|
Insecticide Resistance Action Committee
The Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) was formed in 1984 and works as a specialist technical group of the industry association CropLife to be able to provide a coordinated industry response to prevent or delay the development of insecticide resistance in insect, mite and nematode pests. IRAC strives to facilitate communication and education on insecticide and traits resistance as well as to promote the development and facilitate the implementation of insecticide resistance management strategies. IRAC is recognised by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) of the United Nations as an advisory body on matters pertaining to insecticide resistance. Pesticideresistance.org is a database financed by IRAC, US Department of Agriculture, and others. Sponsors IRAC's sponsors are: ADAMA, BASF, Bayer CropScience, Corteva, FMC, Mitsui Chemicals, Nihon Nohyaku, Sumitomo Chemical, Syngenta and UPL. Mode of action classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CropLife
CropLife International is an international trade association of agrochemical companies founded in 2001. It was previously known as ''Global Crop Protection Federation'' and started out as ''International Group of National Associations of Manufacturers of Agrochemical Products'' in 1967. Its members include the world's largest agricultural biotechnology and agricultural pesticide businesses namely BASF, Bayer CropScience, Corteva, FMC Corp., Sumitomo Chemical and Syngenta. The international body combines several national-level or continent-wide organisations, each one having the same goals but differing according to local language and custom. History In 1967, the International Group of National Associations of Manufacturers of Agrochemical Products (from , GIFAP) was founded. In November 1996, GIFAP was renamed to Global Crop Protection Federation (GCPF). On 7 November 2001, GCPF was renamed to CropLife International. On 2 November 2001, the CROP PROTECTION INSTITUTE OF CANADA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans. Acaricides, which kill mites and ticks, are not strictly insecticides, but are usually classified together with insecticides. Some insecticides (including common bug sprays) are effective against other non-insect arthropods as well, such as scorpions, spiders, etc. Insecticides are distinct from insect repellents, which repel but do not kill. Sales In 2016 insecticides were estimated to account for 18% of worldwide pesticide sales. Worldwide sales of insecticides in 2018 were estimated as $ 18.4 billion, of which 25% were neonicotinoids, 17% were pyrethroids, 13% were diamides, and the rest were many other classes which sold for less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
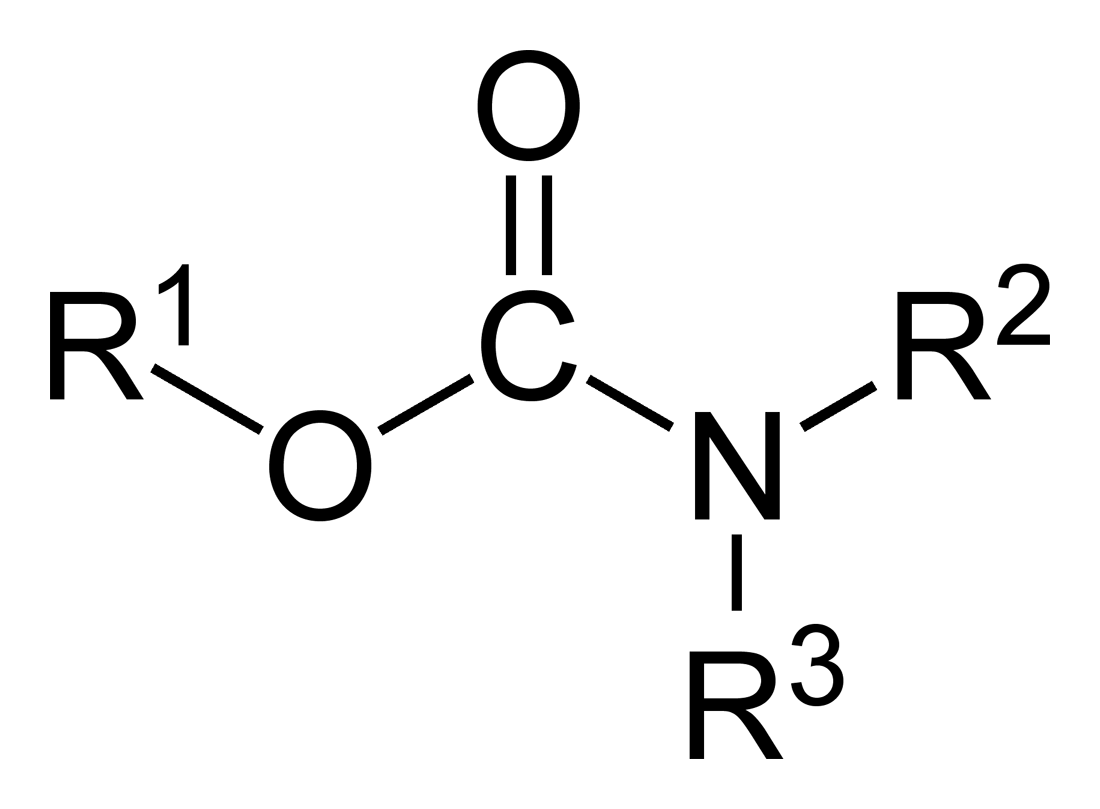
Carbofuran
Carbofuran is a carbamate insecticide, banned in the US, the EU and Canada but still widely used in South America, Australia and Asia. It is a systemic insecticide, which means that the plant absorbs it through the roots, and from there the plant distributes it throughout its organs where insecticidal concentrations are attained. Carbofuran also has contact activity against pests. It is one of the most toxic pesticides still in use. It is marketed under the trade names Furadan, by FMC Corporation and Curaterr 10 GR, by Bayer among several others. Carbofuran exhibits toxicity mediated by the same mechanism as that of the notorious V-series nerve agents and presents a risk to human health. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the United States Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general Chemical formula, formula and Chemical structure, structure , which are formally Derivative (chemistry), derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salt (chemistry), salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salt (chemistry), salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contrasted with the scientific name for the same organism, which is often based in Latin. A common name is sometimes frequently used, but that is not always the case. In chemistry, IUPAC defines a common name as one that, although it unambiguously defines a chemical, does not follow the current systematic naming convention, such as acetone, systematically 2-propanone, while a vernacular name describes one used in a lab, trade or industry that does not unambiguously describe a single chemical, such as copper sulfate, which may refer to either copper(I) sulfate or copper(II) sulfate. Sometimes common names are created by authorities on one particular subject, in an attempt to make it possible for members of the general public (including s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Class
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Classification Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of related drugs that have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prototype Drug
In pharmacology and pharmaceutics, a prototype drug is an individual drug that represents a drug class – group of medications having similar chemical structures, mechanism of action and mode of action. Prototypes are the most important, and typically the first developed drugs within the class, and are used as a reference to which all other drugs are compared. Examples * Morphine is the prototype of opioid analgesics * Propranolol is the prototype of the beta blockers * Chlorpromazine is the prototypical phenothiazine antipsychotic * Imipramine is the prototypical tricyclic antidepressant, and itself a derivative of chlorpromazine * Diazepam is the prototype of the benzodiazepine * Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) is the prototype ethanolamine antihistamine * Nifedipine is the prototype dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker * Chloroquine is the prototypical antimalarial agent * Acyclovir is the prototype antiviral agent that is activated by viral thymidine kinase * Aspirin is the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-in-class Medication
A first-in-class medication is a prototype drug that uses a "new and unique mechanism of action" to treat a particular medical condition. While the Food and Drug Administration's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research tracks first-in-class medications and reports on them annually, first-in-class is not considered a regulatory category. Although many first-in-class medications qualify as breakthrough therapies, Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapies and/or orphan drugs, first-in-class status itself has no regulatory effect. Examples Controversy Safety By definition, a first-in-class drug does not have the safety evidence from analogous products that not-first-in-class drugs would have. However, a study investigating recalls and warnings in relation to first-in-class drugs approved between 1997 and 2012 by Health Canada has found that first-in-class drugs actually have a more favourable benefit-to-harm ratio. Economics First-in-class drugs are often seen as commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure of a molecule is a spatial arrangement of its atoms and their chemical bonds. Its determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen) to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |