|
Intel P67
The Intel P67 is a mainstream chipset created by Intel. It was launched to market in January 2011, the first edition of this chipset had a faulty SATA 3.0 controller and Intel had to issue a hardware fix to resolve this problem. This fix (Revision B3) was launched to market at the beginning of March 2011. Features Standard features: * Supports processor overclocking (Only available for unlocked processors: Core i5-2500K, Core i5-2550K, Core i7-2600K and 2700K) * Supports memory overclocking * 1× PCI Express 2.0 x16 lanes at 16 GB/s bandwidth * 2× Serial ATA (SATA) 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) ports * 4× Serial ATA (SATA) 2.0(3 Gbit/s) ports * 14× Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 ports * Dual-channel DDR3 memory * Integrated Gigabit Ethernet MAC Optional features: * SATA RAID support (0/1/10/5) through Intel Rapid Storage Technology * 2× PCI Express 2.0 x8 lanes at 8 GB/s bandwidth each The P67 chipset is made to work in conjunction with Intel LGA 1155 CPUs and LGA 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
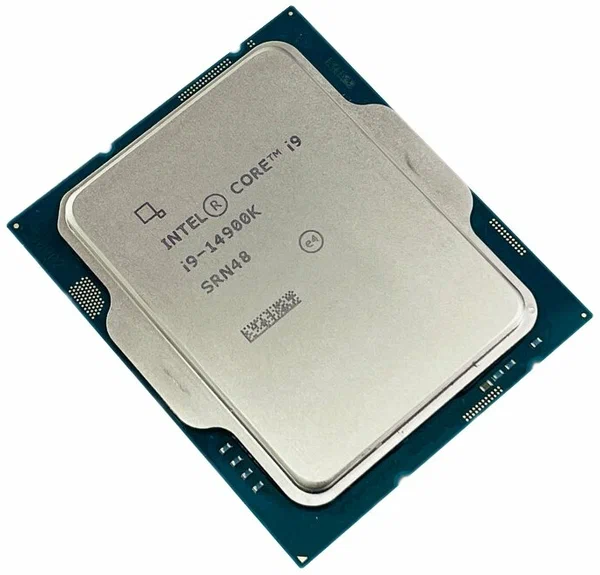
Intel Core
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets. Core was launched in January 2006 as a mobile-only series, consisting of single- and dual-core models. It was then succeeded later in July by the Core 2 series, which included both desktop and mobile processors with up to four cores, and introduced 64-bit support. Since 2008, Intel began introducing the Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 and Core i9 lineup of processors, succeeding Core 2. A new naming scheme debuted in 2023, consisting of Core 3, Core 5, and Core 7 for mainstream processo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sandy Bridge microarchitecture is the successor to Nehalem (microarchitecture), Nehalem and Westmere (microarchitecture), Westmere microarchitecture. Intel demonstrated an A1 stepping Sandy Bridge processor in 2009 during Intel Developer Forum (IDF), and released first products based on the architecture in January 2011 under the Intel Core#Sandy Bridge microarchitecture based, Core brand. Sandy Bridge is manufactured in the 32 nanometer, 32 nm process and has a soldered contact with the die and IHS (Integrated Heat Spreader), while Intel's subsequent generation Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge uses a 22 nanometer, 22 nm die shrink and a TIM (Thermal Interface Material) between the die and the IHS. Technology Intel demonstrated a S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
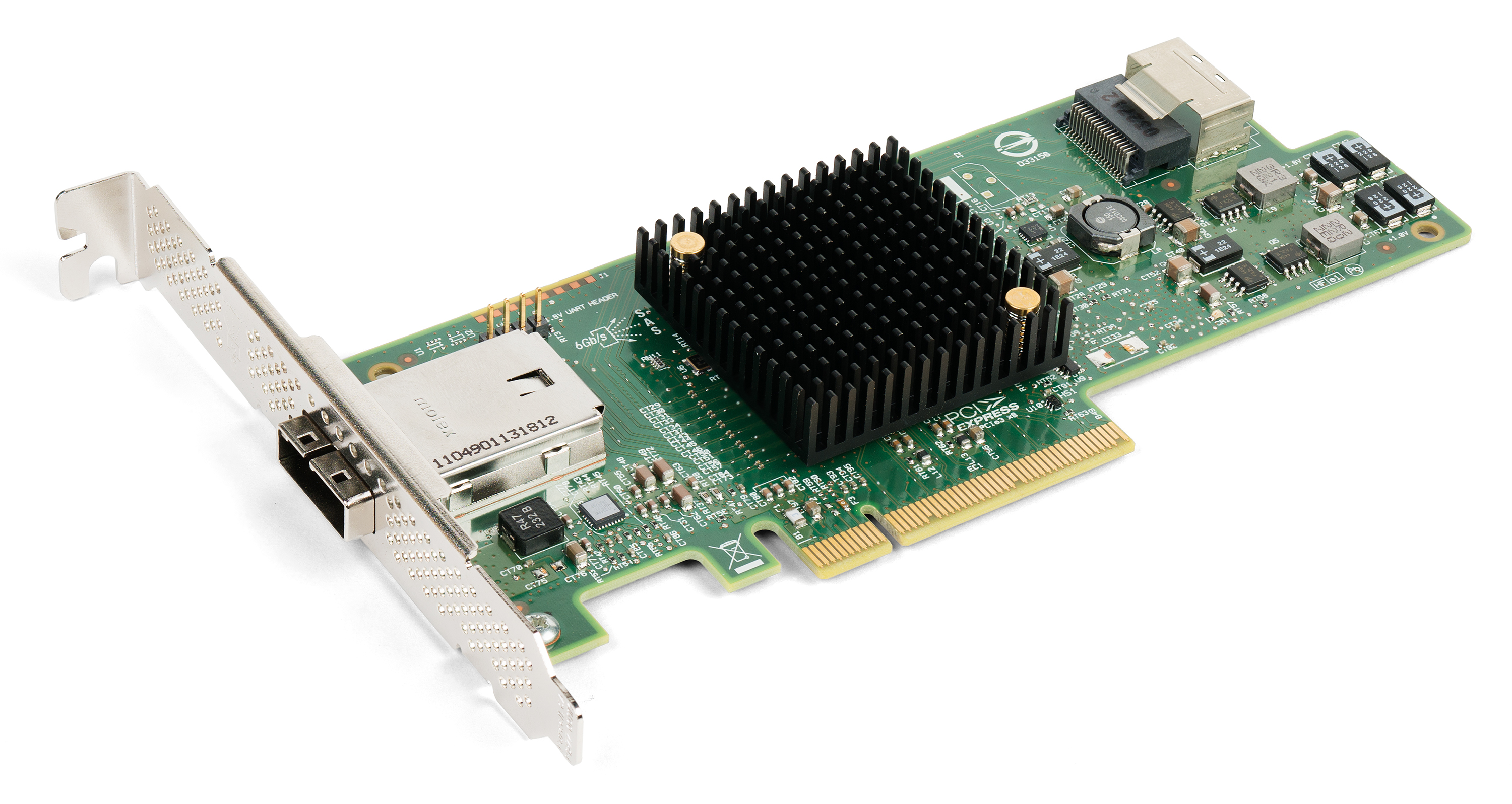
LGA 1155
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for their CPUs based on the Sandy Bridge (second generation core) and Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (third generation) microarchitectures. Introduced in 2011, it is the successor of LGA 1156 (known as ''Socket H'') and was itself succeeded by LGA 1150 in 2013. Along with selected variations of LGA 2011 socket, it was the last Intel socket to fully support Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008. LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The pins are arranged in a 40×40 array with a 24×16 central void and additional 61 omitted pins (two adjoining the central void, six in each of the four corners, and 35 in groups around the perimeter), yielding the 1600 − 384 − 61 = 1155 pin count. Processors for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel P55
The Intel P55 is the first desktop chipset from Intel based on the PCH chipset design. The P55 Express chipset uses the LGA 1156 socket. Compatible CPUs include the first generation Core i series i3, i5, and i7 processor line along with a Pentium G6950. Like any PCH chipset, the P55 uses a Direct Media Interface connection. Features * The chipset does not support onboard graphics. * 6 SATA 3 Gbit/s ports * 8 PCI-Express 2.0 lanes (bandwidth limited to 2.5 GT/s same as PCIe 1.0, normal PCIe 2.0 has 5 GT/s bandwidth) * 14 USB 2.0 ports * Integrated LAN 10/100/1000 * SMBus 2.0 * Integrated clock chip buffer * Intel HD Audio * Intel AC'97 Technology * Intel Rapid Storage Technology See also *List of Intel chipsets *Intel 5 Series Intel 5 Series is a computing architecture introduced in 2008 that improves the efficiency and balances the use of communication channels in the motherboard. The architecture consists primarily of a central processing unit (CPU) (connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engadget
Engadget ( ) is a technology news, reviews and analysis website offering daily coverage of gadgets, consumer electronics, video games, gaming hardware, apps, social media, streaming, AI, space, robotics, electric vehicles and other potentially consumer-facing technology. The site's content includes short-form news posts, reported features, news analysis, product reviews, buying guides, two weekly video shows, The Engadget Podcast, The Morning After newsletter and a weekly deals newsletter. It has been operated by Yahoo! Inc. (2017–present), Yahoo! Inc. since September 2021. History Engadget was founded by former ''Gizmodo'' technology weblog editor and co-founder Peter Rojas. Engadget was the largest blog in Weblogs, Inc., a blog network with over 75 Blog, weblogs, including ''Autoblog.com, Autoblog'' and ''Joystiq,'' which formerly included ''Hackaday''. Weblogs Inc. was purchased by AOL in 2005. Launched in March 2004, Engadget was one of the internet's earliest tech blogs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI Express 2
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial ATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then released by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. #1.0, Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Serial Bus
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical interfaces, and communication protocols to and from ''hosts'', such as personal computers, to and from peripheral ''devices'', e.g. displays, keyboards, and mass storage devices, and to and from intermediate ''hubs'', which multiply the number of a host's ports. Introduced in 1996, USB was originally designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing various interfaces such as serial ports, parallel ports, game ports, and Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) ports. Early versions of USB became commonplace on a wide range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, smartphones, game consoles, and power banks. USB has since evolved into a standard to replace virtually all common ports on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR3
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR SDRAM, DDR and DDR2 SDRAM, DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 SDRAM, DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither Forward compatibility, forward nor Backward compatibility, backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors. DDR3 is a DRAM interface specification. The actual DRAM arrays that store the data are similar to earlier types, with similar performance. The primary benefit of DDR3 SDRAM over its immediate predecessor DDR2 SDRAM, is its ability to transfer data at twice the rate (eight times the speed of its internal memory arrays), enabling higher bandwidth or peak data ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. The first standard for faster 10 Gigabit Ethernet was approved in 2002. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented Physical layer, physical and Data link layer, link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to . The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAID
RAID (; redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical Computer data storage, data storage components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This is in contrast to the previous concept of highly reliable mainframe disk drives known as ''single large expensive disk'' (''SLED''). Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways, referred to as RAID levels, depending on the required level of redundancy (engineering), redundancy and performance. The different schemes, or data distribution layouts, are named by the word "RAID" followed by a number, for example RAID 0 or RAID 1. Each scheme, or RAID level, provides a different balance among the key goals: reliability engineering, reliability, availability, computer performance, performance, and computer data storage#Capacity, capacity. RAID levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |