|
Iron-Ossetic
Iron Ossetian ( ) also known as Iron Ossetic or Iron-Ossetic, is one of the two main dialects of the Ossetic language along with DigorThordarson, Fridrik. 1989. Ossetic. Compendium Linguarum Iranicarum, ed. by Rudiger Schmitt, 456-79. Wiesbaden: Reichert/ref> spoken in the Caucasus. The majority of Ossetians speak Iron, notably in the East, South and Central parts of North Ossetia–Alania, while in the West the Digor dialect is more prevalent. The Iron dialect has been the basis of the Ossetian written language since the abolition of the Digor standard in 1939. The Iron dialect is spoken by the majority of North Ossetians (most of flat Ossetia, as well as the Kurtatin, Tagaur and Alagir gorges). With insignificant lexical borrowings from Digor dialect, it is the basis of one of the variants of the literary Ossetian language. The North Ossetian radio and television broadcasts in it, and the daily republican newspaper Ræstdzinad (in the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania) is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, or Ciscaucasia, is a subregion in Eastern Europe governed by Russia. It constitutes the northern part of the wider Caucasus region, which separates Europe and Asia. The North Caucasus is bordered by the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea to the west, the Caspian Sea to the east, and the Caucasus Mountains to the south. The region shares land borders with the countries of Georgia (country), Georgia and Azerbaijan in the South Caucasus. Located in the southern part of the region, Mount Elbrus is the List of European ultra-prominent peaks, tallest peak in Europe. Krasnodar is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, most populous among the urban area, urban centres in the region. The North Caucasus came under Russian control in the 19th century, following the Caucasian War between the Russian Empire and the various regional powers. The territory is the Southern Russia, southernmost portion of Russia and is divided between a number of Republics of Russia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetic Language
Ossetian ( , , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete, is an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Russian-Georgian border in the Greater Caucasus region. It is the native language of the Ossetians, Ossetian people, and a relative and possibly a descendant of the extinct Scythian languages, Scythian, Sarmatians, Sarmatian, and Alanic language, Alanic languages. The northern half of the Ossetian region is part of Russia and is known as North Ossetia–Alania, while the southern half is part of the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Occupied territories of Georgia, Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia (country), Georgia). Ossetian-speakers number about 614,350, with 451,000 recorded in Russia per the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Russian census. Despite Ossetian being the official languages of both Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; or , or , ) is an Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic region on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia (country), Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed South Ossetia, Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the North Ossetia–Alania, Republic of North Ossetia–Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774-1830 – Expansion of the Russian Empire on Ossetian territory. * 1922 – Creation of the South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast, South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Repub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron People
The Irons (Iron Ossetian, East Ossetian: Ирон ''Iron'', pl.: Ир ''Ir'', Ирӕттӕ ''Irættæ''; Digor Ossetian, West Ossetian: Ирон ''Iron'', pl.: Ирӕ ''Irӕ'', Ирӕнттӕ ''Irænttæ'') are a subgroup of the Ossetians. They speak the Iron Ossetian, Iron dialect of the Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian Ossetian language. The majority of Irons profess Russian Orthodoxy and a small minority profess Sunni Islam mainly in the lowland villages of North Ossetia, while the Uatsdin faith has also been preserved by a minority of Irons. History The ethnonym Iron has the same root, ''Aryan, arya'', as Iran and many Iranian-speaking peoples, including the precursors of the Iron, the Alans, Alana (Alans). Following the Mongol invasions of Durdzuketi, Mongol invasions of the 1200s and incursions by Timur, Tamerlane in the late 1300s, the Alans fled from their homeland to seek refuge in the remote Caucasian valleys while others were incorporated into the conqueri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ræstdzinad
''Ræstdzinad'' (; , spelled in the first issue, , ) is an Ossetian language daily newspaper (excluding Sunday and Monday) published in Vladikavkaz, Russia Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ..., since March 14, 1923. The circulation during recent years stood at 15,000–20,000 copies. External links Official site Newspapers published in the Soviet Union Ossetian-language newspapers Newspapers established in 1923 Vladikavkaz 1923 establishments in Russia Daily newspapers {{russia-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
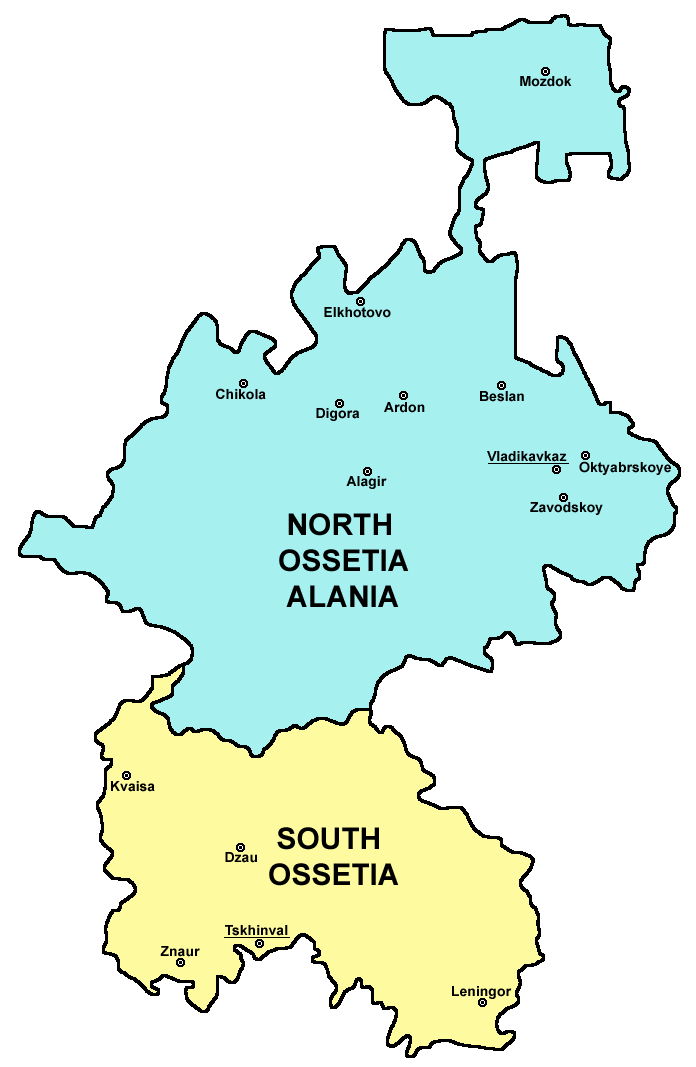
North Ossetia–Alania
North Ossetia–Alania (; ), officially the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. It borders the country of Georgia (country), Georgia to the south, and the Russian federal subjects of Kabardino-Balkaria to the west, Stavropol Krai to the north, Chechnya to the east and Ingushetia to the southeast. Its population according to the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census was 687,357. The republic’s capital city is Vladikavkaz, located on the foothills of the Caucasus Mountains. The majority of the republic's population (68.1% as of 2021) are Ossetians, an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the republic and neighboring South Ossetia. Ossetian language, Ossetian is an east Iranian language descended from the medieval Alans, Alanic and ancient Sarmatian language, Sarmatian languages. Unlike many ethnic groups in the North Caucasus, the majority of Ossetians are Christians, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetians
The Ossetians ( or ; ),Merriam-Webster (2021), s.v"Ossete" also known as Ossetes ( ), Ossets ( ), and Alans ( ), are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains. They natively speak Ossetian language, Ossetic, an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, with most also being fluent in Russian language, Russian as a second language. Currently, the Ossetian homeland of Ossetia is politically divided between North Ossetia–Alania in Russia, and the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Occupied territories of Georgia, Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia (country), Georgia). Their closest historical and linguistic relatives, the Jasz people, Jász people, live in the Jászság, Jászság region within the northwestern part of the Jász-Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have conventionally been considered as a natural barrier between Europe and Asia, bisecting the Eurasian landmass. Mount Elbrus, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus area of Russia. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is mostly located on the territory of sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digor Dialect
Digor Ossetian (; ) also known as Digor Ossetic or Digor-Ossetic, is a dialect of the Ossetic language spoken by the Digor people. It is less widely spoken than Iron, the other extant Ossetian dialect. The two are distinct enough to sometimes be considered separate languages; in the recently published Digor–Russian dictionary, the compiler Fedar Takazov refers to a "Digor language", but the editor in the same book uses "Digor dialect". Digor is spoken in the west of the Republic of North Ossetia (Digora, Chikola, etc.) and in neighboring Kabardino-Balkaria. Digor is used far less than Iron at about a one-to-five ratio and is nearly non-existent in the Republic of South Ossetia. Digor and Iron are not mutually comprehensible, as there are about 2,500 words in the Digor dialect that do not exist in the Iron dialect, and some North Ossetian scholars still consider Digor a separate language, as it was considered until 1937. The phonetic, morphological, and lexical differences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or isolated areas. The non-standard dialects of a language with a writing system will operate at different degrees of distance from the standardized written form. Standard and nonstandard dialects A ''standard dialect'', also known as a "standardized language", is supported by institutions. Such institutional support may include any or all of the following: government recognition or designation; formal presentation in schooling as the "correct" form of a language; informal monitoring of everyday Usage (language), usage; published grammars, dictionaries, and textbooks that set forth a normative spoken and written form; and an extensive formal literature (be it prose, poetry, non-ficti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Ossetia
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek ''boreas'' "north wind, north" which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can mean b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |