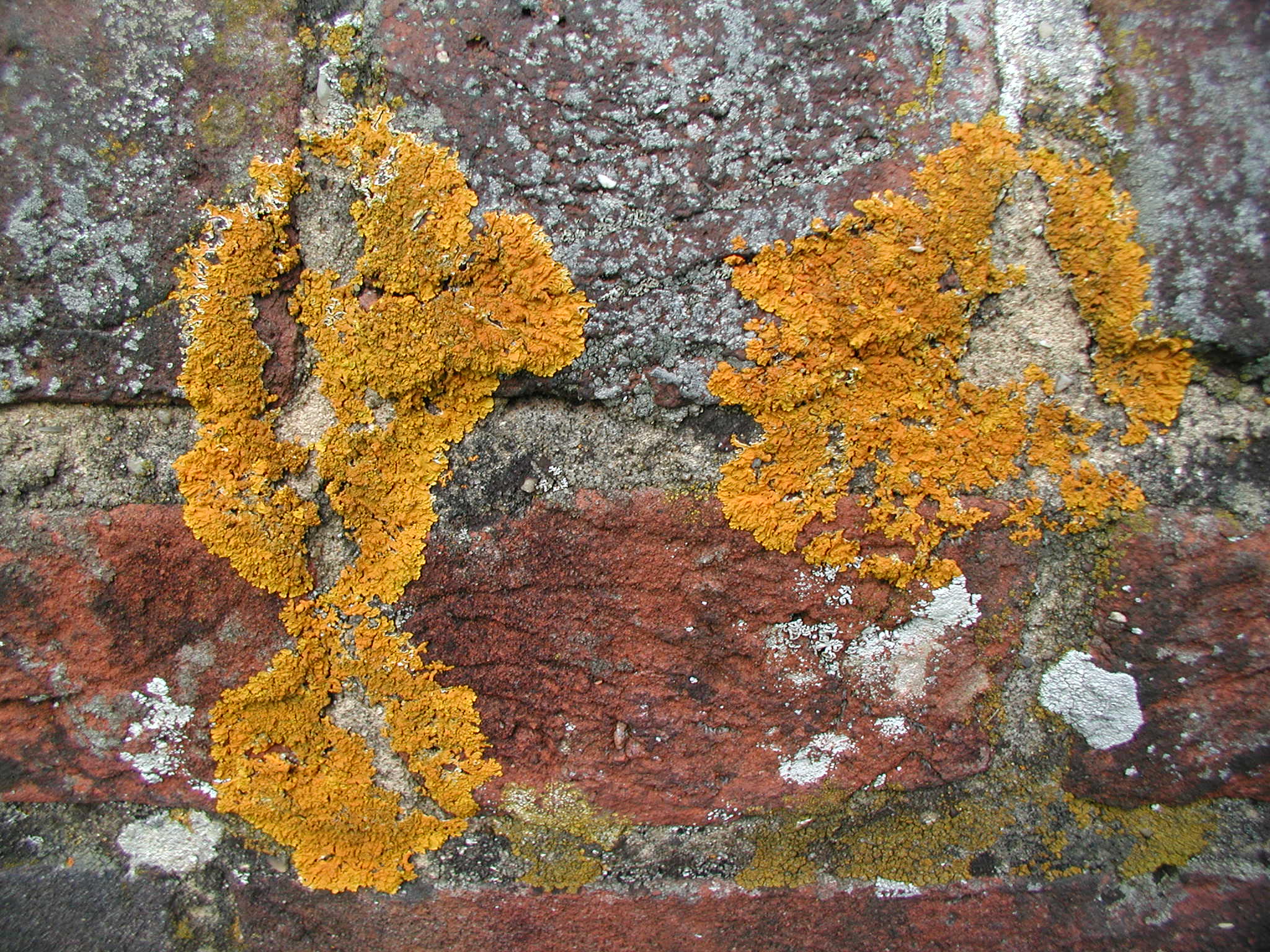|
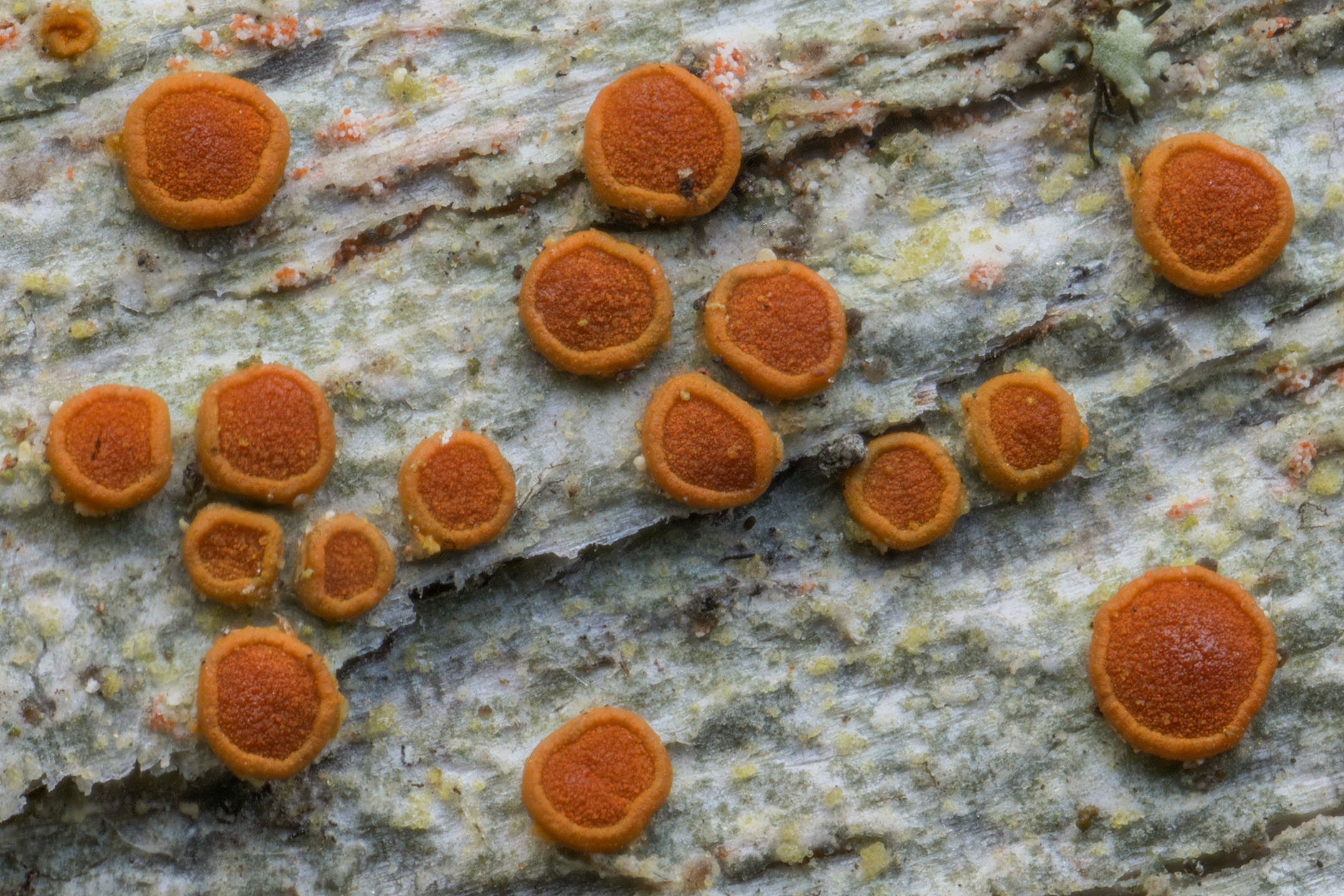
Ioplaca Pindarensis
''Ioplaca'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Teloschistaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1977 by Czech lichenologist Josef Poelt with '' Ioplaca sphalera'' assigned as the type species In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe .... Species *'' Ioplaca pindarensis'' *'' Ioplaca rinodinoides'' *'' Ioplaca sphalera'' References Teloschistales Lichen genera Teloschistales genera Taxa described in 1977 Taxa named by Josef Poelt {{Teloschistales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
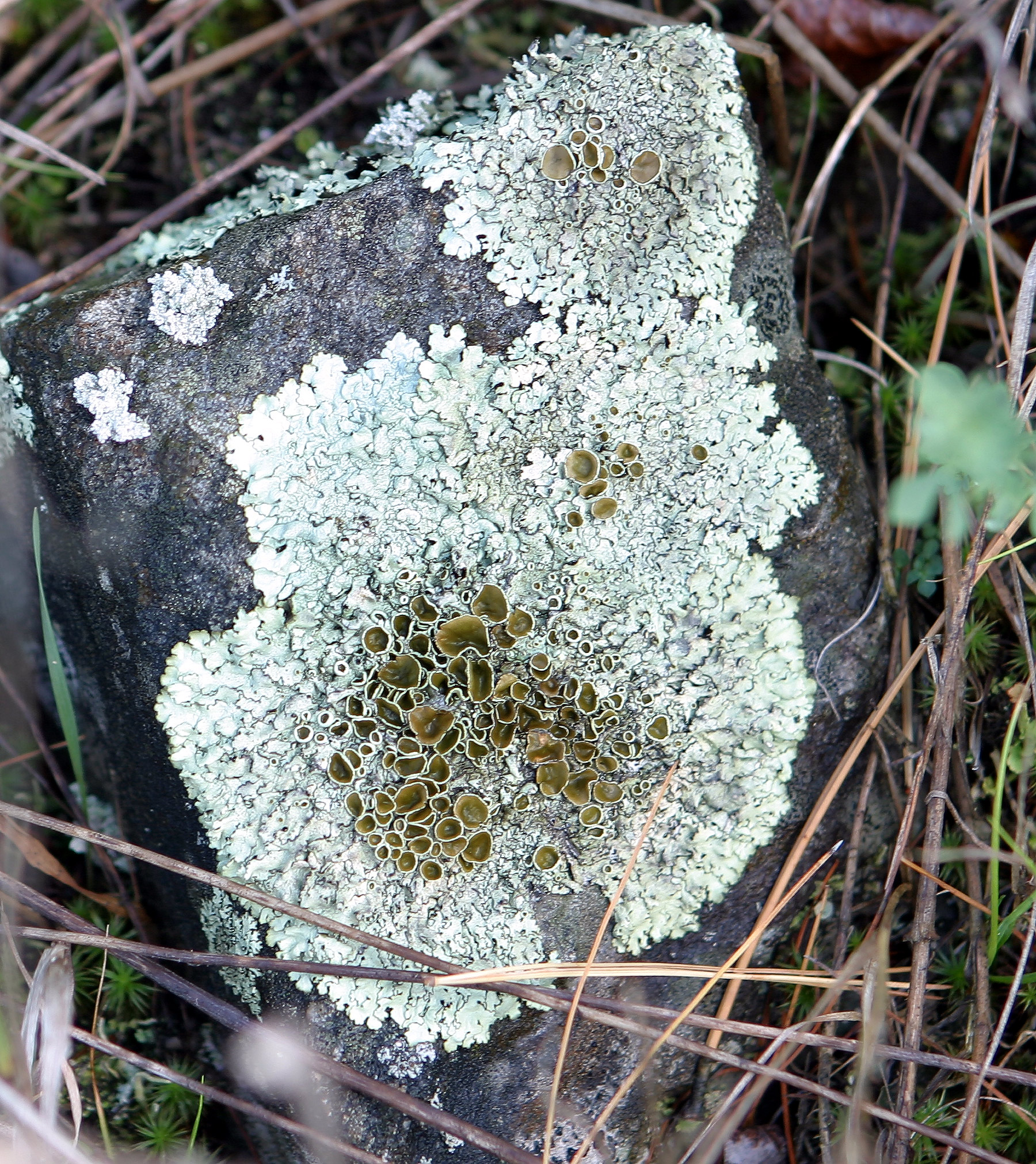
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloschistaceae
The Teloschistaceae are a large family (biology), family of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class (taxonomy), class Lecanoromycetes in the division (botany), division Ascomycota. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, although its members occur predominantly in temperate climate, temperate regions. Most members are lichens that either saxicolous lichen, live on rock or corticolous lichen, on bark, but about 40 species are lichenicolous fungus, lichenicolousmeaning they are non-lichenised fungi that live on other lichens. Many members of the Teloschistaceae are readily identifiable by their vibrant orange to yellow hue, a result of their frequent anthraquinone content. The presence of these anthraquinone biological pigment, pigments, which confer protection from ultraviolet light, enabled this group to expand from shaded forest habitats to harsher environmental conditions of sunny and arid ecosystems during the Late Cretaceous. Teloschistaceae lichens typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscription (taxonomy)
In biological taxonomy, circumscription is the content of a taxon, that is, the delimitation of which subordinate taxa are parts of that taxon. For example, if we determine that species X, Y, and Z belong in genus A, and species T, U, V, and W belong in genus B, those are our circumscriptions of those two genera. Another systematist might determine that T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z all belong in genus A. Agreement on circumscriptions is not governed by the Codes of Zoological or Botanical Nomenclature, and must be reached by scientific consensus. A goal of biological taxonomy is to achieve a stable circumscription for every taxon. This goal conflicts, at times, with the goal of achieving a natural classification that reflects the evolutionary history of divergence of groups of organisms. Balancing these two goals is a work in progress, and the circumscriptions of many taxa that had been regarded as stable for decades are in upheaval in the light of rapid developments in molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological Type (biology), type wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or specimens). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name with that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloschistales
The Teloschistales are an order of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. According to one 2008 estimate, the order contains 5 families, 66 genera, and 1954 species. The predominant photobiont partners for the Teloschistales are green algae from the genera ''Trebouxia'' and ''Asterochloris''. Molecular phylogenetics The higher-level phylogenetic relationships of the Teloschistales and other members of the two major subclasses of Lecanoromycetes, Lecanoromycetidae and Ostropomycetidae, were clarified in a 2018 publication by Kraichak and colleagues. In the Teloschistales, the family Teloschistaceae has a sister taxon relationship with Megalosporaceae, and the clade In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ... containi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Genera
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloschistales Genera
The Teloschistales are an order (taxonomy), order of mostly lichen-forming fungus, fungi belonging to the class (taxonomy), class Lecanoromycetes in the division (mycology), division Ascomycota. According to one 2008 estimate, the order contains 5 Family (biology), families, 66 genera, and 1954 species. The predominant photobiont partners for the Teloschistales are green algae from the genera ''Trebouxia'' and ''Asterochloris''. Molecular phylogenetics The higher-level phylogenetic relationships of the Teloschistales and other members of the two major subclasses of Lecanoromycetes, Lecanoromycetidae and Ostropomycetidae, were clarified in a 2018 publication by Kraichak and colleagues. In the Teloschistales, the family Teloschistaceae has a sister taxon relationship with Megalosporaceae, and the clade containing these two families is itself sister to a clade containing families Brigantiaeaceae and Letrouitiaceae. Families *Brigantiaeaceae *Letrouitiaceae *Megalosporaceae *Telosch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Described In 1977
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |