|
Irwin Silber
Irwin Silber (October 17, 1925 – September 8, 2010) was an American Communism, Communist, Editing, editor, publisher, and activism, political activist. He edited the folk music magazine ''Sing Out!'' and was active in far-left politics throughout his life. Biography Early years Irwin Silber was born in New York City, to Jewish parents.John Pietaro"Irwin Silber, a Craftsman of the Folk Revival, Dies at 84," ''Political Affairs,'' September 2010. As a young man, Silber joined the Young Communist League, the youth section of the Communist Party USA (CPUSA), moving later to membership in the adult party. Silber ultimately severed his ties with the CPUSA in 1955. Silber attended Brooklyn College, where he was instrumental in establishing the American Folksay Group. Through his involvement with folk music, Silber made the acquaintance of Pete Seeger, Alan Lomax, and others influential in that music scene. Activist and author The co-founder, and former long-time editor of ''Sing Out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Massachusetts Press
The University of Massachusetts Press is a university press that is part of the University of Massachusetts Amherst. The press was founded in 1963, publishing scholarly books and non-fiction. The press imprint is overseen by an interdisciplinary faculty committee. The press is currently a member of the Association of University Presses. Juniper Prizes The press also publishes fiction and poetry through its annual Juniper Prizes.Herman (2007) The Juniper Prize was named in honor of local poet Robert Francis and his house ('Fort Juniper'). The Juniper Prizes include: * 2 prizes for poetry: one for a previously published poet, one for a poet not previously published * 2 prizes for fiction: one for a novel, one for a collection of short stories * creative non-fiction The poetry award began in 1975, the fiction award in 2004, and the award for creative non-fiction in 2018. Controversies University of Massachusetts Press joined The Association of American Publishers trade organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly news magazine based in New York City. Founded as a weekly print magazine in 1933, it was widely distributed during the 20th century and has had many notable editors-in-chief. It is currently co-owned by Dev Pragad, the president and chief executive officer (CEO), and Johnathan Davis, who sits on the board; each owns 50% of the company. In August 2010, revenue decline prompted Graham Holdings, the Washington Post Company to sell ''Newsweek'' to the audio pioneer Sidney Harman for one US dollar and an assumption of the magazine's liabilities. Later that year, ''Newsweek'' merged with the news and opinion website ''The Daily Beast'', forming The Newsweek Daily Beast Company, later called ''NewsBeast''. ''Newsweek'' was jointly owned by the estate of Harman and the company IAC (company), IAC. ''Newsweek'' continued to experience financial difficulties, leading to the suspension of print publication at the end of 2012. In 2013, IBT Media acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Integration Of Major League Baseball
The color line, also known as the color barrier, in American baseball excluded players of black African descent from Major League Baseball and its affiliated Minor Leagues until 1947 (with a few notable exceptions in the 19th century before the line was firmly established). Racial segregation in professional baseball was sometimes called a gentlemen's agreement, meaning a tacit understanding, as there was no written policy at the highest level of organized baseball, the major leagues. A high minor league's vote in 1887 against allowing new contracts with black players within its league sent a powerful signal that eventually led to the disappearance of blacks from the sport's other minor leagues later that century, including the low minors. After the line was in virtually full effect in the early 20th century, many black baseball clubs were established, especially during the 1920s to 1940s when there were several Negro leagues. During this period, American Indians and native Hawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Worker
The ''Daily Worker'' was a newspaper published in Chicago founded by communists, socialists, union members, and other activists. Publication began in 1924. It generally reflected the prevailing views of members of the Communist Party USA (CPUSA); it also reflected a broader spectrum of left-wing opinion. At its peak, the newspaper achieved a circulation of 35,000. Contributors to its pages included Robert Minor and Fred Ellis (cartoonists), Lester Rodney (sports editor), David Karr, Richard Wright, John L. Spivak, Peter Fryer, Woody Guthrie, and Louis F. Budenz. History Origins The origins of the ''Daily Worker'' were with the weekly ''Ohio Socialist'' published by the Socialist Party of Ohio in Cleveland from 1917 to November 1919. The Ohio party joined the nascent Communist Labor Party of America (CLP) at the 1919 Emergency National Convention. The ''Ohio Socialist'' only used whole numbers. Its final issue was #94 November 19, 1919. The ''Toiler'' continued t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
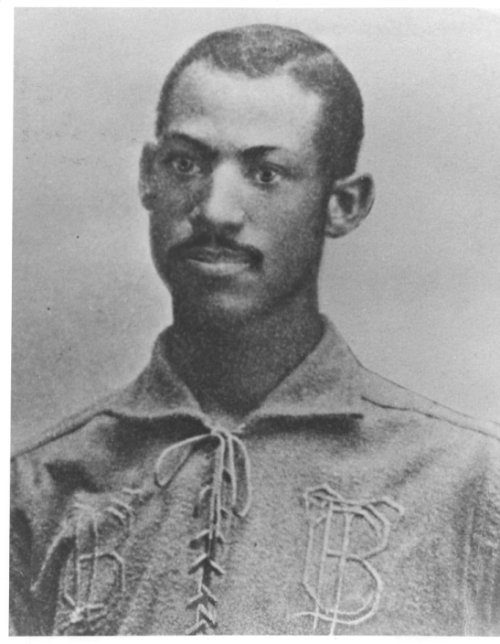
Lester Rodney
Lester Rodney (April 17, 1911 – December 20, 2009) was an American journalist who helped break down the color barrier in baseball as sports writer for the ''Daily Worker''. Early life Rodney was born in Manhattan, New York City, the third of four children of Isabel Cotton and Max Rodney. The Rodneys moved from the Bronx to Brooklyn when Lester was 6, where his lifelong love of the Dodgers developed. Rodney’s father lost his business, and then the family home, in the 1929 stock market crash that began the Great Depression, an era in which communism and other radical social philosophies captured the attention of the intelligentsia. Rodney earned a partial track scholarship to Syracuse University, but his family could not afford the other half of his tuition so he did not complete his formal education. To supplement the family income, he took odd jobs, including helping his attorney brother-in-law and chauffeuring rich children to school. Sports writer for the ''Daily W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Folkways
Smithsonian Folkways is the nonprofit record label of the Smithsonian Institution. It is a part of the Smithsonian's Smithsonian Center for Folklife and Cultural Heritage, located at Capital Gallery in downtown Washington, D.C. The label was founded in 1987 after the family of Moses Asch, founder of Folkways Records, donated the entire Folkways Records label to the Smithsonian. The donation was made on the condition that the Institution continue Asch's policy that each of the more than 2,000 albums of Folkways Records remain in print forever, regardless of sales. Since then, the label has expanded on Asch's vision of documenting the sounds of the world, adding six other record labels to the collection, as well as releasing over 300 new recordings. Some well-known artists have contributed to the Smithsonian Folkways collection, including Pete Seeger, Ella Jenkins, Woody Guthrie, and Lead Belly. Famous songs include " This Land Is Your Land", " Goodnight, Irene", and " Midnig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paredon Records
Paredon Records was a record label founded in 1969 by Barbara Dane and Irwin Silber to publish recordings of cultural expressions, especially protests, in order to preserve them. Paredon wanted to spread awareness of multiple movements and topics. Dane and Silber were both connected with politically engaged artists and musicians, as well as progressive groups, through their work. Dane formed friendships with artists she met while protesting the Vietnam War and other current events. Her active participation in these movements provided her with the inside knowledge and ear to recognize whose voices would be historically significant. Part of the era's social activism and movements for economic, racial and social justice, as well as national liberation, the label released 50 titles between 1970 and 1985 including songs, poetry and oratory. The label's founders were inspired by Cuba and recorded a lot of protest music, including ''The People Gonna Rise!'' with Bev Grant's band Human Condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Of March
The Trend was a Marxist-Leninist political movement of the mid-1970s through the mid-1990s in the United States. It consisted of a loose collection of small communist organizations, newspapers, and theoretical groups that staked out a line that was intermediate between the Soviet-aligned Communist Party, USA and the Third-worldist-oriented, Maoist New Communist Movement. Groups that were part of The Trend include ''The Guardian'' newspaper (now defunct, not to be confused with ''The Guardian (UK) ''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...'') and the associated Guardian Clubs, Line of March (later Frontline Political Organization), ''Crossroads'', Organizing Committee for an Ideological Center, El Comite-MINP, and other groups.Elbaum, ''Revolution in the Air'', pp. 240–24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Elbaum
Max Elbaum is an American author and left-wing activist. He has written extensively about the New Left, the civil rights movement and the Peace movement, anti-war movement. His book on the "new communist movement" of the 1970s and 1980s, ''Revolution in the Air: Sixties Radicals turn to Lenin, Mao and Che'', was praised by historian David Garrow as "an absolutely first-rate work of political scholarship". He was a member of Students for a Democratic Society and later a founder of Line of March. References External links Revolution in The Air By Max Elbaum (archived March 2016) 21st-century American historians American male non-fiction writers American activists Year of birth missing (living people) Living people American Marxists American historians American Maoists {{US-historian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Communist Movement
The New Communist movement (NCM) was a diverse left-wing political movement during the 1970s and 1980s in the United States. The NCM were a movement of the New Left that represented a diverse grouping of Marxist–Leninists and Maoists inspired by Cuban, Chinese, and Vietnamese revolutions. This movement emphasized opposition to racism and sexism, solidarity with oppressed peoples of the third-world, and the establishment of socialism by popular revolution. The movement, according to historian and NCM activist Max Elbaum, had an estimated 10,000 cadre members at its peak influence. History Origins Until the 1960s the largest and most influential organization to the left of the Democratic Party within the United States was the Communist Party, USA (CPUSA), which achieved peak influence during the Great Depression and World War II, before declining in the post war years due to a number of factors, including state-repression (McCarthyism, the Smith Act, the Rosenberg Trial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writers And Editors War Tax Protest
Tax resistance, the practice of refusing to pay taxes that are considered unjust, has probably existed ever since rulers began imposing taxes on their subjects. It has been suggested that tax resistance played a significant role in the collapse of several empires, including the Egyptian, Roman, Spanish, and Aztec. Many rebellions and revolutions have been prompted by resentment of taxation or had tax refusal as a component. Examples of historic events that originated as tax revolts include the Magna Carta, the American Revolution, and the French Revolution. This page is a partial list of global tax revolts and tax resistance actions that have come to the attention of Wikipedia's editors. This includes actions in which a person or people refused to pay a tax of some sort, either through passive resistance or by actively obstructing the tax collector or collecting authorities, and actions in which people boycotted some taxed good or activity or engaged in a strike to reduce or e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |