|
Innermost Stable Circular Orbit
The innermost stable circular orbit (often called the ISCO) is the smallest marginally stable circular orbit in which a test particle can stably orbit a massive object in general relativity. The location of the ISCO, the ISCO-radius (r_), depends on the mass and angular momentum (spin) of the central object. The ISCO plays an important role in black hole accretion disks since it marks the inner edge of the disk. The ISCO should not be confused with the Roche limit, the innermost point where a physical object can orbit before tidal forces break it up. The ISCO is concerned with theoretical ''test particle''s, not real objects. In general terms, the ISCO will be far closer to the central object than the Roche limit. Basic concept In classical mechanics, an orbit is achieved when a test particle's angular momentum is enough to resist the gravity force of the central object. As the test particle approaches the central object, the required amount of angular momentum grows, due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Particle
In physical theories, a test particle, or test charge, is an idealized model of an object whose physical properties (usually mass, charge, or size) are assumed to be negligible except for the property being studied, which is considered to be insufficient to alter the behaviour of the rest of the system. The concept of a test particle often simplifies problems, and can provide a good approximation for physical phenomena. In addition to its uses in the simplification of the dynamics of a system in particular limits, it is also used as a diagnostic in computer simulations of physical processes. Electrostatics In simulations with electric fields the most important characteristics of a test particle is its electric charge and its mass. In this situation it is often referred to as a test charge. The electric field created by a point charge ''q'' is : \textbf = \frac , where ''ε''0 is the vacuum electric permittivity. Multiplying this field by a test charge q_\textrm gives an el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzschild Metric
In Einstein's theory of general relativity, the Schwarzschild metric (also known as the Schwarzschild solution) is an exact solution to the Einstein field equations that describes the gravitational field outside a spherical mass, on the assumption that the electric charge of the mass, angular momentum of the mass, and universal cosmological constant are all zero. The solution is a useful approximation for describing slowly rotating astronomical objects such as many stars and planets, including Earth and the Sun. It was found by Karl Schwarzschild in 1916. According to Birkhoff's theorem, the Schwarzschild metric is the most general spherically symmetric vacuum solution of the Einstein field equations. A Schwarzschild black hole or static black hole is a black hole that has neither electric charge nor angular momentum (non-rotating). A Schwarzschild black hole is described by the Schwarzschild metric, and cannot be distinguished from any other Schwarzschild black hole except by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event Horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an outside observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s. In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact objects that even light cannot escape. At that time, the Newtonian theory of gravitation and the so-called corpuscular theory of light were dominant. In these theories, if the escape velocity of the gravitational influence of a massive object exceeds the speed of light, then light originating inside or from it can escape temporarily but will return. In 1958, David Finkelstein used general relativity to introduce a stricter definition of a local black hole event horizon as a boundary beyond which events of any kind cannot affect an outside observer, leading to information and firewall paradoxes, encouraging the re-examination of the concept of local event horizons and the notion of black holes. Several theories were subsequently d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrograde Motion
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or nutation of an object's rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also refer to an object other than the primary if so described. The direction of rotation is determined by an inertial frame of reference, such as distant fixed stars. In the Solar System, the orbits around the Sun of all planets and dwarf planets and most small Solar System bodies, except many comets and few distant objects, are prograde. They orbit around the Sun in the same direction as the sun rotates about its axis, which is counterclockwise when observed from above the Sun's north pole. Except for Venus and Uranus, planetary rotations around their a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prograde Motion
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or nutation of an object's rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also refer to an object other than the primary if so described. The direction of rotation is determined by an inertial frame of reference, such as distant fixed stars. In the Solar System, the orbits around the Sun of all planets and dwarf planets and most small Solar System bodies, except many comets and few distant objects, are prograde. They orbit around the Sun in the same direction as the sun rotates about its axis, which is counterclockwise when observed from above the Sun's north pole. Except for Venus and Uranus, planetary rotations around their axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
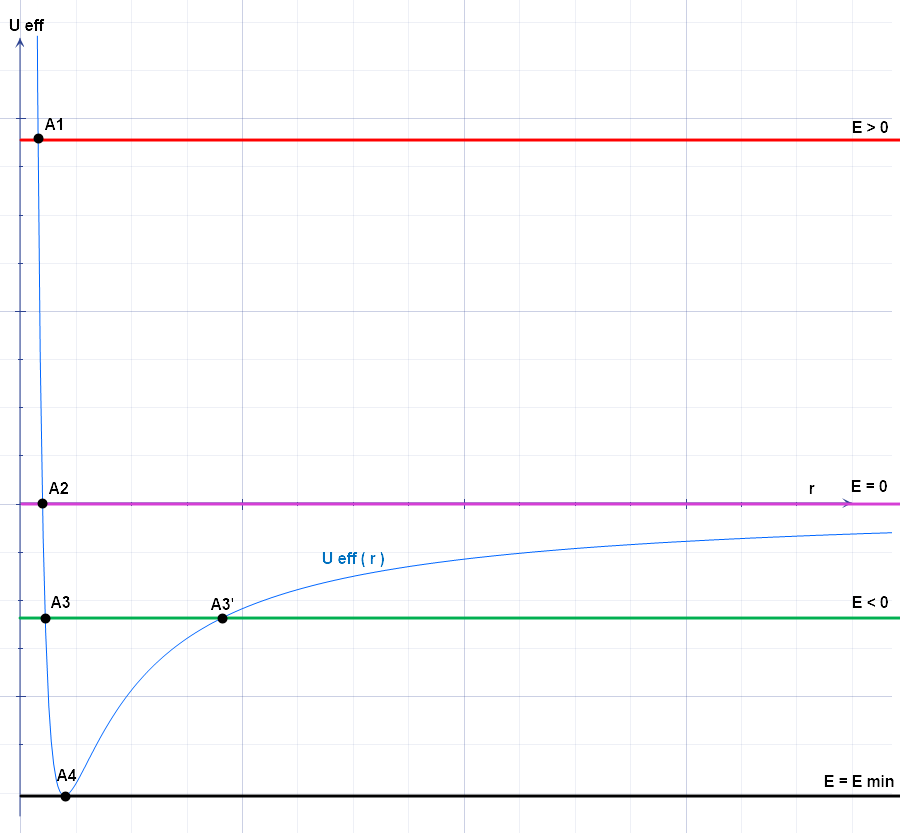
Effective Potential
The effective potential (also known as effective potential energy) combines multiple, perhaps opposing, effects into a single potential. In its basic form, it is the sum of the "opposing" centrifugal potential energy with the potential energy of a dynamical system. It may be used to determine the orbits of planets (both Newtonian and relativistic) and to perform semi-classical atomic calculations, and often allows problems to be reduced to fewer dimensions. Definition The basic form of potential U_\text is defined as U_\text(\mathbf) = \frac + U(\mathbf), where : ''L'' is the angular momentum, : ''r'' is the distance between the two masses, : ''μ'' is the reduced mass of the two bodies (approximately equal to the mass of the orbiting body if one mass is much larger than the other), : ''U''(''r'') is the general form of the potential. The effective force, then, is the negative gradient of the effective potential: \begin \mathbf_\text &= -\nabla U_\text(\mathbf) \\ &= \fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4 Trajectoires D'un Photon Autour D'un Trou Noir
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is a square number, the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. Evolution of the Hindu-Arabic digit Brahmic numerals represented 1, 2, and 3 with as many lines. 4 was simplified by joining its four lines into a cross that looks like the modern plus sign. The Shunga would add a horizontal line on top of the digit, and the Kshatrapa and Pallava evolved the digit to a point where the speed of writing was a secondary concern. The Arabs' 4 still had the early concept of the cross, but for the sake of efficiency, was made in one stroke by connecting the "western" end to the "northern" end; the "eastern" end was finished off with a curve. The Europeans dropped the finishing curve and gradually made the digit less cursive, ending up with a digit very close to the original Brahmin cross. While the shape of the character for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Star
A neutron star is the gravitationally collapsed Stellar core, core of a massive supergiant star. It results from the supernova explosion of a stellar evolution#Massive star, massive star—combined with gravitational collapse—that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. Surpassed only by black holes, neutron stars are the second smallest and densest known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about . Stars that collapse into neutron stars have a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses (), or possibly more for those that are especially rich in Metallicity, elements heavier than hydrogen and helium. Once formed, neutron stars no longer actively generate heat and cool over time, but they may still evolve further through Stellar collision, collisions or Accretion (astrophysics), accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that they are composed almost entirely o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. A black hole has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, but has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the Orders of magnitude (temperature), order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Metric
The Kerr metric or Kerr geometry describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating uncharged axially symmetric black hole with a quasispherical event horizon. The Kerr metric is an exact solution of the Einstein field equations of general relativity; these equations are highly non-linear, which makes exact solutions very difficult to find. Overview The Kerr metric is a generalization to a rotating body of the Schwarzschild metric, discovered by Karl Schwarzschild in 1915, which described the geometry of spacetime around an uncharged, spherically symmetric, and non-rotating body. The corresponding solution for a ''charged'', spherical, non-rotating body, the Reissner–Nordström metric, was discovered soon afterwards (1916–1918). However, the exact solution for an uncharged, ''rotating'' black hole, the Kerr metric, remained unsolved until 1963, when it was discovered by Roy Kerr.Melia, Fulvio (2009). "Cracking the Einstein code: relativity and the birth of black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime, also called the space-time continuum, is a mathematical model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum. Spacetime diagrams are useful in visualizing and understanding relativistic effects, such as how different observers perceive ''where'' and ''when'' events occur. Until the turn of the 20th century, the assumption had been that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its description in terms of locations, shapes, distances, and directions) was distinct from time (the measurement of when events occur within the universe). However, space and time took on new meanings with the Lorentz transformation and special theory of relativity. In 1908, Hermann Minkowski presented a geometric interpretation of special relativity that fused time and the three spatial dimensions into a single four-dimensional continuum now known as Minkowski space. This interpretation proved vital t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |