|
Inpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care provider. Etymology The word patient originally meant 'one who suffers'. This English noun comes from the Latin word , the present participle of the deponent verb, , meaning , and akin to the Greek verb ( ) and its cognate noun (). This language has been construed as meaning that the role of patients is to passively accept and tolerate the suffering and treatments prescribed by the healthcare providers, without engaging in shared decision-making about their care. Outpatients and inpatients An outpatient (or out-patient) is a patient who attends an outpatient clinic with no plan to stay beyond the duration of the visit. Even if the patient will not be formally admitted with a note as an outpatient, their attendance is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inpatient Care
Inpatient care is the care of patients whose condition requires admission to a hospital. Progress in modern medicine and the advent of comprehensive out-patient clinics ensure that patients are only admitted to a hospital when they are extremely ill or have severe physical trauma. Progress Patients enter inpatient care mainly from previous ambulatory care such as referral from a family doctor, or through emergency medicine departments. The patient formally becomes an " inpatient" at the writing of an admission note. Likewise, it is formally ended by writing a discharge note. Planning for patient discharge Health care professionals involved in rehabilitation are often involved in discharge planning for patients. When considering patient discharge, there are a number of factors to take into consideration: the patient's current state, their place of residence and the type of support available. When considering the patient's current state, although the patient may be eligible f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by Health professional, healthcare professionals. The patient is most often Disease, ill or Major trauma, injured and in need of therapy, treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care provider. Etymology The word wikt:patient, patient originally meant 'one who suffers'. This English noun comes from the Latin word , the present participle of the deponent verb, , meaning , and akin to the Ancient Greek, Greek verb ( ) and its cognate noun (). This language has been construed as meaning that the role of patients is to passively accept and tolerate the suffering and treatments prescribed by the healthcare providers, without engaging in Shared decision-making in medicine, shared decision-making about their care. Outpatients and inpatients An outpatient (or out-patient) is a patient who attends an Outpatient clinic (hospital department), outpatient clinic with no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapy
A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, ''treatment'' and ''therapy'', are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx. As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different types of therapy. Not all therapies are effective. Many therapies can produce unwanted adverse effects. ''Treatment'' and ''therapy'' are often synonymous, especially in the usage of health professionals. However, in the context of mental health, the term ''therapy'' may refer specifically to psychotherapy. Semantic field The words ''care'', ''therapy'', ''treatment'', and ''intervention'' overlap in a semantic field, and thus they can be synonymous depending on context. Moving rightward through that order, the connotative level of holism decreases and the level of specificity (to concrete instances) increases. Thus, in health-care contexts (where its senses are always nonc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outpatient Clinic (hospital Department)
An outpatient department or outpatient clinic is the part of a hospital designed for the treatment of Patient#Outpatients and inpatients, outpatients, people with health problems who visit the hospital for diagnosis or treatment, but do not at this time require a bed or to be admitted for overnight care. Modern outpatient departments offer a wide range of treatment services, diagnostic tests and minor surgical procedures. Department Outpatient department of a hospital provides diagnosis and care for patients that do not need to stay overnight. The departments are also sometimes called outpatient clinics, but are distinct from clinic, clinics independent of hospitals, almost all of which are designed mostly or exclusively for outpatient care and may be also be called outpatient clinics. The outpatient department is an important part of the overall running of the hospital. It is normally integrated with the in-patient services and staffed by consultant physicians and surgeons who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health professions, allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. The term includes work done in providing primary care, wikt:secondary care, secondary care, tertiary care, and public health. Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions and health policy, health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor's Visit
A doctor's visit, also known as a physician office visit or a consultation, or a ward round in an inpatient care context, is a meeting between a patient with a physician to get health advice or treatment plan for a symptom or condition, most often at a professional health facility such as a doctor's office, clinic or hospital. According to a survey in the United States, a physician typically sees between 50 and 100 patients per week, but it may vary with medical specialty, but differs only little by community size such as metropolitan versus rural areas. Procedure The four great cornerstones of diagnostic medicine are anatomy (structure: what is there), physiology (how the structure/s work), pathology (what goes wrong with the anatomy and physiology), and psychology (mind and behavior). In addition, the physician should consider the patient in their 'well' context rather than simply as a walking medical condition. This means the socio-political context of the patient (fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptionist Attending To Clients At The Out Patient
A receptionist is an employee taking an office or administrative support position. The work is usually performed in a waiting area such as a lobby or front office desk of an organization or business. The title ''receptionist'' is attributed to the person who is employed by an organization to receive or greet any visitors, patients, or clients and answer telephone calls. The term ''front desk'' is used in many hotels for an administrative department where a receptionist's duties also may include room reservations and assignment, guest registration, cashier work, credit checks, key control, and mail and message service. Such receptionists are often called ''front desk clerks''. Receptionists cover many areas of work to assist the businesses they work for, including setting appointments, filing, record keeping, and other office tasks. Responsibilities The business duties of a receptionist may include answering visitors' enquiries about a company and its products or services, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medicine, medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are Drug class, classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of controlled substance, control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise require physical restraint in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * ''General anesthesia'' suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of Sensation (psychology), sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * ''Sedation'' suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiolysis, anxiety and creation of long-term memory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
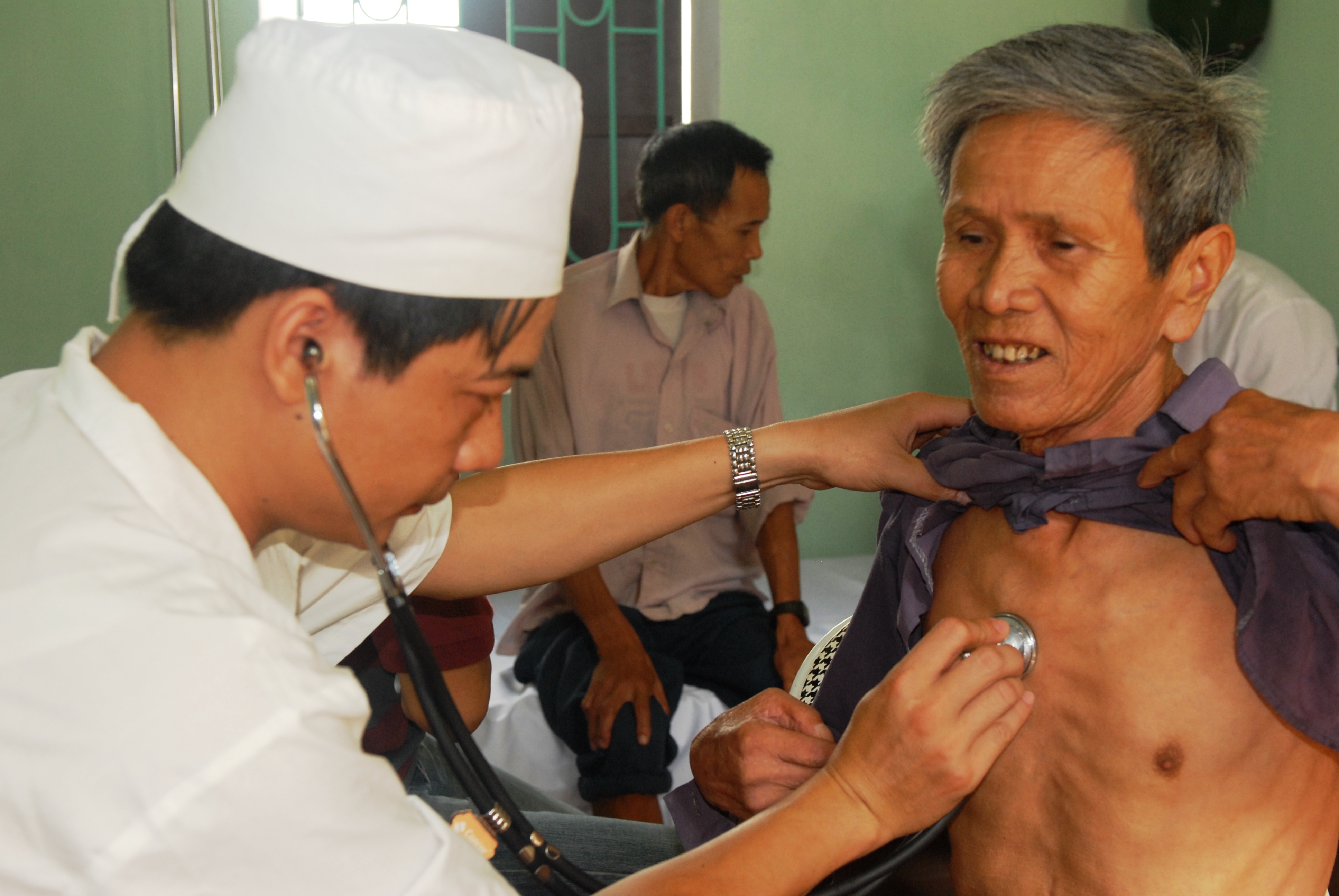
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical History
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and eventually people close to them, so to collect reliable/objective information for managing the medical diagnosis and proposing efficient medical treatments. The medically relevant complaints reported by the patient or others familiar with the patient are referred to as symptoms, in contrast with clinical signs, which are ascertained by direct examination on the part of medical personnel. Most health encounters will result in some form of history being taken. Medical histories vary in their depth and focus. For example, an ambulance paramedic would typically limit their history to important details, such as name, history of presenting complaint, allergies, etc. In contrast, a psychiatric history is frequently lengthy and in depth, as man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |