|
Iron Brigade
The Iron Brigade, also known as The Black Hats, Black Hat Brigade, Iron Brigade of the West, and originally King's Wisconsin Brigade was an infantry brigade in the Union Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Although it fought entirely in the Eastern Theater, it was composed of regiments from three Western states that are now within the region of the Midwest. Noted for its excellent discipline, ferocity in battle, and extraordinarily strong morale, the Iron Brigade suffered 1,131 men killed out of 7,257 total enlistments: the highest percentage of loss suffered by any brigade in the United States Army during the war. The nickname "Iron Brigade," with its connotation of fighting men with iron dispositions, was applied formally or informally to a number of units in the Civil War and in later conflicts. The Iron Brigade of the West was the unit that received the most lasting publicity in its use of the nickname. The brigade fought in the battles of Second Bull Run, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltese Cross
The Maltese cross is a cross symbol, consisting of four " V" or arrowhead shaped concave quadrilaterals converging at a central vertex at right angles, two tips pointing outward symmetrically. It is a heraldic cross variant which developed from earlier forms of eight-pointed crosses in the 16th century. Although chiefly associated with the Knights Hospitaller (Order of St. John, now the Sovereign Military Order of Malta), and by extension with the island of Malta, it has come to be used by a wide array of entities since the early modern period, notably the Order of Saint Stephen, the city of Amalfi, the Polish Order of the White Eagle (1709), the Prussian order ''Pour le Mérite'' (1740), and the Bavarian Military Merit Order (1866). Unicode defines a character named "Maltese cross" in the Dingbats range at code point U+2720 (✠); however, most computer fonts render the code point as a cross pattée. History The Knights Hospitaller during the Crusades used a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam ( ), also called the Battle of Sharpsburg, particularly in the Southern United States, took place during the American Civil War on September 17, 1862, between Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union Major General George B. McClellan's Army of the Potomac near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek. Part of the Maryland Campaign, it was the first field army–level engagement in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War to take place on Union soil. It remains the bloodiest day in American history, with a tally of 22,727 dead, wounded, or missing on both sides. Although the Union Army suffered heavier casualties than the Confederates, the battle was a major turning point in the Union's favor. After pursuing Confederate General Robert E. Lee into Maryland, Major General George B. McClellan of the Union Army launched attacks against Lee's army who were in defensive positions behind Antietam Creek. At dawn on Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward S
Edward is an English language, English male name. It is derived from the Old English, Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements ''wikt:ead#Old English, ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and ''wikt:weard#Old English, weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the House of Normandy, Norman and House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III of England, Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I of England, Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian Peninsula#Modern Iberia, Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte (name), Duart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William W
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Meredith
Solomon Meredith (May 29, 1810 – October 2, 1875) was an Indiana farmer, politician, and lawman who became a controversial Union Army general in the American Civil War. One of the commanders of the Iron Brigade of the Army of the Potomac, Meredith led the brigade in the Battle of Gettysburg. Although he never fully recovered from the wounds he received that day, he became a prize-winning farmer and cattleman at home and hosted veterans of his unit. Early and family life Solomon Meredith was born in Guilford County, North Carolina, the youngest of twelve children born to David and Mary Farrington Meredith. Meredith's grandfather, James Meredith, fought at the Battle of Guilford Courthouse during the American Revolutionary War. The Merediths were Quaker, and educated young Solomon at home. He was nicknamed "Long Sol" for his towering 6' 7" body. In 1836 Meredith married Anna Hannah, a daughter of Samuel Hannah, who later became the 6th Indiana State Treasurer. Although their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gibbon
John Gibbon (April 20, 1827 – February 6, 1896) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars. Early life Gibbon was born in the Holmesburg, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Holmesburg section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the fourth child of 10 born to Dr. John Heysham Gibbons and Catharine Lardner Gibbons. He was the brother of Lardner Gibbon, publisher of ''Exploration of the Valley of the Amazon''. When Gibbon was nearly 11 years old, the family moved near Charlotte, North Carolina, after his father took a position as chief assayer at the U.S. Mint. He graduated from the United States Military Academy in 1847 and was commissioned a brevet (military), brevet Second Lieutenant#United States, second lieutenant in the 3rd Air Defense Artillery Regiment, 3rd U.S. Artillery. He served in the Mexican–American War without seeing combat, attempted to keep the peace between Seminoles and settlers in south Florida, and taught artil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rufus King (general)
Rufus King (January 26, 1814October 13, 1876) was an American newspaper editor, public servant, diplomat, and soldier. He served as a Union Army brigadier general in the American Civil War, and was responsible for assembling the famed Iron Brigade of the Army of the Potomac. He was later U.S. minister (ambassador) to the Papal States from 1864 to 1867 and was instrumental in the capture of accused Lincoln assassination plotter . Earlier in life, he had been a member of the first board of regents of the University of Wisconsin. Early life King was born in New York City, New York, to Charles King, president of Columbia College, and Eliza Gracie. He was the grandson of Rufus King, delegate for Massachusetts to the Continental Congress and the Constitutional Convention and U.S. Senator from New York. The Kings were part of the King family of Massachusetts, New York, and Maine. After graduation from Columbia Grammar & Preparatory School, King enrolled in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Appomattox Court House
The Battle of Appomattox Court House, fought in Appomattox County, Virginia, on the morning of April 9, 1865, was one of the last, and ultimately one of the most consequential, battles of the American Civil War (1861–1865). It was the final engagement of Confederate General in Chief Robert E. Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia before they surrendered to the Union Army of the Potomac under the Commanding General of the United States Army, Ulysses S. Grant. Lee, having abandoned the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia, after the nine-and-a-half-month Siege of Petersburg and Richmond, retreated west, hoping to join his army with Confederate forces, the Army of Tennessee in North Carolina. Union infantry and cavalry forces under General Philip Sheridan pursued and cut off the Confederates' retreat at the central Virginia village of Appomattox Court House. Lee launched a last-ditch attack to break through the Union forces to his front, assuming the Union force consiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War. Although it is more popularly known as the siege of Petersburg, it was not a classic military siege, in which a city is Encirclement, encircled with fortifications blocking all routes of ingress and egress, nor was it strictly limited to actions against Petersburg. The campaign consisted of nine months of trench warfare in which Union Army, Union forces commanded by Lieutenant general (United States), Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant assaulted Petersburg unsuccessfully and then constructed trench lines that eventually extended over from the eastern outskirts of Richmond, Virginia, to around the eastern and southern outskirts of Petersburg. Petersburg was crucial to the supply of Confederate States Army, Confederate General (CSA), General Robert E. Lee's army and the Confederate States of America, Confederate capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overland Campaign
The Overland Campaign, also known as Grant's Overland Campaign and the Wilderness Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during May and June 1864, towards the end of the American Civil War. Lieutenant general (United States), Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, general-in-chief of all Union Army, Union armies, directed the actions of the Army of the Potomac, commanded by Major general (United States), Maj. Gen. George G. Meade, and other forces against Confederate States Army, Confederate General (CSA), Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia. Although Grant suffered severe losses during the campaign, it was a strategic Union victory. It inflicted proportionately higher losses on Lee's army and maneuvered it into a siege at Richmond in the American Civil War, Richmond and Petersburg, Virginia, in just over eight weeks. Crossing the Rapidan River on May 4, 1864, Grant sought to defeat Lee's army by quickly placing his forces between Lee and Richmond and inviting an ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
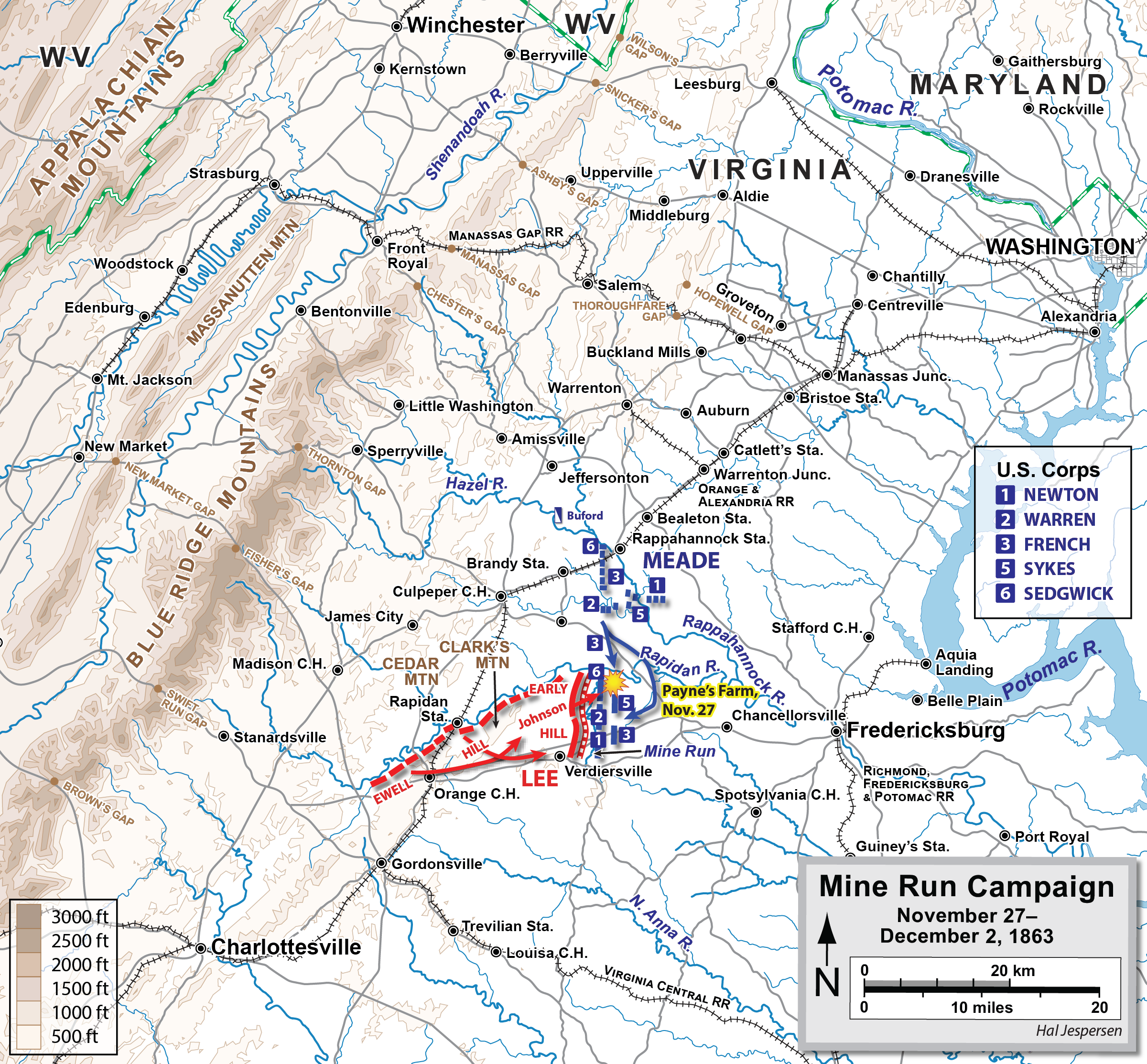
Battle Of Mine Run
The Battle of Mine Run, also known as Payne's Farm, or New Hope Church, or the Mine Run campaign (November 27 – December 2, 1863), was conducted in Orange County, Virginia, in the American Civil War. An unsuccessful attempt of the Union Army of the Potomac to defeat the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, it was marked by false starts and low casualties and ended hostilities in the Eastern Theater for the year. Background After the Battle of Gettysburg in July, Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee and his command retreated back across the Potomac River into Virginia. Union commander Maj. Gen. George G. Meade was widely criticized for failing to pursue aggressively and defeat Lee's army. Meade planned new offensives in Virginia for the fall. His first attempt was a series of inconclusive duels and maneuvers in October and November known as the Bristoe campaign. In late November, Meade attempted to steal a march through the Wilderness of Spotsylvania and strike th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |