|
Isaberrysaura Mollensis
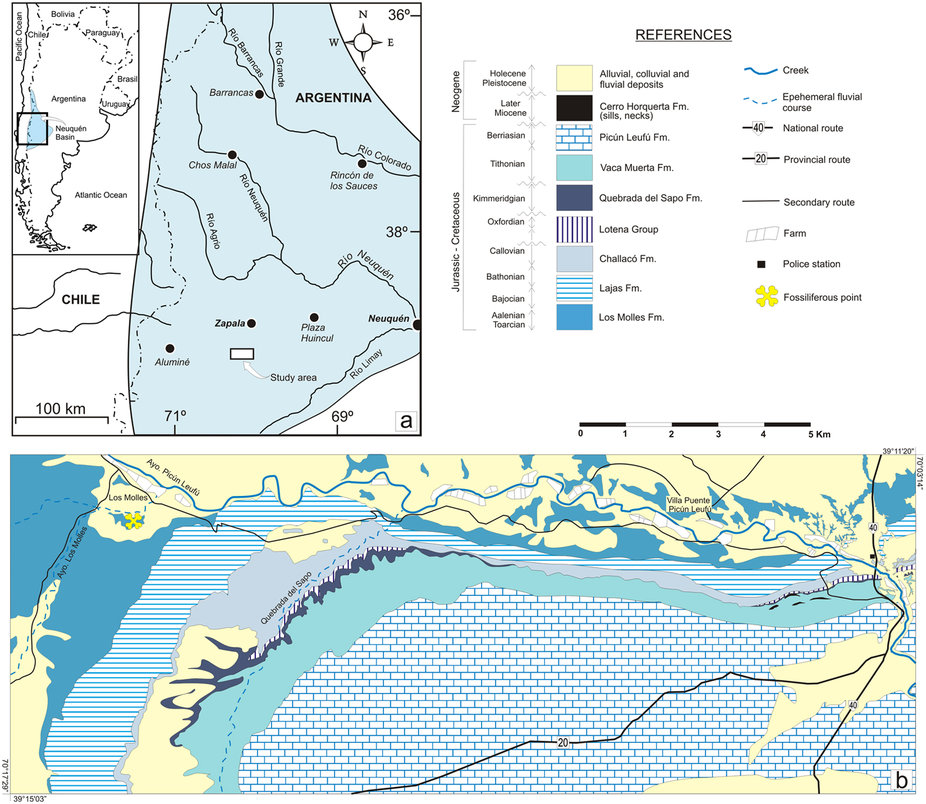
''Isaberrysaura'' is an extinct genus of stegosaurian ornithischian dinosaurs from the Middle Jurassic Los Molles Formation of Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, ''I. mollensis'', described by Salgado in 2017 based on a single specimen. Although initially classified as a basal neornithischian, subsequent analyses have allied it with the Stegosauria as the morphology of its skull resembles those of other members of the group. Discovery The ''Isaberrysaura'' holotype specimen, MOZ-Pv 6459, was discovered in the marine to deltaic sediments of the Los Molles Formation, which is of Bajocian age, by Isabel Valdivia Berry, who is honoured in the generic name. The specimen consists of a partial skeleton (the postcranial material of which is still unprepared) with a nearly complete skull , six cervical vertebrae, fifteen dorsal vertebrae, a sacrum with a partial ilium and apparently complete pubis, nine caudal vertebrae, part of a scapula, ribs, and other un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajocian
In the geologic timescale, the Bajocian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 170.9 ±0.8 Ma to around 168.2 ±1.2 Ma (million years ago). The Bajocian Age succeeds the Aalenian Age and precedes the Bathonian Age. Stratigraphic definitions The Bajocian Stage takes its name from the Latin name (Bajocae) of the town of Bayeux, in the region of Normandy in France. The stage was named and introduced in scientific literature by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842. The base of the Bajocian stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic column where fossils of the ammonite genus '' Hyperlioceras'' first appear. A global reference profile (a GSSP) for the base is located at Murtinheira, close to Cabo Mondego in Portugal.The GSSP is described by Pavia & Enay (1997) The top of the Bajocian (the base of the Bathonian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species ''Parkinsonia convergens''. Subdivision The Bajocian is often divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing ( ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bashanosaurus Primitivus
''Bashanosaurus'' (meaning "Bashan lizard") is an extinct genus of stegosaurian dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian age) Shaximiao Formation of Yunyang County, China. The genus contains a single species, ''Bashanosaurus primitivus'', known from incomplete skeletons belonging to three individuals. It is one of the basalmost stegosaurs, as well as one of the oldest known stegosaurs, along with ''Adratiklit'', ''Isaberrysaura'', and ''Thyreosaurus''. Discovery and naming In 2016, a quarry of dinosaur fossils representing outcrops of the lower Shaximiao Formation was found in Laojun Village of Pu’an Township in Yunyang County, Chongqing Municipality, China. The ''Bashanosaurus'' fossil material was among the bones found in the outcrops, consisting of three specimens collected from the same horizon. The holotype specimen, CLGPR V00006-1, includes one dorsal and two caudal vertebrae, the right scapulocoracoid, a partial left hindlimb (femur, tibia, fibula, and a metat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huayangosauridae
Stegosauria is a group of herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and early Cretaceous periods. Stegosaurian fossils have been found mostly in the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia), Africa and South America. Their geographical origins are unclear; the earliest unequivocal stegosaurian, '' Bashanosaurus primitivus'', was found in the Bathonian Shaximiao Formation of China. Stegosaurians were armored dinosaurs (thyreophorans). Originally, they did not differ much from more primitive members of that group, being small, low-slung, running animals protected by armored scutes. An early evolutionary innovation was the development of spikes as defensive weapons. Later species, belonging to a subgroup called the Stegosauridae, became larger, and developed long hindlimbs that no longer allowed them to run. This increased the importance of active defence by the thagomizer, which could ward off even large predators because the tail was in a hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genasauria
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek stem ' (), meaning "bird", and ' (), meaning "hip". However, as theropod dinosaurs, birds are only distantly related to this group. Ornithischians with well known anatomical adaptations include the ceratopsians or "horn-faced" dinosaurs (e.g. ''Triceratops''), the pachycephalosaurs or "thick-headed" dinosaurs, the armored dinosaurs (Thyreophora) such as stegosaurs and ankylosaurs, and the ornithopods. There is strong evidence that certain groups of ornithischians lived in herds, often segregated by age group, with juveniles forming their own flocks separate from adults. Some were at least partially covered in filamentous (hair- or feather- like) pelts, and there is much debate over whether these filaments found in specimens of '' Tianyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyreophora
Thyreophora ("shield bearers", often known simply as "armored dinosaurs") is a group of armored ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic until the end of the Cretaceous. Thyreophorans are characterized by the presence of body armor lined up in longitudinal rows along the body. Primitive forms had simple, low, keeled scutes or osteoderms, whereas more derived forms developed more elaborate structures including spikes and plates. Most thyreophorans were herbivorous A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat n ... and had relatively small brains for their body size. Thyreophora includes two major subgroups, Ankylosauria and Stegosauria. In both clades, the forelimbs were much shorter than the hindlimbs, particularly in stegosaurs. Thyreophora has been defined a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms (Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic islands, oceanic Archipelago, island chains. The grouping is Paraphyly, paraphyletic as some lizards are more closely related to snakes than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards") have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some lizards, such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco (genus), Draco'', are able to glide. They are often Territory (animal), territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguanidae
The Iguanidae is a family of lizards composed of the iguanas, chuckwallas, and their prehistoric relatives, including the widespread green iguana. Taxonomy Iguanidae is thought to be the sister group to the Crotaphytidae, collared lizards (family Crotaphytidae). This family likely first appeared in Cenozoic, previously identified two Cretaceous genera (''Pristiguana'' and ''Pariguana'') are unlikely to belong to this family. The subfamily Iguaninae, which contains all modern genera, likely originated in the earliest Paleocene, about 62 million years ago. The most Basal (phylogenetics), basal extant genus, ''Desert iguana, Dipsosaurus,'' diverged from the rest of Iguaninae during the late Eocene, about 38 million years ago, with ''Brachylophus'' following a few million years later at about 35 million years ago, presumably after its dispersal event to the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. All other modern iguana genera formed in the Neogene period. A phylogenetic tree of Iguaninae is shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodont
In anatomy, a heterodont (from Greek, meaning 'different teeth') is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology. Human dentition is heterodont and diphyodont as an example. In vertebrates, heterodont pertains to animals where teeth are differentiated into different forms. For example, members of the Synapsida generally possess incisors, canines ("dogteeth"), premolars, and molars. The presence of heterodont dentition is evidence of some degree of feeding and or hunting specialization in a species. In contrast, homodont or isodont dentition refers to a set of teeth that possess the same tooth morphology. In invertebrates, the term heterodont refers to a condition where teeth of differing sizes occur in the hinge plate, a part of the Bivalvia Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |