|
International Business Communication Standards
{{More citations needed, date=June 2025 The International Business Communication Standards (IBCS) are practical proposals for designing business communication, available for free use under a Creative Commons license (CC BY-SA). IBCS are used to optimize reports, presentations, and dashboards in terms of their conceptual design, visual perception, and semantic notation. The IBCS proposals formed the basis of the "ISO/AWI 24896 Standard notation for business reports" project, launched in July 2024. Requirements Business communication meets IBCS standards if it adheres to the rules of the following three pillars: * Conceptual rules assist in the clear transmission of content by providing an appropriate storyline. These rules draw on the work of authors such as Barbara Minto. Based on scientific studies and practical experience, they are widely recognized. These conceptual rules are divided into the SAY and STRUCTURE themes from the SUCCESS concept. * Perceptual rules assist in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creative Commons License
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by Creative Commons, a U.S. non-profit corporation founded in 2001. There have also been five versions of the suite of licenses, numbered 1.0 through 4.0. Released in Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Minto
Barbara Minto is an American author and consultant focused on the subject of executive communication. Biography Minto's career began as a secretary at an American railway company in the 1950s "making 400 bucks a month". Concerned that her supervisor's age and ill-health would result in the loss of her well-paying position, she applied to Harvard Business School, which at the time did not require an undergraduate degree, and was admitted upon passing the entry exam. Minto graduated from Harvard Business School in 1963. She was one of only eight women to graduate in a class of 600. Minto was the first female MBA hired by McKinsey & Company, starting with the firm in Cleveland, Ohio in 1963, and moving to London in 1966, where she served until 1973. After layoffs at McKinsey arising from the 1973 Oil Crisis, Minto began her own training business focused on the executive communication techniques she pioneered during her tenure. Minto published her book, ''The Pyramid Principle: L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
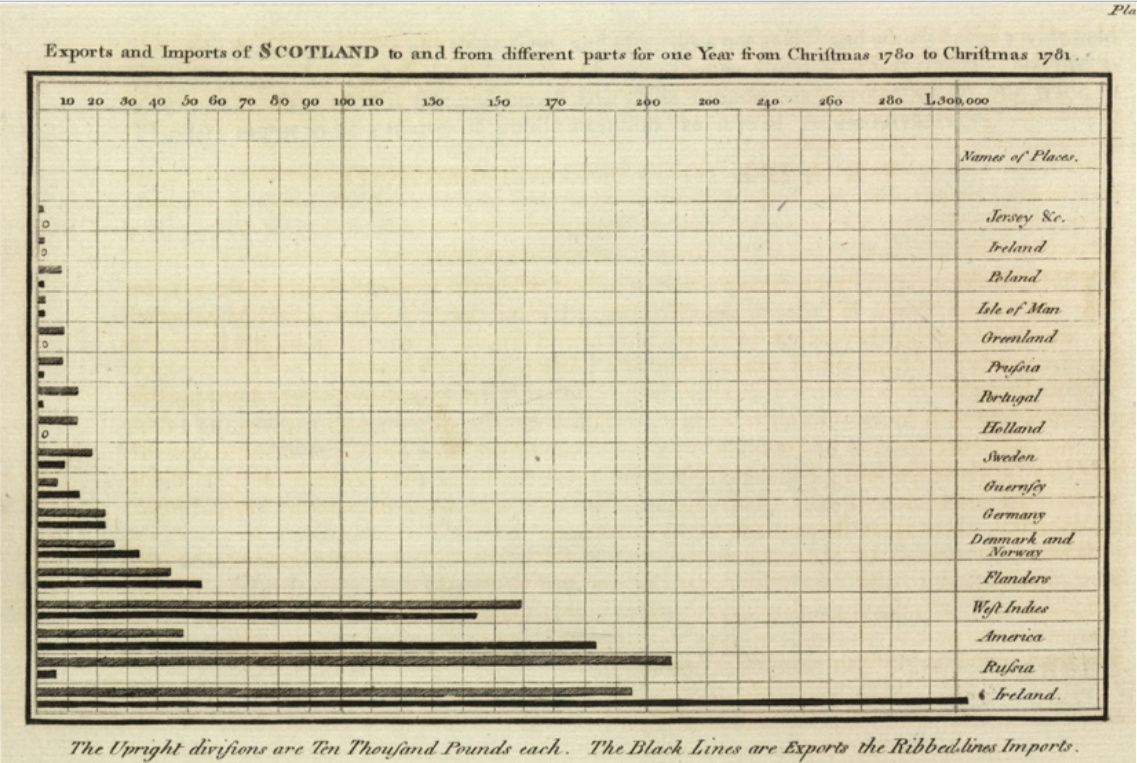
William Playfair
William Playfair (22 September 1759 – 11 February 1823) was a Scottish engineer and political economist. The founder of graphical methods of statistics, Playfair invented several types of diagrams: in 1786 he introduced the line, area and bar chart of economic data, and in 1801 he published what were likely the first pie chart and circle graph, used to show part-whole relations. Playfair has been reported to have been a secret agent for the British Government, although this is a subject of controversy. Biography William Playfair was born in 1759 in Scotland. He was the fourth son (named after his grandfather) of the Reverend James Playfair of the parish of Liff & Benvie near the city of Dundee in Scotland; his notable brothers were architect James Playfair and mathematician John Playfair. His father died in 1772 when he was 13, leaving the eldest brother John to care for the family and his education. After his apprenticeship with Andrew Meikle, the inventor of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willard Cope Brinton
Willard Cope Brinton (December 22, 1880 – November 29, 1957''Mechanical Engineering,'' Vol. 80, 1958. p. 158) was an American consulting engineer, president of Brinton Associates, and information visualisation pioneer, particularly known for publication of the 1914 textbook on graphic methods, entitled ''Graphic methods for presenting facts.'' Biography Brinton was born in West Chester, Pennsylvania to Samuel Lewis and Elizabeth (Smith) Brinton. He received his BS in Mechanical engineering from Harvard University in 1907.''Harvard's College Class of 1907''. Secretary's Report. Nr III. 1907-1913. p. 57-58 Brinton started his career as mechanical engineer working for various companies,Howard Wainer (2013). ''Graphic Discovery: A Trout in the Milk and Other Visual Adventures.'' p. 153 and travelled through the United States, and to Europe, Japan and China. Back in New York he started his own consulting company. One of his notable works in the early 1920s was the proposal to ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Zelazny
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first copied into RNA. RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype of the individual. Most biological traits occur under the combined influence of polygenes (a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Tufte
Edward Rolf Tufte (; born March 14, 1942), sometimes known as "ET",. is an American statistician and professor emeritus of political science, statistics, and computer science at Yale University. He is noted for his writings on information design and as a pioneer in the field of data visualization. Early life and education Edward Rolf Tufte was born in 1942 in Kansas City, Missouri, to Virginia Tufte (1918–2020) and Edward E. Tufte (1912–1999). He grew up in Beverly Hills, California, where his father was a longtime city official. He graduated from the public Beverly Hills High School.Reynolds, Christopher."ART; Onward means going upward; Edward Tufte has spent his career fighting the visually dull and flat. Even his sculpture is a leap." ''Los Angeles Times'', November 14, 2002. Accessed April 23, 2008. " dward Tufte who shares in Cheshire, Conn., with his wife, graphic design professor Inge Druckrey, and three golden retrievers, is a 1960 graduate of Beverly Hills High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Few
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" (and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolf Hichert
Rolf is a male given name and a surname. It originates in the Germanic name ''Hrolf'', itself a contraction of ''Hrodwulf'' ( Rudolf), a conjunction of the stem words ''hrod'' ("renown") + ''wulf'' ("wolf"). The Old Norse cognate is ''Hrólfr''. An alternative but less common variation of ''Rolf'' in Norway is ''Rolv''. The oldest evidence of the use of the name Rolf in Sweden is an inscription from the 11th century on a runestone in Forsheda, Småland. The name also appears twice in the Orkneyinga sagas, where a scion of the jarls of Orkney, Gånge-Rolf, is said to be identical to the Viking Rollo who captured Normandy in 911. This Saga of the Norse begins with the abduction of Gói daughter by a certain Hrolf of Berg, (the Mountain). She is the daughter of Thorri, a Jotun of Gandvik, and sister of Gór and Nór. The latter is regarded as a first king and eponymous anchestor of Nórway. After a fierce duell (Holmgang) where none is able to overcome the other, Hrolf and Nór becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McKinsey & Company
McKinsey & Company (informally McKinsey or McK) is an American multinational strategy and management consulting firm that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. Founded in 1926 by James O. McKinsey, McKinsey is the oldest and largest of the " MBB" management consultancies. The firm mainly focuses on the finances and operations of their clients. Under the direction of Marvin Bower, McKinsey expanded into Europe during the 1940s and 1950s. In the 1960s, McKinsey's Fred Gluck—along with Boston Consulting Group's Bruce Henderson, Bill Bain at Bain & Company, and Harvard Business School's Michael Porter—initiated a program designed to transform corporate culture. A 1975 publication by McKinsey's John L. Neuman introduced the business practice of "overhead value analysis" that contributed to a downsizing trend that eliminated many jobs in middle management. McKinsey has been the subject of significant controversy and is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether Intention, unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits semantics, meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a code, coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a Communication channel, channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies. A common way to classify communication is by whether information is exchanged between humans, members of other species, or non-living entities such as computers. For human communication, a central contrast is between Verbal communication, verbal and non-verbal communication. Verba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |