|
Ishūretsuzō
, also known as or ''A Series of Paintings of Ainu Chieftains'' or ''Portraits of Ezo Chieftains'', is a series of twelve painted portraits, dating to 1790, of Ainu people, Ainu elders in the aftermath of the Menashi–Kunashir rebellion. They are by the Japanese artist and Matsumae Domain retainer Kakizaki Hakyo, Kakizaki Hakyō (1764–1826). Eleven of the twelve paintings survive, in the collection of the Musée des Beaux-Arts et d'Archéologie de Besançon. A number of preparatory drawings and copies are to be found in collections in Japan. The clothing worn and other accoutrements depicted help cast light on late eighteenth-century connections between the indigenous inhabitants of Ezo, Ezochi, the ''Japanese people, Wajin'', China, and Russia. The portrait of Ininkari from the series also represents the earliest known documentation of brown bears (''Ursus arctos'') with white Fur, pelage, the so-called "Ininkari bears" that are to be found on Kunashir (Kunashiri) and Iturup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsumae Domain
The was a Japanese clan that was confirmed in the possession of the area around Matsumae, Hokkaidō as a march fief in 1590 by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, and charged with defending it, and by extension the whole of Japan, from the Ainu "barbarians" of the north. The clan, originally known as the Kakizaki clan (蠣崎氏), had settled in Kakizaki, Kawauchi, Mutsu on the Shimokita Peninsula. Claiming descent from the Takeda clan of Wakasa Province, the family later took the name Matsumae. In exchange for their service in defending the country, the Matsumae were made exempt from owing rice to the shogunate in tribute, and from the ''sankin-kōtai'' system, under which most ''daimyōs'' (feudal lords of Edo period Japan) were required to spend half the year at Edo, while their families spent the entire year at Edo and were, essentially, held hostage to prevent rebellion. Relations with the Ainu and Russia Due to their location, and their role as border defenders, the Matsumae were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu Genre Painting
or (アイヌ絵 ''Ainu-e'') is the Japanese art historical term for depictions of Ainu by '' Wajin'', prevalent from the mid- Edo period to the early Meiji period (eighteenth and nineteenth centuries). The preliterate Ainu had no painting tradition of their own. Typical subjects include myths and legends, rituals, encounters with ''wajin'', hunting, fishing, and forms of entertainment. Artists active in the genre include , , , Kakizaki Hakyō, , , , and . See also * Ishūretsuzō * Namban art * Orientalism In art history, literature and cultural studies, Orientalism is the imitation or depiction of aspects in the Eastern world. These depictions are usually done by writers, designers, and artists from the Western world. In particular, Orientalist p ... References {{Reflist Japanese painting Ainu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsumae Clan
The was a Japanese clan that was confirmed in the possession of the area around Matsumae, Hokkaidō as a march fief in 1590 by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, and charged with defending it, and by extension the whole of Japan, from the Ainu "barbarians" of the north. The clan, originally known as the Kakizaki clan (蠣崎氏), had settled in Kakizaki, Kawauchi, Mutsu on the Shimokita Peninsula. Claiming descent from the Takeda clan of Wakasa Province, the family later took the name Matsumae. In exchange for their service in defending the country, the Matsumae were made exempt from owing rice to the shogunate in tribute, and from the ''sankin-kōtai'' system, under which most ''daimyōs'' (feudal lords of Edo period Japan) were required to spend half the year at Edo, while their families spent the entire year at Edo and were, essentially, held hostage to prevent rebellion. Relations with the Ainu and Russia Due to their location, and their role as border defenders, the Matsumae wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1604 Ezo Trade Letter From Tokugawa Ieyasu To Matsumae Yoshihiro (Hokkaido Museum)
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: * 16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * ''Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band * Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from '' Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
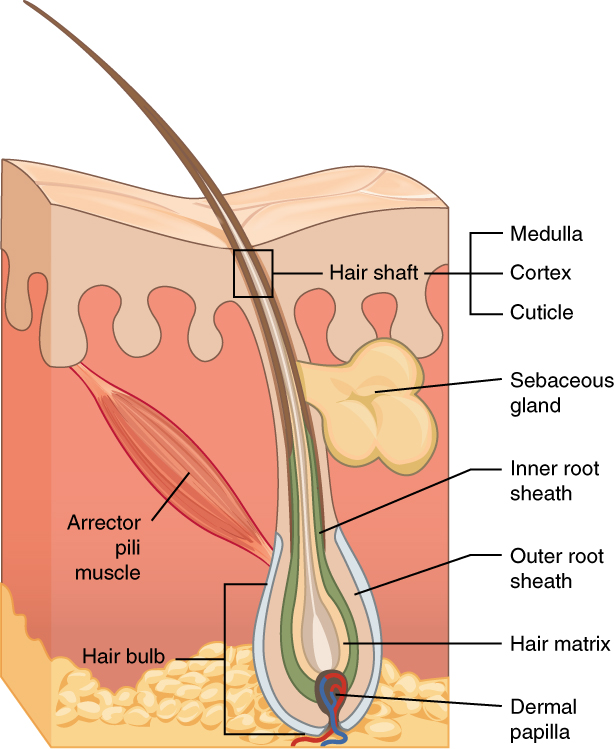
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alterity
Alterity is a philosophical and anthropological term meaning "otherness", that is, the " other of two" (Latin ''alter''). It is also increasingly being used in media to express something other than "sameness", or something outside of tradition or convention. Philosophy Within the phenomenological tradition, alterity is usually understood as the entity in contrast to which an identity is constructed, and it implies the ability to distinguish between self and not-self, and consequently to assume the existence of an alternative viewpoint. The concept was further developed by Emmanuel Levinas in a series of essays, collected in ''Altérité et transcendance'' (''Alterity and Transcendence'') (1995). Castoriadis For Cornelius Castoriadis (''L'institution imaginaire de la société'', 1975; ''The Imaginary Institution of Society'', 1997) radical alterity/otherness (french: altérité radicale) denotes the element of creativity in history: "For what is given in and through history is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsumae, Hokkaido
is a town located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. The former home of the Matsumae Han, it has an Edo period castle, Matsumae Castle, the only one in Hokkaido, and Ryūun-in. The total area of the town is . History *1900: Fukuyama town was founded. *1940: Fukuyama changed its name to Matsumae. *1953: Matsumae Line opened. *1954: Matsumae town, Oshima village, Osawa village, and Kojima village were merged to form Matsumae town. *1988: Matsumae Line was abolished. Geography The town is located on the southern end of the Matsumae Peninsula. In addition the town governs the two islands in the Tsugaru Strait, Oshima and Kojima. Along with Kaminokuni, Hokkaido, and Fukushima, Hokkaido, Matsumae shares a border with Mount Daisengen, and contains the newest and shortest climbing route to the summit of the mountain. Climate Demographics As of September 2016, the town has an estimated population of 7,843 and a density of 26.7 persons per km2. Culture and life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urup
Urup ( ja, 得撫島, Uruppu-to; russian: Уру́п, Urúp, ain, ウルㇷ゚, Urup) is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Kuril Islands chain in the south of the Sea of Okhotsk, northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language word for salmon trout. It was formerly known as Company's Land. Geography and climate Urup has a roughly rectangular shape, measuring along its long axis and approximately along its narrow axis. It is the fourth largest of the Kuril Islands, with an area of . The highest point is Gora Ivao at . The strait between Urup and Iturup is known as the Vries Strait, after Netherlands, Dutch explorer Maarten Gerritsz Vries, the first recorded European to explore the area. The strait between Urup and Simushir is known as Bussol Strait, after the French word for "compass", which was the name of one of Jean-François de Galaup, comte de La Pérouse, La Pérouse's vessels. This French mariner explored the area of the Kuril Islands in 1787. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
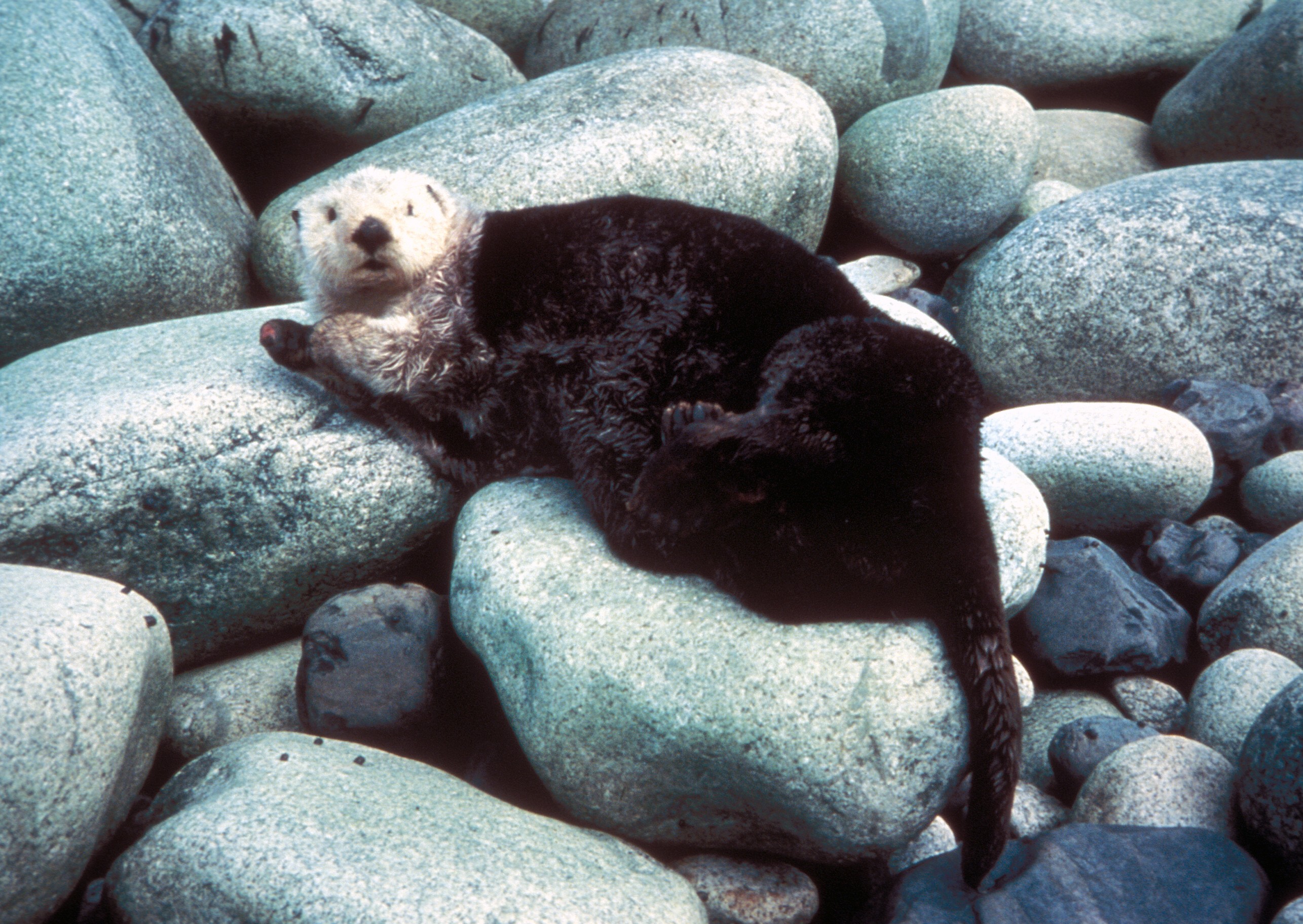
Sea Otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smallest marine mammals. Unlike most marine mammals, the sea otter's primary form of insulation is an exceptionally thick coat of fur, the densest in the animal kingdom. Although it can walk on land, the sea otter is capable of living exclusively in the ocean. The sea otter inhabits nearshore environments, where it dives to the sea floor to forage. It preys mostly on marine invertebrates such as sea urchins, various mollusks and crustaceans, and some species of fish. Its foraging and eating habits are noteworthy in several respects. Its use of rocks to dislodge prey and to open shells makes it one of the few mammal species to use tools. In most of its range, it is a keystone species, controlling sea urchin populations which would otherwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menashi District, Hokkaido
is a district located in Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. As of 2010, its population is estimated at 6,069 and its area is 397.88 km2, with a population density of 15.3/km2 (according to the ''Basic Resident Register'' 住民基本台帳, 31 March 2010.) The origin of the name "Menashi" comes from the Ainu word ''menashi'', meaning "to the east". The local government in Nemuro, which includes Shiretoko and The Northern Territories, decided to name the whole region "Menashi". Menashi's only town is Rausu. The district was one of the settings of the Menashi-Kunashiri Battle of 1789. Towns * Rausu History During the Edo period (1603–1868), the ruling Tokugawa ''shōgun'' allowed the Matsumae clan (''Matsumae han'' 松前藩) to settle in the Menashi region, which was then named Nemuro. According to the Matsumae clan's ''Chronicles of Shiragi'' (''Shiragi no kiroku'' 新羅の記録), from the first year of the Genna era to about Genna 7 (1615–1622) the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)