|
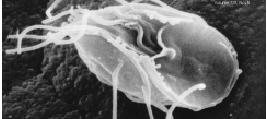
Iodamoeba
''Iodamoeba buetschlii'' is a species of amoeba. It gets its name from its appearance when stained with iodine. Named for Otto Bütschli by Prowazek in 1912, ''Iodamoeba buetschlii'' is a nonpathogenic parasitic ameba, commonly found in the large intestines of people, pigs and other mammals. The distribution of ''I. buetschlii'' is worldwide. Most likely to be the original host, pigs are often targeted with ''I. buetschlii''. ''I. buetschlii'' is identified as a non-pathogenic parasite. Often, this parasite is mistaken as a pathogenic parasite because non-pathogenic and pathogenic parasites have the same characteristics. In terms of illnesses, humans have a low prevalence of ''I. buetschlii'' (4-8%). ''I. buetschlii'' is an indicator of oral-fecal contamination and humans may experience diarrhea. Trophozoite The trophozoites are 9–14 micrometres in diameter. Trophozoites are one of the two forms of ''I. buetschlii''. This form has a pseudopodia for locomotion. The pseudopod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose members share common descent. Consequently, amoeboid organisms are no longer classified together in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms of energy reserves, creatine phosphate being for very short-term, glycogen being for short-term and the triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) being for long-term storage. Protein, broken down into amino acids, is seldom used as a main energy source except during starvation and glycolytic crisis ''(see bioenergetic systems)''. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight: the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass): the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It is taken by mouth. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the COVID-19 pandemic, pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the northern summer of 2020, and the National Institutes of Health, NIH does not recommend its use for this purpose. Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and aplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydroemetine
Dehydroemetine is a synthetically produced antiprotozoal agent similar to emetine in its anti-amoebic properties and structure (they differ only in a double bond next to the ethyl substituent), but it produces fewer side effects. In the United States, it is manufactured by Roche. Mechanism Its exact mechanism is not known, but ''in vitro'' it inhibits translocation. Uses It was at one-time, but is no longer distributed by the Center for Disease Control on a compassionate use basis as an investigational drug for the treatment of metronidazole-resistant amoebiasis. Amoebic infections Some examples of the use of dehydroemetine in the treatment of amoebic infections include: # In 1993, the successful treatment of cutaneous amebiasis in a 7-year-old girl with dehydroemetine and metronidazole in Mexico. # A double-blind study of oral dehydroemetine in the treatment of amoebiasis performed at St. Mary's Hospital, Catholic Medical College, Seoul, Republic of Korea in 1973-1974 show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amebiasis
Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba ''Entamoeba histolytica''. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ulcerations, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea. Complications can include inflammation and ulceration of the colon with tissue death or perforation, which may result in peritonitis. Anemia may develop due to prolonged gastric bleeding. Cysts of ''Entamoeba'' can survive for up to a month in soil or for up to 45 minutes under fingernails. Invasion of the intestinal lining results in bloody diarrhea. If the parasite reaches the bloodstream it can spread through the body, most frequently ending up in the liver where it can cause amoebic liver abscesses. Liver abscesses can occur without previous diarrhea. Diagnosis is made by stool examination using microscopy, but it can be difficult to distinguish ''E. histolytica'' from other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in Solutes, solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane Vesicle (biology), vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described the plant vacuole in 1676. Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Félix Dujardin, Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the ''Giardia'' group. The complementary form of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled microbial cyst, cyst form. They are often different from the cyst stage, which is a protective, dormant form of the protozoa. Trophozoites are often found in the host's body fluids and tissues and in many cases, they are the form of the protozoan that causes disease in the host. In the protozoan, ''Entamoeba histolytica'' it invades the intestinal mucosa of its host, causing dysentery, which aid in the trophozoites traveling to the liver and leading to the production of hepatic abscesses. Life cycle stages ''Plasmodium falciparium'' The causative organism of malaria is a protozoan, ''Plasmodium falciparium'', that is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito, ''Anopheles'' mosquito. Malaria is reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Bütschli
Johann Adam Otto Bütschli (3 May 1848 – 2 February 1920) was a German zoologist and professor at the University of Heidelberg. He specialized in invertebrates and insect development. Many of the groups of protists were first recognized by him. He was the first scientist to recognize the structures now known as chromosomes. Life Bütschli was born in Frankfurt am Main. He studied mineralogy, chemistry, and paleontology in Karlsruhe and became assistant of Karl Alfred von Zittel (geology and paleontology). He moved to Heidelberg in 1866 and worked with Robert Bunsen (chemistry). He received his PhD from the University of Heidelberg in 1868, after passing examinations in geology, paleontology, and zoology. He joined Rudolf Leuckart at the University of Leipzig in 1869. After leaving his studies to serve as an officer in the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), Bütschli worked in his private laboratory and then for two years (1873–1874) with Karl Möbius at the University of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |