|
Isaac Oviedo
Isaac Oviedo (July 6, 1902 – June 16, 1992) was a Cuban tres player, singer and songwriter. He was the founder and leader of the Septeto Matancero for over 50 years, and the author of many famous '' sones'' such as "Engancha carretero". Throughout his long career Oviedo only recorded a handful of sessions, mostly for American record labels. He has been called "one of the greatest Cuban tres players" by other musicians such as Efraín Ríos and Pancho Amat. According to the latter, Oviedo was the pioneering and most influential ''tresero'' of the ''septeto'' format (the major type of son ensemble of the 1920s and '30s). His technical innovations include the ''alzapúa'' thumb stroke and the use of the pinky finger. His son Ernesto played in his band since the 1940s and became a successful bolero singer, while his other son Gilberto, known as Papi Oviedo, has also had a long career as a ''tresero'', playing with Conjunto Chappottín, Estrellas de Chocolate and Orquesta Revé. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unión De Reyes
Unión de Reyes is a municipality and town in the Matanzas Province of Cuba. It is located in the western part of the province, south of Matanzas, Cuba, Matanzas, the provincial capital. History Unión de Reyes was founded in 1844, and it was established as a municipality on July 1, 1879. Its name derives from ''Unión en el Punto de Reyes'', so named for its location at a railway junction. Geography The municipality, originally divided into the barrios of Iglesia and Unión, is divided into 9 ''consejos populares'' (i.e. "people's councils"): the town of Unión de Reyes and the villages of Alacranes, Bermejas, Cabezas (Unión de Reyes), Cabezas, Cidra, Estante, Juan Ávila, Juan G. Gómez and Puerto Rico. Demographics In 2022, the municipality of Unión de Reyes had a population of 35,021. With a total area of , it has a population density of . See also *Municipalities of Cuba *List of cities in Cuba References External links * Populated places in Matanzas Provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancho Amat
Francisco Amat Rodríguez (born April 22, 1950), better known as Pancho Amat, is a Cuban musician specialized in the Tres (musical instrument), tres. In 1971, he became a founding member of Manguaré, which would become one of the leading ensembles within the nueva trova movement. He later played in Adalberto Álvarez, Adalberto Álvarez y su Son. Currently, he is the leader of his own group, El Cabildo del Son. In 2010, he won the National Music Award given by the Cuban Music Institute. Biography He obtained his degree in pedagogy from the University of Havana in 1971 and studied classical guitar at the Ignacio Cervantes Conservatory. Also in 1971, he founded Grupo Manguaré, which he directed for more than 15 years. He has workedin trios, quartets, ensembles, charangas, even making arrangements for symphonic orchestra. He has collaborated with artists such as Joaquín Sabina, Oscar D'León, Pablo Milanés, Rosana, Ry Cooder, Silvio Rodríguez, Víctor Víctor, Yomo Toro, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtuoso
A virtuoso (from Italian ''virtuoso'', or ; Late Latin ''virtuosus''; Latin ''virtus''; 'virtue', 'excellence' or 'skill') is an individual who possesses outstanding talent and technical ability in a particular art or field such as fine arts, music, singing, playing a musical instrument, or composition. Meaning This word also refers to a person who has cultivated appreciation of artistic excellence, either as a connoisseur or Collecting, collector. The plural of ''virtuoso'' is either ''virtuosi'' or the Anglicisation ''virtuosos'', and the feminine forms are ''virtuosa'' and ''virtuose''. According to ''Music in the Western World'' by Piero Weiss and Richard Taruskin: ..."A virtuoso was, originally, a highly accomplished musician, but by the nineteenth century the term had become restricted to performers, both vocal and instrumental, whose technical accomplishments were so pronounced as to dazzle the public." The defining element of virtuosity is the performance ability of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamenco
Flamenco () is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the Gitanos, gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Region of Murcia, Murcia. In a wider sense, the term is used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani people, Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage. The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' (The Moroccan Letters) by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Belafonte
Harry Belafonte ( ; born Harold George Bellanfanti Jr.; March 1, 1927 – April 25, 2023) was an American singer, actor, and civil rights activist who popularized calypso music with international audiences in the 1950s and 1960s. Belafonte's career breakthrough album ''Calypso (album), Calypso'' (1956) was the first million-selling LP album, LP by a single artist. Belafonte was best known for his recordings of "Day-O (The Banana Boat Song)", "Jump in the Line (Shake, Senora)", "Jamaica Farewell", and "Mary's Boy Child". He recorded and performed in many genres, including blues, folk music, folk, gospel music, gospel, show tunes, and Great American Songbook, American standards. He also starred in films such as ''Carmen Jones (film), Carmen Jones'' (1954), ''Island in the Sun (film), Island in the Sun'' (1957), ''Odds Against Tomorrow'' (1959), ''Buck and the Preacher'' (1972), and ''Uptown Saturday Night'' (1974). He made his final feature film appearance in Spike Lee's ''Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Music (genre)
Latin music ( Portuguese and ) is a term used by the music industry as a catch-all category for various styles of music from Ibero-America, which encompasses Latin America, Spain, Portugal, and the Latino population in Canada and the United States, as well as music that is sung in either Spanish and/or Portuguese. It may also include music from other territories where Spanish- and Portuguese-language music is made. Terminology and categorization Because the majority of Latino immigrants living in New York City in the 1950s were of Puerto Rican or Cuban descent, "Latin music" had been stereotyped as music simply originating from the Spanish Caribbean. The popularization of bossa nova and Herb Alpert's Mexican-influenced sounds in the 1960s did little to change the perceived image of Latin music. In 1969, the first international organization which attempted to define Latin music was the Festival Mundial de la Canción Latina which included Spanish, Portuguese, French, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marianao
Marianao is one of the 15 municipalities or boroughs (''municipios'' in Spanish) in the city of Havana, Cuba. It lies 6 miles southwest of the original city of Havana, with which it is connected by the Marianao railway. In 2022 the municipality had a population of 134,057. Marianao is on a range of hills of about 1500 above sea level and is noted for its salubrious climate. The city dates back to 1830. Overview As Havana expanded during the 1930s and 1940s, Marianao became a suburb of the city. A famous landmark is the monument built to honor Carlos Juan Finlay, a doctor who helped eradicate yellow fever in Cuba in the 19th century. It is shaped like a syringe. The monument is at the junction of Calles 100 and 31, close to several major hospitals. Marianao is home to the famous Tropicana Club and was home to the Oriental Park Racetrack. One of the most notable foods made in Marianao is "Pollo A La Barbacoa". Personalities *Alicia Alonso, prima ballerina assoluta * Camilo Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauto Theater
The Sauto Theater opened in 1863 in Matanzas, Cuba, and has since then been a proud symbol of the city. The U-shaped 775-seat theatre is almost entirely covered with wood-panelling. It has three balconies, and its floor can be raised to convert the auditorium into a ballroom. The original theater curtain is a painting of the Puente de la Concordia over the Yumurí River. The lobby is graced by Carrara marble statues of Greek goddesses and the main hall ceiling bears paintings of the muses. History When it opened in 1863, it was named Teatro Esteban, after the Civil Governor of Matanzas at the time, Pedro Esteban y Arranz. But soon it adopted the last name of Ambrosio de la Concepción Sauto, a patron of the arts who contributed much to its construction and splendour. Due to the proximity of Matanzas to Havana, the cultural awareness of its people, and the solvency of its rich landowners, the Sauto Theater was visited regularly by the great performers who appeared in Havana. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
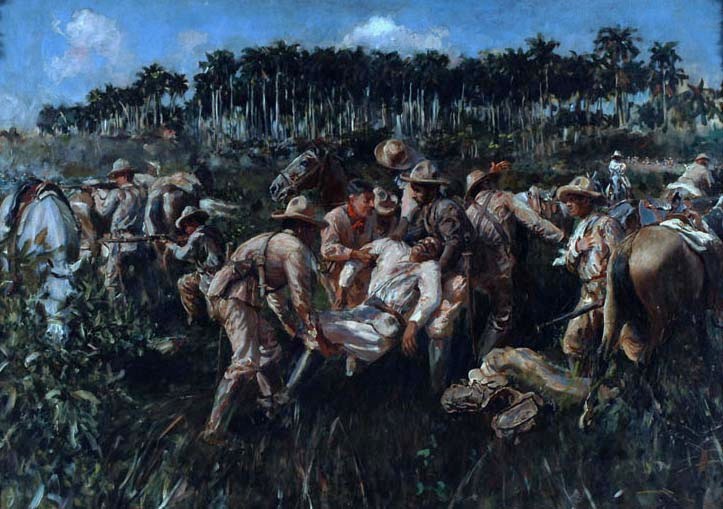
Cuban War Of Independence
The Cuban War of Independence (), also known in Cuba as the Necessary War (), fought from 1895 to 1898, was the last of three liberation wars that Cuba fought against Spain, the other two being the Ten Years' War (1868–1878) and the Little War (1879–1880). During the war, Spain sent 220,285 soldiers to Cuba—according to the Library of Congress, the largest army to cross the Atlantic until World War II. The final three months of the conflict escalated to become the Spanish–American War, with United States forces being deployed in Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines against Spain. Historians disagree as to the extent that United States officials were motivated to intervene for humanitarian reasons but agree that yellow journalism exaggerated atrocities attributed to Spanish forces against Cuban civilians. Background During the years 1879–1888 of the so-called "Rewarding Truce", lasting for 17 years from the end of the Ten Years' War in 1878, there were fundament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago De Cuba
Santiago de Cuba is the second-largest city in Cuba and the capital city of Santiago de Cuba Province. It lies in the southeastern area of the island, some southeast of the Cuban capital of Havana. The municipality extends over , and contains the communities of Antonio Maceo, Bravo, Castillo Duany, Daiquirí, El Caney, El Cobre, Cuba, El Cobre, El Cristo, Guilera, Leyte Vidal, Moncada and Siboney, Cuba, Siboney. Historically Santiago de Cuba was the second-most important city on the island after Havana, and remains the second-largest. It is on a bay connected to the Caribbean Sea and an important sea port. In the 2022, the city of Santiago de Cuba recorded a population of 507,167 people. History Santiago de Cuba was the seventh village founded by Spanish conquistador Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar on 25 July 1515. The settlement was destroyed by fire in 1516, and was immediately rebuilt. This was the starting point of the expeditions led by Juan de Grijalba and Hernán Cort� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-taught
Autodidacticism (also autodidactism) or self-education (also self-learning, self-study and self-teaching) is the practice of education without the guidance of schoolmasters (i.e., teachers, professors, institutions). Overview Autodidacts are ''self-taught'' humans who learn a subject-of-study's aboutness through self-study. This educative praxis (process) may involve, complement, or be an alternative to formal education. Formal education itself may have a hidden curriculum that requires self-study for the uninitiated. Generally, autodidacts are individuals who choose the subject they will study, their studying material, and the studying rhythm and time. Autodidacts may or may not have formal education, and their study may be either a complement or an alternative to formal education. Many notable contributions have been made by autodidacts. The self-learning curriculum is infinite. One may seek out alternative pathways in education and use these to gain compet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orquesta Revé
Timba is a Cuban genre of music based on Cuban ''son'' with '' salsa'', American Funk/R&B and the strong influence of Afro-Cuban folkloric music. Timba rhythm sections differ from their salsa counterparts, because timba emphasizes the bass drum, which is not used in salsa bands. Timba and salsa use the same tempo range and they both use the standard conga marcha. Almost all timba bands have a trap drummer. Timbas also often break the basic tenets of arranging the music in- clave. Timba is considered to be a highly aggressive type of music, with rhythm and "swing" taking precedence over melody and lyricism. Associated with timba is a radically sexual and provocative dance style known as despelote (literally meaning chaos or frenzy). It is a dynamic evolution of salsa, full of improvisation and Afro Cuban heritage, based on son, Rumba and mambo, taking inspiration from Latin jazz, and is highly percussive with complex sections. Timba is more flexible than salsa and includes a mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |