|
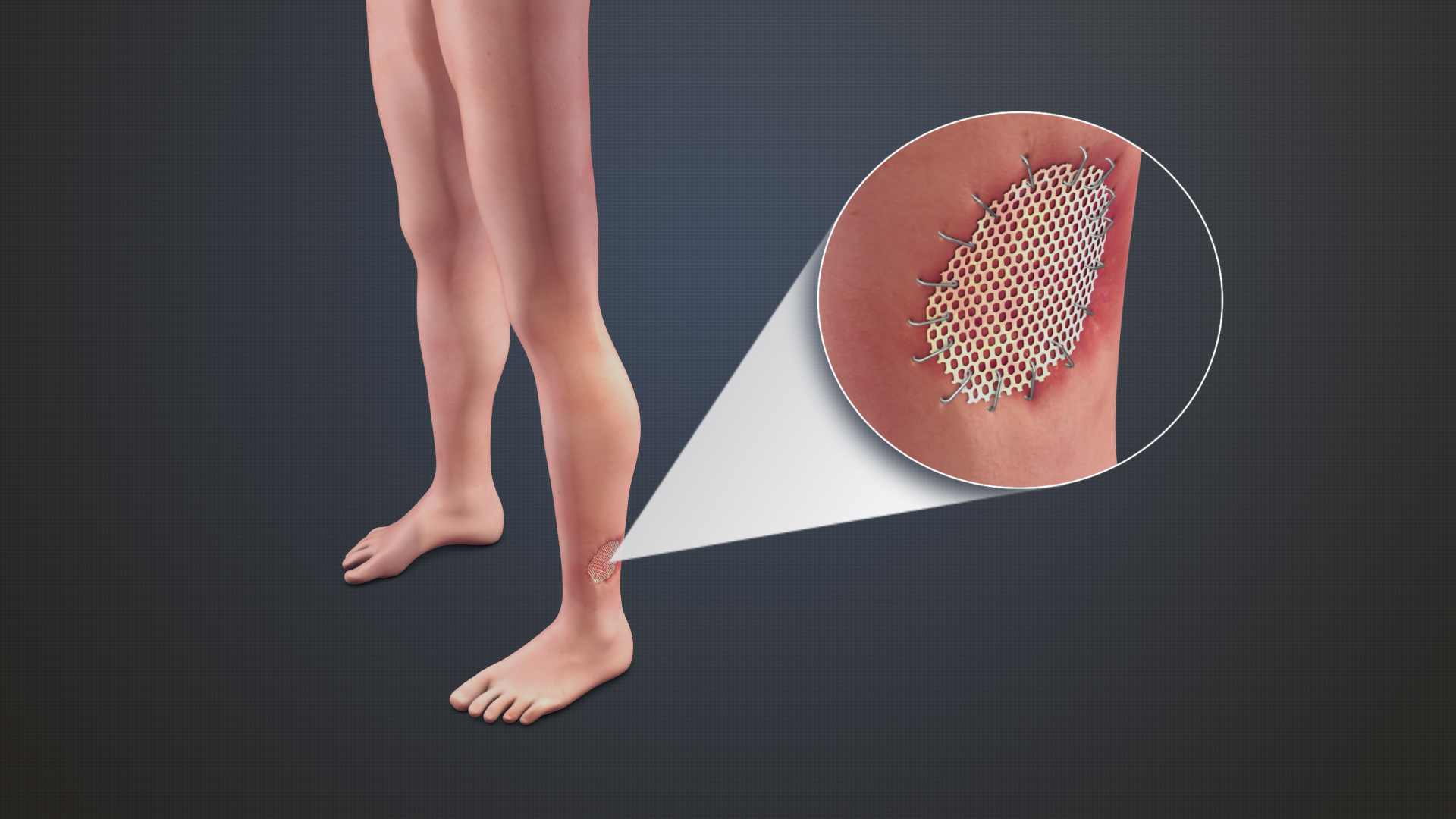
Intimal Hyperplasia
Intimal hyperplasia is the thickening of the tunica intima of a blood vessel as a complication of a reconstruction procedure or endarterectomy. Intimal hyperplasia is the universal response of a vessel to injury. It is a restenosis and this is an important reason of late bypass graft failure, particularly in vein and synthetic vascular grafts. Cause Intimal hyperplasia is due to a dysfunction of endothelial cells which results in a reprogramming of the vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). As a result, VSMCs proliferate and change their phenotype. Possible treatment A possible treatment to avoid this could be hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide () works as a vasculoprotective gasotransmitter in the human body but is also tested to reduced intimal hyperplasia. There are different kinds of donors: NaHS (the reference in scientific literature despite the fact it is too toxic to use it in human patients) and STS (already used in patient to treat cyanide poisoning). See also * Hyperp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Intima
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (biology), tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelium, endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flow), and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic artery, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endarterectomy
Endarterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the atheromatous ''plaque'' material, or blockage, in the lining of an artery constricted by the buildup of deposits. It is carried out by separating the plaque from the arterial wall. It was first performed on a subsartorial artery in 1946 by a Portuguese surgeon, João Cid dos Santos, at the University of Lisbon. In 1951, E. J. Wylie, an American, performed it on the abdominal aorta. The first successful reconstruction of the carotid artery was performed by Carrea, Molins, and Murphy in Argentina, later in the same year. An endarterectomy of the carotid artery in the neck is recommended to reduce the risk of stroke when the carotid artery is severely narrowed, particularly after a stroke to reduce the risk of additional strokes. Coronary endarterectomy involves removing atheroma from the wall of blocked blood vessels (coronary) supplying the heart muscle. The concept was first introduced by Bailey in the 1950s prior to the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restenosis
Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis, a narrowing of a blood vessel, leading to restricted blood flow. Restenosis usually pertains to an artery or other large blood vessel that has become narrowed, received treatment to clear the blockage, and subsequently become re-narrowed. This is usually restenosis of an artery, or other blood vessel, or possibly a vessel within an organ. Restenosis is a common adverse event of endovascular procedures. Procedures frequently used to treat vascular damage from atherosclerosis and related narrowing and re-narrowing (restenosis) of blood vessels include vascular surgery, cardiac surgery, and angioplasty. When a stent is used and restenosis occurs, this is called in-stent restenosis or ISR. If it occurs following balloon angioplasty, this is called post-angioplasty restenosis or PARS. The diagnostic threshold for restenosis in both ISR and PARS is ≥50% stenosis. If restenosis occurs after a procedure, follow-up imaging is not the only way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bypass Graft
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis. Classification Autografts and isografts are usually not considered as foreign and, therefore, do not elicit rejection. Allografts and xenografts may be recognized as foreign by the recipient and rejected. * Autograft: graft taken from one part of the body of an individual and transplanted onto another site in the same individual, e.g., skin graft. * Isograft: graft taken from one individual and placed on another individual of the same genetic constitution, e.g., grafts between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelial Cells
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the interior s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Vascular smooth muscle is the type of smooth muscle that makes up most of the walls of blood vessels. Structure Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood vessels. Nerve supply Vascular smooth muscle is innervated primarily by the sympathetic nervous system through adrenergic receptors (adrenoceptors). The three types present are: alpha-1, alpha-2 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, . The main endogenous agonist of these cell receptors is norepinephrine (NE). The adrenergic receptors exert opposite physiologic effects in the vascular smooth muscle under activation: * alpha-1 receptors. Under NE binding alpha-1 receptors cause vasoconstriction (contraction of the vascular smooth muscle cells decreasing the diameter of the vessels). These receptors are activated in response to shock or low blood pressure as a defensive reaction trying to restore the normal blood pressure. Antagonists of alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, and its behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code (its genotype) and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting the phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddisfly larva cases and beaver dams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the human body produces small amounts of this sulfide and its mineral salts, and uses it as a signalling molecule. Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasotransmitter
Gasotransmitters is a class of neurotransmitters. The molecules are distinguished from other bioactive endogenous gaseous signaling molecules based on a need to meet distinct characterization criteria. Currently, only nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide are accepted as gasotransmitters. According to in vitro models, gasotransmitters, like other gaseous signaling molecules, may bind to gasoreceptors and trigger signaling in the cells. The name gasotransmitter is not intended to suggest a gaseous physical state such as infinitesimally small gas bubbles; the physical state is dissolution in complex body fluids and cytosol. These particular gases share many common features in their production and function but carry on their tasks in unique ways which differ from classical signaling molecules. Criteria The terminology and characterization criteria of “gasotransmitter” were first introduced in 2002. For one gas molecule to be categorized as a gasotransmitter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanide Poisoning
Cyanide poisoning is poisoning that results from exposure to any of a number of forms of cyanide. Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting. This phase may then be followed by seizures, slow heart rate, low blood pressure, loss of consciousness, and cardiac arrest. Onset of symptoms usually occurs within a few minutes. Some survivors have long-term neurological problems. Toxic cyanide-containing compounds include hydrogen cyanide gas and a number of cyanide salts, such as potassium cyanide. Poisoning is relatively common following breathing in smoke from a house fire. Other potential routes of exposure include workplaces involved in metal polishing, certain insecticides, the medication sodium nitroprusside, and certain seeds such as those of apples and apricots. Liquid forms of cyanide can be absorbed through the skin. Cyanide ions interfere with cellular respiration, resulting in the body's tissues being unable to use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of Tissue (biology), organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the Gross anatomy, gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the Cellular adaptation, adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the cell size, ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, Chronic inflammation, chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Grafting
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis. Classification Autografts and isografts are usually not considered as foreign and, therefore, do not elicit rejection. Allografts and xenografts may be recognized as foreign by the recipient and rejected. * Autograft: graft taken from one part of the body of an individual and transplanted onto another site in the same individual, e.g., skin graft. * Isograft: graft taken from one individual and placed on another individual of the same genetic constitution, e.g., grafts be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |