|
Iron Peak
The iron peak is a local maximum in the vicinity of Iron, Fe (Chromium, Cr, Manganese, Mn, Fe, Cobalt, Co and Nickel, Ni) on the graph of the abundances of the chemical elements. For elements lighter than iron on the periodic table, nuclear fusion exothermic, releases energy. For iron, and for all of the heavier elements, nuclear fusion endothermic, consumes energy. Chemical elements up to the iron peak are produced in ordinary stellar nucleosynthesis, with the alpha elements being particularly abundant. Some heavier elements are produced by less efficient processes such as the r-process and s-process. Elements with atomic numbers close to iron are produced in large quantities in Supernova, supernovae due to explosive Oxygen-burning process, oxygen and Silicon-burning process, silicon fusion, followed by radioactive decay of nuclei such as Nickel-56. On average, heavier elements are less abundant in the universe, but some of those near iron are comparatively more abundant than w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Maximum
In mathematical analysis, the maximum and minimum of a function (mathematics), function are, respectively, the greatest and least value taken by the function. Known generically as extremum, they may be defined either within a given Interval (mathematics), range (the ''local'' or ''relative'' extrema) or on the entire domain of a function, domain (the ''global'' or ''absolute'' extrema) of a function. Pierre de Fermat was one of the first mathematicians to propose a general technique, adequality, for finding the maxima and minima of functions. As defined in set theory, the maximum and minimum of a set (mathematics), set are the greatest and least elements in the set, respectively. Unbounded infinite sets, such as the set of real numbers, have no minimum or maximum. In statistics, the corresponding concept is the sample maximum and minimum. Definition A real-valued Function (mathematics), function ''f'' defined on a Domain of a function, domain ''X'' has a global (or absolute) m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
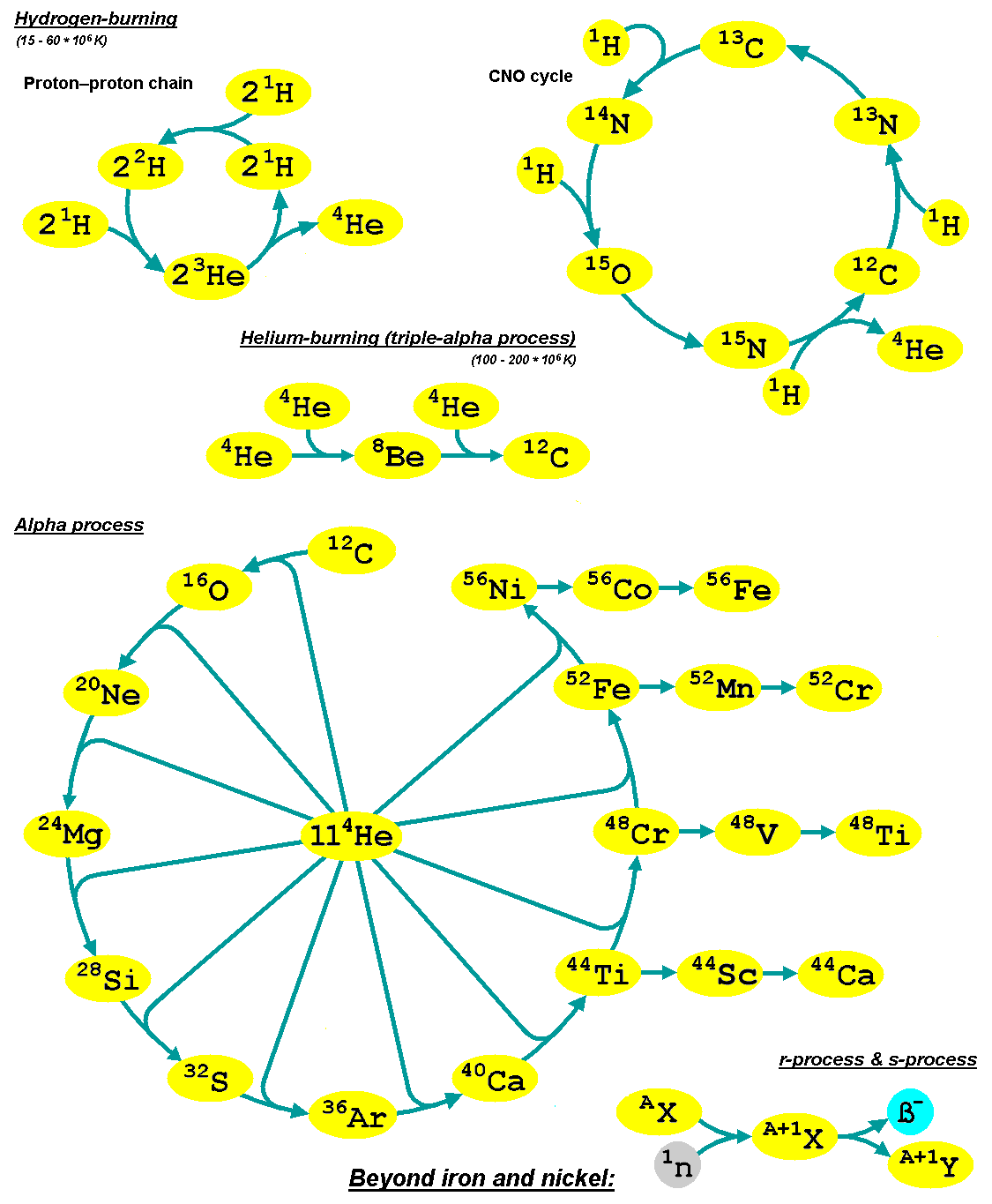
Oxygen-burning Process
The oxygen-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in massive stars that have used up the lighter elements in their cores. Oxygen-burning is preceded by the neon-burning process and succeeded by the silicon-burning process. As the neon-burning process ends, the core of the star contracts and heats until it reaches the ignition temperature for oxygen burning. Oxygen burning reactions are similar to those of carbon burning; however, they must occur at higher temperatures and densities due to the larger Coulomb barrier of oxygen. Reactions Oxygen ignites in the temperature range of (1.5–2.6)×109 KEl Eid, M. F., B. S. Meyer, and L.‐S. The. "Evolution of Massive Stars Up to the End of Central Oxygen Burning." ApJ The Astrophysical Journal 611.1 (2004): 452–65. Arxiv.org. 21 July 2004. Web. 8 Apr. 2016. and in the density range of (2.6–6.7)×1012 kg·m−3.Hirschi. "Evolution and nucleosynthesis of Very Massive Stars". arXiv:1409.7053v1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Process
The alpha process, also known as alpha capture or the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements. The other class is a cycle of reactions called the triple-alpha process, which consumes only helium, and produces carbon. The alpha process most commonly occurs in massive stars and during supernovae. Both processes are preceded by hydrogen fusion, which produces the helium that fuels both the triple-alpha process and the alpha ladder processes. After the triple-alpha process has produced enough carbon, the alpha-ladder begins and fusion reactions of increasingly heavy elements take place, in the order listed below. Each step only consumes the product of the previous reaction and helium. The later-stage reactions which are able to begin in any particular star, do so while the prior stage reactions are still under way in outer layers of the star. :\begin \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel-62
Nickel-62 is an isotope of nickel having 28 protons and 34 neutrons. It is a stable isotope, with the highest binding energy per nucleon of any known nuclide (8.7945 MeV). It is often stated that 56Fe is the "most stable nucleus", but only because 56Fe has the lowest ''mass'' per nucleon (not binding energy per nucleon) of all nuclides. The lower mass per nucleon of 56Fe is possible because 56Fe has 26/56 ≈ 46.43% protons, while 62Ni has only 28/62 ≈ 45.16% protons. Protons are less massive than neutrons, meaning that the larger fraction of protons in 56Fe lowers its mean mass-per-nucleon ratio in a way that has no effect on its binding energy. In other words, Nickel-62 still has the least massive protons and neutrons of any isotope. Properties The high binding energy of nickel isotopes in general makes nickel an "end product" of many nuclear reactions (including neutron capture reactions) throughout the universe and accounts for the high relative abundance of nickel—al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron-58
Natural iron (Fe) consists of four stable isotopes: 5.845% Fe (possibly radioactive with half-life > years), 91.754% Fe, 2.119% Fe and 0.286% Fe. There are 28 known radioisotopes and 8 nuclear isomers, the most stable of which are Fe (half-life 2.6 million years) and Fe (half-life 2.7 years). Much of the past work on measuring the isotopic composition of iron has centered on determining Fe variations due to processes accompanying nucleosynthesis (i.e., meteorite studies) and ore formation. In the last decade however, advances in mass spectrometry technology have allowed the detection and quantification of minute, naturally occurring variations in the ratios of the stable isotopes of iron. Much of this work has been driven by the Earth and planetary science communities, though applications to biological and industrial systems are beginning to emerge. List of isotopes , -id=Iron-45 , rowspan=4, 45Fe , rowspan=4 style="text-align:right" , 26 , rowspan=4 style="text-al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its stellar mass, total mass mainly determines it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay. Nuclear fission was discovered by chemists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann and physicists Lise Meitner and Otto Robert Frisch. Hahn and Strassmann proved that a fission reaction had taken place on 19 December 1938, and Meitner and her nephew Frisch explained it theoretically in January 1939. Frisch named the process "fission" by analogy with biological fission of living cells. In their second publication on nuclear fission in February 1939, Hahn and Strassmann predicted the existence and liberation of additional neutrons during the fission process, opening up the possibility of a nuclear chain reaction. For heavy nuclides, it is an exothermic reaction which can release large amounts of energy both as electromagnetic radiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms or "decays" into a daughter product, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of and a mass of , and is represented as ^_\alpha. For example, uranium-238 undergoes alpha decay to form thorium-234. While alpha particles have a charge , this is not usually shown because a nuclear equation describes a nuclear reaction without considering the electrons – a convention that does not imply that the nuclei necessarily occur in neutral atoms. Alpha decay typically occurs in the heaviest nuclides. Theoretically, it can occur only in nuclei somewhat heavier than nickel (element 28), where the overall binding energy per nucleon is no longer a maximum a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number. Until the 1960s, nucleons were thought to be elementary particles, not made up of smaller parts. Now they are understood as composite particles, made of three quarks bound together by the strong interaction. The interaction between two or more nucleons is called internucleon interaction or nuclear force, which is also ultimately caused by the strong interaction. (Before the discovery of quarks, the term "strong interaction" referred to just internucleon interactions.) Nucleons sit at the boundary where particle physics and nuclear physics overlap. Particle physics, particularly quantum chromodynamics, provides the fundamental equations that describe the properties of quarks and of the strong interaction. These equations describe quantitatively how quarks can bind together into protons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Energy Curve - Common Isotopes
Binding may refer to: Computing * Binding, associating a network socket with a local port number and IP address * Data binding, the technique of connecting two data elements together ** UI data binding, linking a user interface element to an element of a domain model, such as a database field ** XML data binding, representing XML document data using objects and classes * Key binding, or keyboard shortcut, mapping key combinations to software functionality * Language binding, a library providing a functional interface to second library in a different programming language * Name binding, the association of code or data with an identifier in a programming language ** Late binding, name binding which is resolved at run-time rather than in pre-execution time Science * Binding problem, a term for several problems in cognitive science and philosophy ** Neural binding, synchronous activity of neurons and neuronal ensembles * Molecular binding, an attractive interaction between two molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |