history faculty at the University of California, Los Angeles in the mid-1960s, where he served as the director of the G. E. von Grunebaum Center for Near Eastern Studies. In 1987 he was tapped to head the Alexander S. Onassis for Hellenic Studies at New York University. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (''ummah''). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1517). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517 until the Ottoman caliphate was Abolition of the Caliphate, formally abolished as part of the Atatürk's reforms, 1924 secularisation of Turkey. An attempt to preserve the title was tried, with the Sharifian Caliphate, but this caliphate fell quickly after its conquest by the Sultanate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvin (ancient City)
Dvin ( or ; , ''Doúbios'' or Τίβιον, ''Tíbion''; , Dabīl or Doubil) was a large commercial city and the capital of early medieval Armenia. It was situated north of the previous ancient capital of Armenia, the city of Artaxata, along the banks of the Metsamor River, 35 km to the south of modern Yerevan Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev .... It is claimed it was one of the largest cities east of Constantinople prior to its destruction by the Mongols in the 13th century, but with an overall area of approximately 1 km2, it was far smaller than many of the great cities of Asia. It had an estimated population of 45,000 in 361, 47,000 in 622, and around 100,000 at its height in the 8th-9th centuries. Nyura Hakobyan proposed a peak population of 100,000 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostikan
''Ostikan'' () was the title used by Armenians for the governors of the early Caliphates. In modern historiography, it is chiefly used for the caliphal governors of the province of Arminiya, which included Greater Armenia. Arab governors of Armenia Early governors These are reported as governors under the Caliphs Uthman (r. 644–656) and Ali (r. 656–661), as well as the early Umayyads: * Hudhayfa ibn al-Yaman * Al-Mughira ibn Shu'ba * Al-Qasim ibn Rabi'a ibn Umayya ibn Abi al-Salt al-Thaqafi * Habib ibn Maslama al-Fihri * Al-Ash'ath ibn Qays al-Kindi (ca. 657) * Al-Muhallab ibn Abi Sufra (ca. 686) Emirs (Ostikans) With the submission of Armenia to Muhammad ibn Marwan after 695, the province was formally incorporated into the Caliphate, and an Arab governor (''ostikan'') installed at Dvin: * Muhammad ibn Marwan (c. 695–705), represented by the following deputies: ** Uthman ibn al-Walid ibn 'Uqba ibn Aban Abi Mu 'ayt ** Abdallah ibn Hatim al-Bahili * Abd al- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
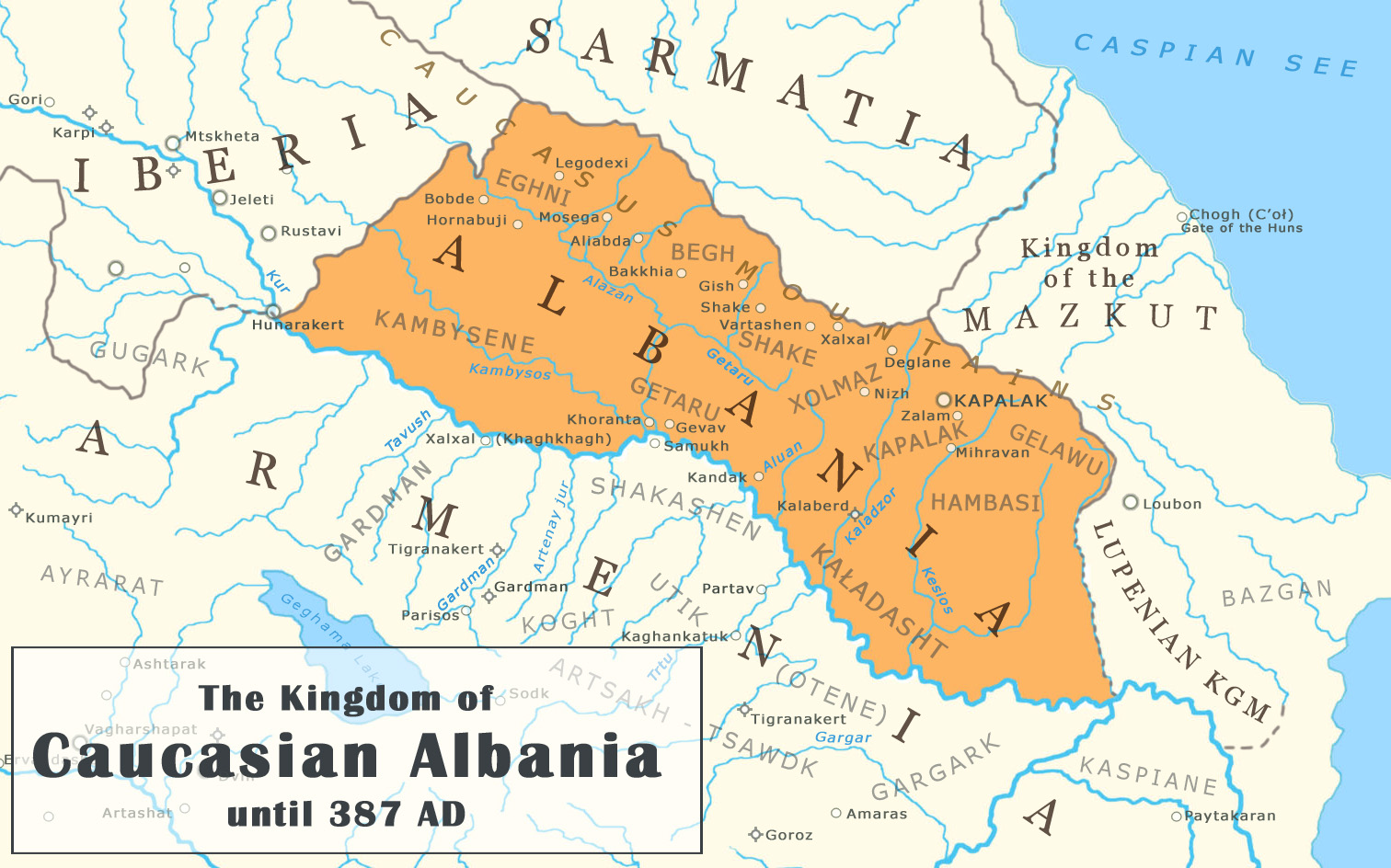
Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus, mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown. The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek name and Latin , created from Greek sources that incorrectly translated the Armenian language. The prefix "Caucasian" is used to avoid confusion with Albania in the Balkans, which has no geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania. Little is known of the region's prehistory, including the origins of Caucasian Albania as a geographical and/or ethnolinguistic concept. In the 1st century BC and the 1st century AD, the area south of the Greater Caucasus and north of the Lesser Caucasus was divided between Caucasian Albania in the east, Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region on the coast of the Black Sea. It is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia, and is today generally regarded as part of Europe. It is bordered to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. Georgia covers an area of . It has a Demographics of Georgia (country), population of 3.7 million, of which over a third live in the capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city, Tbilisi. Ethnic Georgians, who are native to the region, constitute a majority of the country's population and are its titular nation. Georgia has been inhabited since prehistory, hosting the world's earliest known sites of winemaking, gold mining, and textiles. The Classical antiquity, classical era saw the emergence of several kingdoms, such as Colchis and Kingdom of Iberia, Iberia, that formed the nucleus of the modern Georgian state. In the early fourth centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Known colloquially in Syria as () and dubbed, poetically, the "City of Jasmine" ( ), Damascus is a major cultural center of the Levant and the Arab world. Situated in southwestern Syria, Damascus is the center of a large metropolitan area. Nestled among the eastern foothills of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range inland from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean on a plateau above sea level, Damascus experiences an arid climate because of the rain shadow effect. The Barada, Barada River flows through Damascus. Damascus is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. First settled in the 3rd millennium BC, it was chosen as the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate from 661 to 750. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoros Rshtuni
Theodore or Theodoros Rshtuni (, ; AD 590–655 or 656), equated with Pasagnathes (), the "''patrikios'' of the Armenians" from the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor, at, '' of the Byzantine Empire 641-867'' (PBE I) online edition, . Accessed 2021-09-16. was an (magnate), famous for resisting the first Arab invasions of Armenia. After the previous (prince) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taron (historic Armenia)
Taron (; Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Daron''; , ''Tarōn''; ) was a canton of the Turuberan province of Greater Armenia, roughly corresponding to the Muş Province of modern Turkey. Early Middle Ages The main source on the principality's history during the Early Middle Ages is the ''History of Taron'', a relatively short "historical" romance in five parts, purporting to describe significant events occurring in the district of Taron during the Byzantine–Sassanid Wars when the Sassanid emperor was Khosrau II (590-628). During Khosrau's reign, Taron was frequently invaded by the Persians. The ''History'' describes the actions of five generations of Mamikonians (Taron's princely house), in defending and avenging the district. Each section or cycle of the story is devoted to the exploits of one of the defenders: Mushegh, Vahan, Smbat, his son Vahan Kamsarakan, and the latter's son Tiran. The heroes are at times superhumanly brave or duplicitous, wise or cunning, humble or bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Ar-Rahman Ibn Rabiah
ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn Rabīʿa al-Bāhilī () was a prominent Arab general of the Rashidun Caliphate, who led the Arab forces during the First Arab–Khazar War and the early Islamic conquests of the 7th century. He served under the Rashidun Caliphate and led expeditions that aimed to expand Muslim control northward. He led significant battles and encounters with the Khazar Khaganate. His campaigns in the Caucasus were marked by both military successes and setbacks, reflecting the challenges of warfare in the mountainous terrain. Abd al-Rahman's died in 652 along with 4,000 of his men, following a siege on the city of Balanjar. Life A member of the Bahila tribe, Abd al-Rahman ibn Rabi'a was also known as Dhu'l-Nur or Dhu'l-Nun after his sword. He was the older brother of Salman ibn Rabi'a. He served with Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas at the Battle of Qadisiyya against the Sassanid Persians, and then as a at the Arab garrison town of Kufa until 641. From 642 until his death in 652, Abd al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Muslim Conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests (), also known as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the founder of Islam. He established the first Islamic state in Medina, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia that expanded rapidly under the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate, culminating in Muslim rule being established on three continents (Asia, Africa, and Europe) over the next century. According to historian James Buchan: "In speed and extent, the first Arab conquests were matched only by those of Alexander the Great, and they were more lasting." At their height, the territory that was conquered by the Arab Muslims stretched from Iberian Peninsula, Iberia (at the Pyrenees) in the west to Indian subcontinent, India (at Sind (caliphal province), Sind) in the east; Muslim control spanned Sicily, most of the Middle East and North Africa, and the Caucasus and Central Asia. Among other drastic changes, the early Muslim conquests brought about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |