|
Institute For Plasma Research
The Institute for Plasma Research (IPR) is a public research institute in India. The institute conducts research in plasma science, including basic plasma physics, magnetically confined hot plasmas, and plasma technologies for industrial applications. It is the leading plasma physics organization of India and houses the largest tokamak of India - SST1. IPR plays a major scientific and technical role in Indian partnership in the international fusion energy initiative ITER. It is part of the IndiGO consortium for research on gravitational waves. It is an autonomous body funded by the Department of Atomic Energy. History In 1982, the Government of India initiated the Plasma Physics Programme (PPP) for research on magnetically confined high-temperature plasmas. In 1986, the PPP evolved into the autonomous Institute for Plasma Research under the Department of Science and Technology. With the commissioning of ADITYA in 1989, full-fledged tokamak experiments started at IPR. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Physics
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including the Sun), but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. The presence of charged particles makes plasma electrically conductive, with the dynamics of individual particles and macroscopic plasma motion governed by collective electromagnetic fields and very sensitive to externally applied fields. The response of plasma to electromagnetic fields is used in many modern devices and technologies, such as plasma televisions or plasma etching. Depending on temperature and density, a certain number of neutral particles may also be present, in which case plasma is called partially ioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic Electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and Atomic spectral line, atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Research Laboratory
The Physical Research Laboratory ( PRL; Hindi: भौतिक अनुसंधान प्रयोगशाला, IAST: ''Bhoutik Anusandhan Prayogashala'') is a National Research Institute for space and allied sciences, supported mainly by the Department of Space, Government of India. This research laboratory has ongoing research programmes in astronomy and astrophysics, atmospheric sciences and aeronomy, planetary and geosciences, Earth sciences, Solar System studies and theoretical physics. It also manages the Udaipur Solar Observatory and Mount Abu InfraRed Observatory. The PRL is located in Ahmedabad. The Physical Research Laboratory was founded on 11 November 1947 by Dr. Vikram Sarabhai. The laboratory had a modest beginning at his residence, with research on cosmic rays. The institute was formally established at the M.G. Science Institute, Ahmedabad, with support from the Karmkshetra Educational Foundation and the Ahmedabad Education Society. Prof. K. R. Rama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
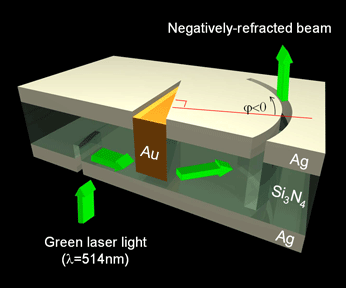
Plasmonics
Plasmonics or nanoplasmonics refers to the generation, detection, and manipulation of signals at optical frequencies along metal-dielectric interfaces in the nanometer scale. Inspired by photonics, plasmonics follows the trend of miniaturizing optical devices (see also nanophotonics), and finds applications in sensing, microscopy, optical communications, and bio-photonics. Principles Plasmonics typically utilizes Surface plasmon polariton, surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), that are coherent electron oscillations travelling together with an Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic wave along the interface between a dielectric (e.g. glass, air) and a metal (e.g. silver, gold). The SPP modes are strongly confined to their supporting interface, giving rise to strong light-matter interactions. In particular, the electron gas in the metal oscillates with the electro-magnetic wave. Because the moving electrons are scattered, ohmic losses in plasmonic signals are generally large, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma-enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) is a chemical vapor deposition process used to deposit thin films from a gas state (vapor) to a solid state on a substrate. Chemical reactions are involved in the process, which occur after creation of a plasma of the reacting gases. The plasma is generally created by radio frequency (RF) alternating current (AC) frequency or direct current (DC) discharge between two electrodes, the space between which is filled with the reacting gases. Discharges for processes A plasma is any gas in which a significant percentage of the atoms or molecules are ionized. Fractional ionization in plasmas used for deposition and related materials processing varies from about 10−4 in typical capacitive discharges to as high as 5–10% in high-density inductive plasmas. Processing plasmas are typically operated at pressures of a few millitorrs to a few torr, although arc discharges and inductive plasmas can be ignited at atmospheric pressure. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Nitriding
Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface. These processes are most commonly used on low-alloy steels. They are also used on titanium, aluminium and molybdenum. Typical applications include gears, crankshafts, camshafts, cam followers, valve parts, extruder screws, die-casting tools, forging dies, extrusion dies, firearm components, injectors and plastic mold tools. Processes The processes are named after the medium used to donate. The three main methods used are: ''gas nitriding'', ''salt bath nitriding'', and ''plasma nitriding''. Gas nitriding In gas nitriding the donor is a nitrogen-rich gas, usually ammonia (NH3), which is why it is sometimes known as ''ammonia nitriding''. When ammonia comes into contact with the heated work piece it dissociates into nitrogen and hydrogen. The nitrogen then diffuses onto the surface of the material creating a nitride layer. This process has existed for nearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Diffractometer
A diffractometer is a measuring instrument for analyzing the structure of a material from the scattering pattern produced when a beam of radiation or particles (such as X-rays or neutrons) interacts with it. Principle A typical diffractometer consists of a source of radiation, a monochromator to choose the wavelength, slits to adjust the shape of the beam, a sample and a detector. In a more complicated apparatus, a goniometer can also be used for fine adjustment of the sample and the detector positions. When an area detector is used to monitor the diffracted radiation, a beamstop is usually needed to stop the intense primary beam that has not been diffracted by the sample, otherwise the detector might be damaged. Usually the beamstop can be completely impenetrable to the X-rays or it may be semitransparent. The use of a semitransparent beamstop allows the possibility to determine how much the sample absorbs the radiation using the intensity observed through the beamstop. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermax
Thermax Ltd is an Indian multinational engineering conglomerate, involved in clean air, clean energy and clean water, headquartered in Pune. History Thermax was founded by A. S. Bhathena in 1966 as Wanson India Ltd, manufacturing package boilers. The company subsequently began manufacturing equipment related to cogeneration, air pollution control, water treatment and absorption refrigeration among others. In 1981, Bhathena was succeeded by his son-in-law Rohinton Aga as chairman. In February 1995, the company went public and listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange. After Aga's death in 1996, his wife Anu Aga took over the operations. In 2009, it signed a 51–49 joint venture with US firm SPX Corporation to provide equipment and services for the Indian power sector. In 2010, it signed a joint venture agreement with US-based Babcock & Wilcox to manufacture super-critical boilers for the power sector. See also * List of boiler types, by manufacturer There have been a vast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical technologies corporation headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Its common stock is a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and the company is ranked No. 42 on the 2024 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations. In 2024, the company was ranked 45th in the ''Forbes'' Global 2000. Johnson & Johnson has a global workforce of approximately 138,000 employees who are led by the company's current chairman and chief executive officer, Joaquin Duato. Johnson & Johnson was founded in 1886 by three brothers, Robert Wood Johnson, James Wood Johnson, and Edward Mead Johnson, selling ready-to-use sterile surgical dressings. In 2023, the company split-off its consumer healthcare business segment into a new publicly traded company, Kenvue. The company is exclusively focused on developing and producing ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport
Ahmedabad Airport, officially Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport , is an international airport in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It is named after Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, the first Deputy Prime Minister of India. The airport is the busiest and largest airport in the state of Gujarat, and is the seventh busiest airport in India. In fiscal year 2024–25, it handled over 13 million passengers, making it the seventh-busiest airport in terms of passenger traffic in India. The airport serves as a focus city for Air India and an operating base for IndiGo. In 2015, the government started the procedure for the privatisation of the airport. The new Dholera International Airport is being developed due to expansion constraints at the current airport. History The airport was set up in 1937, while international operations began on 26 January 1991. It was categorised as an International airport on 23 May 2000. In March 2004, Air India commenced service to London's Heathrow Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |