|
Iron Act
The Iron Act, also called the Importation, etc. Act 1749 (23 Geo. II c. 29), was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain, which was one of the legislative measures introduced within the system of Trade and Navigation Acts. The Act sought to increase the importation of pig and bar iron from its American colonies and to prevent the building of iron-related production facilities within these colonies, particularly in North America where these raw materials were identified. The dual purpose of the Act was to increase manufacturing capacity within Great Britain itself, and to limit potential competition from the colonies possessing the raw materials. The Act The Act repealed the duties on pig iron and bar iron imported from British America and imported into London respectively. Bar iron might be carried coastwise or by land from there to Royal Navy dockyards, but otherwise not beyond 10 miles from London. The iron must be marked with its place of origin, with most, if not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George II Of Great Britain
George II (George Augustus; german: link=no, Georg August; 30 October / 9 November 1683 – 25 October 1760) was King of Great Britain and Ireland, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg ( Hanover) and a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire from 11 June 1727 ( O.S.) until his death in 1760. Born and brought up in northern Germany, George is the most recent British monarch born outside Great Britain. The Act of Settlement 1701 and the Acts of Union 1707 positioned his grandmother, Sophia of Hanover, and her Protestant descendants to inherit the British throne. After the deaths of Sophia and Anne, Queen of Great Britain, in 1714, his father, the Elector of Hanover, became George I of Great Britain. In the first years of his father's reign as king, George was associated with opposition politicians until they rejoined the governing party in 1720. As king from 1727, George exercised little control over British domestic policy, which was largely controlled by the Parliament of Great Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nail (engineering)
In woodworking and construction, a nail is a small object made of metal (or wood, called a tree nail or "trunnel") which is used as a fastener, as a peg to hang something, or sometimes as a decoration. Generally, nails have a sharp point on one end and a flattened head on the other, but headless nails are available. Nails are made in a great variety of forms for specialized purposes. The most common is a ''wire nail''. Other types of nails include '' pins'', '' tacks'', '' brads'', ''spikes'', and '' cleats.'' Nails are typically driven into the workpiece by a hammer or nail gun. A nail holds materials together by friction in the axial direction and shear strength laterally. The point of the nail is also sometimes bent over or ''clinched'' after driving to prevent pulling out. History The history of the nail is divided roughly into three distinct periods: * Hand-wrought (forged) nail (pre-history until 19th century) * Cut nail (roughly 1800 to 1914) * Wire nail (roughly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
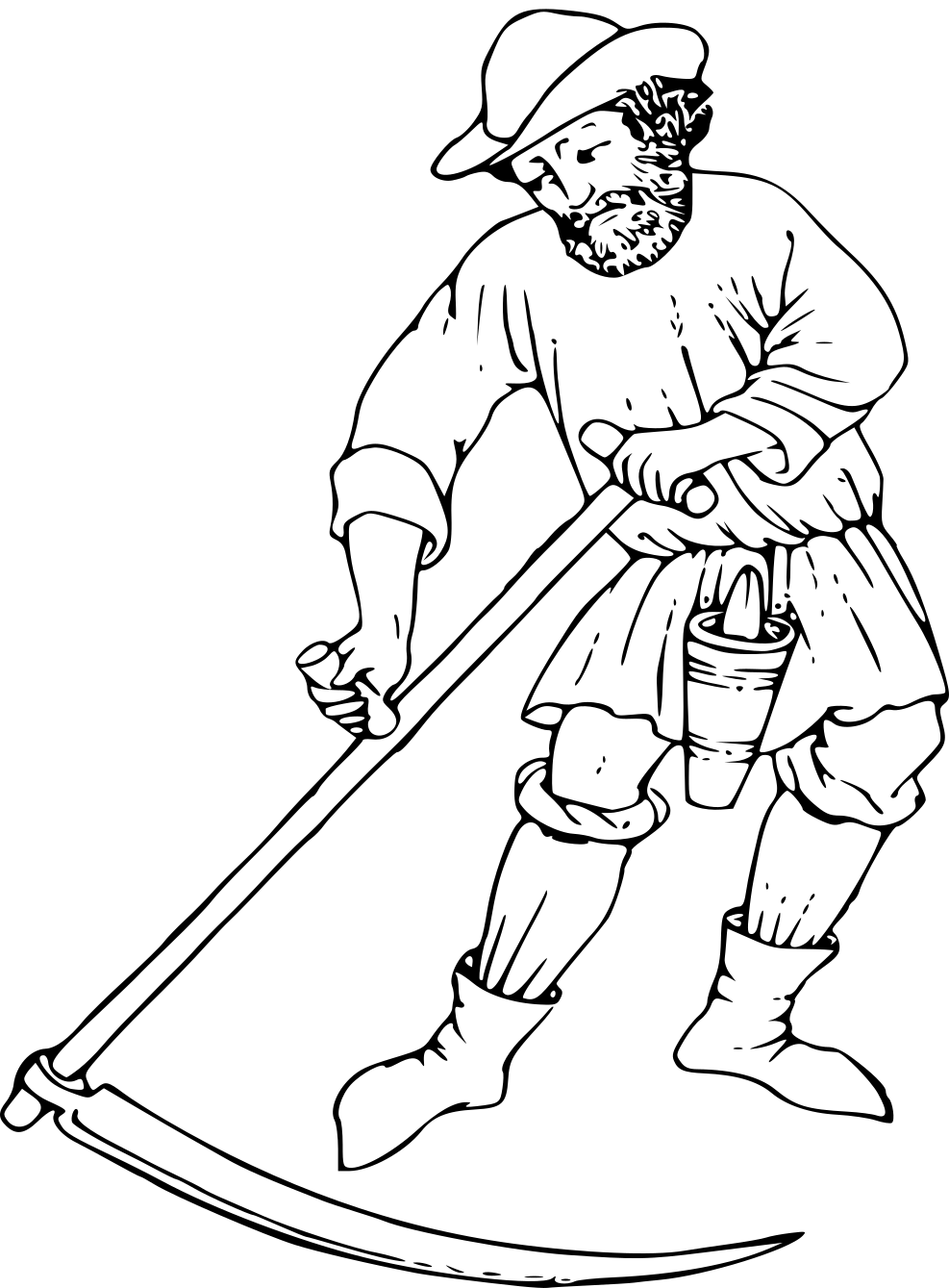
Sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting, or reaping, grain crops or cutting succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock, either freshly cut or dried as hay. Falx was a synonym but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge such as a scythe. Since the beginning of the Iron Age hundreds of region-specific variants of the sickle have evolved, initially of iron and later steel. This great diversity of sickle types across many cultures can be divided into smooth or serrated blades, both of which can be used for cutting either green grass or mature cereals using slightly different techniques. The serrated blade that originated in prehistoric sickles still dominates in the reaping of grain and is even found in modern grain-harvesting machines and in some kitchen knives. History Pre-Neolithic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythe
A scythe ( ) is an agricultural hand tool for mowing grass or harvesting crops. It is historically used to cut down or reap edible grains, before the process of threshing. The scythe has been largely replaced by horse-drawn and then tractor machinery, but is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia. Reapers are bladed machines that automate the cutting of the scythe, and sometimes subsequent steps in preparing the grain or the straw or hay. The word "scythe" derives from Old English ''siðe''. In Middle English and later, it was usually spelt ''sithe'' or ''sythe''. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the ''sc-'' spelling as they thought (wrongly) the word was related to the Latin ''scindere'' (meaning "to cut"). Nevertheless, the ''sithe'' spelling lingered and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries. A scythe consists of a shaft about long called a ''snaith'', ''snath'', ''snathe'' or ''sned'', traditionally made of wood but now some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knife
A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone (such as flint and obsidian), over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin. Knives can serve various purposes. Hunters use a hunting knife, soldiers use the combat knife, scouts, campers, and hikers carry a pocket knife; there are kitchen knives for preparing foods (the chef's knife, the paring knife, bread knife, cleaver), table knives ( butter knives and steak knives), weapons ( daggers or switchblades), knives for throwing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trip Hammer
A trip hammer, also known as a tilt hammer or helve hammer, is a massive powered hammer. Traditional uses of trip hammers include pounding, decorticating and polishing of grain in agriculture. In mining, trip hammers were used for crushing metal ores into small pieces, although a stamp mill was more usual for this. In finery forges they were used for drawing out blooms made from wrought iron into more workable bar iron. They were also used for fabricating various articles of wrought iron, latten (an early form of brass), steel and other metals. One or more trip hammers were set up in a forge, also known variously as a hammer mill, hammer forge or hammer works. The hammers were usually raised by a cam and then released to fall under the force of gravity. Historically, trip hammers were often powered hydraulically by a water wheel. Trip hammers are known to have been used in Imperial China since the Western Han dynasty. They also existed in the contemporary Greco-Roman w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finery Forge
A finery forge is a forge used to produce wrought iron from pig iron by decarburization in a process called "fining" which involved liquifying cast iron in a fining hearth and removing carbon from the molten cast iron through oxidation. Finery forges were used as early as the 3rd century BC in China. The finery forge process was replaced by the puddling process and the roller mill, both developed by Henry Cort in 1783–4, but not becoming widespread until after 1800. History A finery forge was used to refine wrought iron at least by the 3rd century BC in ancient China, based on the earliest archaeological specimens of cast and pig iron fined into wrought iron and steel found at the early Han Dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD) site at Tieshengguo.Pigott, Vincent C. (1999). ''The Archaeometallurgy of the Asian Old World''. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. , p. 186-187. Pigott speculates that the finery forge existed in the prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrought Iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" that is visible when it is etched, rusted, or bent to failure. Wrought iron is tough, malleable, ductile, corrosion resistant, and easily forge welded, but is more difficult to weld electrically. Before the development of effective methods of steelmaking and the availability of large quantities of steel, wrought iron was the most common form of malleable iron. It was given the name ''wrought'' because it was hammered, rolled, or otherwise worked while hot enough to expel molten slag. The modern functional equivalent of wrought iron is mild steel, also called low-carbon steel. Neither wrought iron nor mild steel contain enough carbon to be hardenable by heating and quenching. Wrought iron is highly refined, with a small amount of silic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. Baltimore is the largest city in the state, and the capital is Annapolis, Maryland, Annapolis. Among its occasional nicknames are ''Maryland 400, Old Line State'', the ''Free State'', and the ''Chesapeake Bay State''. It is named after Henrietta Maria, the French-born queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland, who was known then in England as Mary. Before its coastline was explored by Europeans in the 16th century, Maryland was inhabited by several groups of Native Americans – mostly by Algonquian peoples and, to a lesser degree, Iroquoian peoples, Iroquoian and Siouan languages, Siouan. As one of the original Thirteen Colonies of England, Maryland was founded by George Calvert, 1st Baron Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond, Virginia, Richmond; Virginia Beach, Virginia, Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's population was over 8.65million, with 36% of them living in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The area's history begins with Native American tribes in Virginia, several indigenous groups, including the Powhatan. In 1607, the London Company established the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English overseas posse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementation Process
The cementation process is an obsolete technology for making steel by carburization of iron. Unlike modern steelmaking, it increased the amount of carbon in the iron. It was apparently developed before the 17th century. Derwentcote Steel Furnace, built in 1720, is the earliest surviving example of a cementation furnace. Another example in the UK is the cementation furnace in Doncaster Street, Sheffield. Origins The process was described in a treatise published in Prague in 1574. It was again invented by Johann Nussbaum of Magdeburg, who began operations at Nuremberg (with partners) in 1601. The process was patented in England by William Ellyot and Mathias Meysey in 1614. At that date, the "invention" could consist merely of the introduction of a new industry or product, or even a mere monopoly. They evidently soon transferred the patent to Sir Basil Brooke, but he was forced to surrender it in 1619. A clause in the patent prohibiting the import of steel was foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_und_ihre_Kinder_Georg_August_und_Sophie_Dorothea.jpg)

.jpg)