|
Intermontane Belt
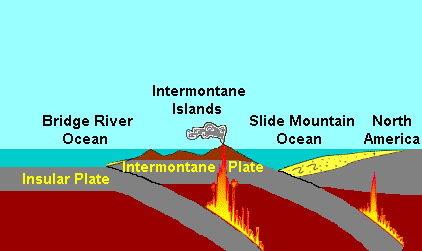
The Intermontane Belt is a physical geology, physiogeological region in the Pacific Northwest of North America, stretching from northern Washington (U.S. state), Washington into British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska. It comprises rolling hills, high plateaus and deeply cut valleys. The rocks in the belt have very little similarities with the North American continent. Geology The formation of the Intermontane Belt is complex. It began forming during the early Jurassic period when an volcanic arc, island arc called the Intermontane Islands collided against a pre-existing continental margin. This island arc is believed to have formed on a pre-existing plate tectonics, tectonic plate called the Intermontane Plate about 245 million years ago by subduction of the former Insular Plate during the Triassic period. This subduction zone records another subduction zone called the Intermontane Trench under an ancient ocean between the Intermontane Islands and the former continental margin of No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Belts Of Western Canada
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their Geochronology, absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methow Valley
The Methow River ( ) is a tributary of the Columbia River in northern Washington in the United States. The river's watershed drains the eastern North Cascades, with a population of about 5,000 people. The Methow's watershed is characterized by relatively pristine habitats, as much of the river basin is located in national forests and wildernesses. Many tributaries drain the large Pasayten Wilderness. An earlier economy based on agriculture is giving way to one based on recreation and tourism. History The river was named after the Methow Native Americans (today part of the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Indian Reservation). The name "Methow" comes from the Okanagan placename ''/mətxʷú/'', meaning "sunflower (seeds)". The Native American name for the river was ''Buttlemuleemauch'', meaning "salmon falls river". In 1841 the Wilkes Expedition named the river "Barrier River". Alexander Ross said the native name was Buttle-mule-emauch. In 1811 David Thompson met the tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kootenay Fold Belt
Kootenay, Kootenai, and Kutenai may refer to: Ethnic groups *The Kutenai, also known as the Ktunaxa, Kootenai, or Kootenay, an indigenous people of the United States and Canada ** Kutenai language, the traditional language of the Kutenai ** Ktunaxa Nation, a First Nations government in British Columbia, Canada ** Kootenai Tribe of Idaho, a federally recognized tribe in Idaho, United States, ** Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes, a federally recognized tribe in Montana, United States Places Communities * Kootenai, Idaho, United States * Kootenay, British Columbia, Canada * Kootenay Bay, an unincorporated community in British Columbia, Canada * Kootenai County, Idaho, United States * Diocese of Kootenay, a diocese of the Ecclesiastical Province of British Columbia and the Yukon of the Anglican Church of Canada * List of electoral districts in the Kootenays, electoral districts in the Kootenays region of British Columbia ** Kootenay (federal electoral district), a former electo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny. Mountain ranges are formed by a variety of geological processes, but most of the significant ones on Earth are the result of plate tectonics. Mountain ranges are also found on many planetary mass objects in the Solar System and are likely a feature of most terrestrial planets. Mountain ranges are usually segmented by highlands or mountain passes and valleys. Individual mountains within the same mountain range do not necessarily have the same geologic structure or petrology. They may be a mix of different orogenic expressions and terranes, for example thrust sheets, uplifted blocks, fold mountains, and volcanic landforms resulting in a variety of rock types. Major ranges Most geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or Mass wasting, mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from aqueous solution, water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fold (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary rock, sedimentary stratum, strata, that are bent or curved (''"folded"'') during permanent deformation (engineering), deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). wikt:synsedimentary, Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress (physics), stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sedimentary rock, sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogeny, orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a social constructionism, historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Mobile Belt
In the geology of the Philippines, the Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian plate and the Philippine Sea plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction zones, the Manila Trench to the west and the Philippine Trench to the east, as well as the Philippine fault system. Within the Belt, a number of crustal blocks or microplates which have been shorn off the adjoining major plates are undergoing massive deformation. Most segments of the Philippines, including northern Luzon, are part of the Philippine Mobile Belt, which is bounded by the Philippine Sea plate to the east, the Molucca Sea Collision Zone to the south, Sunda plate to the southwest, and the Tectonics of the South China Sea, South China Sea Basin to the west and north-west. To the north it ends in eastern Taiwan, the zone of active collision between the North Luzon Trough portion of the Luzon Volcanic Arc and South China. The Phili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slide Mountain Ocean
The Slide Mountain Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America beginning around 245 million years ago in the Triassic The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ... period. It is named after the Slide Mountain terrane, which is composed of rocks from the ancient oceanic floor. There was a subduction zone on the Slide Mountain Ocean's floor called the Intermontane Trench where the Intermontane Plate was being subducted under North America. The floor of the Slide Mountain Ocean was pushed up onto the ancient margin of North America. References Historical oceans Triassic paleogeography {{triassic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |