|
Ingeo
Ingeo is a range of polylactic acid (PLA) biopolymers owned by NatureWorks. Resinex Group distributes Ingeo in Europe. Ingeo is created using carbon stored in plants via photosynthesis and takes the form of dextrose sugar. These sugars are then converted into a biopolymer through the processes of fermentation and separation. The resulting resin can then be injection molded into plastic goods, extruded for film applications, thermoformed into packaging, or extruded for use in textiles. However, its use in textiles is limited because of its limited comfort properties. Due to its biodegradability, PLA is applied in geotextiles, where the objective is that the material over time disappears. PLA is more resistant to ultraviolet light than some synthetic plastics and has relatively low flammability. Due to its relatively higher hydrophobic character compared to the common polyester fibers, Ingeo is often blended with cotton and wool. This blend of materials results in lighter garme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polylactide
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a plastic material. As a thermoplastic polyester (or polyhydroxyalkanoate) it has the backbone formula or . PLA is formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide , the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit. Often PLA is blended with other polymers. PLA can be biodegradable or long-lasting, depending on the manufacturing process, additives and copolymers. PLA has become a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resources and the possibility to use it for compostable products. In 2022, PLA had the highest consumption volume of any bioplastic of the world, with a share of ca. 26 % of total bioplastic demand. Although its production is growing, PLA is still not as important as traditional commodity polymers like PET or PVC. Its widespread application has been hinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include some naturally occurring chemicals, such as those found in plants and insects. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing. Polyester fibers are sometimes spun together with natural fibers to produce a cloth with blended properties. Cotton-polyester blends can be strong, wrinkle- and tear-resistant, and reduce shrinking. Synthetic fibers using polyester have high water, wind, and environmental resistance compared to plant-derived fibers. They are less Fireproofing, fire-resistant and can melt when ignited. Liquid crystalline polyesters are among the first industrially used liquid crystal polymers. They are used for their mechanical propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioplastics
Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources. Historically, bioplastics made from natural materials like shellac or cellulose had been the first plastics. Since the end of the 19th century they have been increasingly superseded by fossil-fuel plastics derived from petroleum or natural gas (''fossilized'' biomass is not considered to be renewable in reasonable short time). Today, in the context of bioeconomy and circular economy, bioplastics are gaining interest again. Conventional petro-based polymers are increasingly blended with bioplastics to manufacture "bio-attributed" or "mass-balanced" plastic products - so the difference between bio- and other plastics might be difficult to define. Bioplastics can be produced by: * processing directly from natural biopolymers including polysaccharides (e.g., corn starch or rice starch, cellulose, chitosan, and alginate) and proteins (e.g., soy protein, gluten, and gelatin), * chemical synthesis from su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyolefin
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More specialized polyolefins include Polyisobutene, polyisobutylene and polymethylpentene. They are all colorless or white oils or solids. Many copolymers are known, such as polybutene, which derives from a mixture of different butene isomers. The name of each polyolefin indicates the olefin from which it is prepared; for example, polyethylene is derived from ethylene, and polymethylpentene is derived from 4-methyl-1-pentene. Polyolefins are not olefins themselves because the double bond of each olefin monomer is opened in order to form the polymer. Monomers having more than one double bond such as butadiene and isoprene yield polymers that contain double bonds (polybutadiene and polyisoprene) and are usually not considered polyolefins. Polyolefins are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grease (lubricant)
Grease is a solid or semisolid lubricant formed as a dispersion of thickening agents in a liquid lubricant. Grease generally consists of a soap emulsified with mineral or vegetable oil. A common feature of greases is that they possess high initial viscosities, which upon the application of shear, drop to give the effect of an oil-lubricated bearing of approximately the same viscosity as the base oil used in the grease. This change in viscosity is called shear thinning. Grease is sometimes used to describe lubricating materials that are simply soft solids or high viscosity liquids, but these materials do not exhibit the shear-thinning properties characteristic of the classical grease. For example, petroleum jellies such as Vaseline are not generally classified as greases. Greases are applied to mechanisms that can be lubricated only infrequently and where a lubricating oil would not stay in position. They also act as sealants to prevent the ingress of water and incompressible ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped, and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
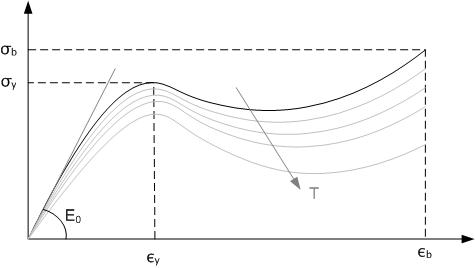
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials, the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to air and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, with the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene is naturally transparent to visible light, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging (such as packing peanuts and optical disc jewel cases), containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room temperature but flows if heated above about 100 °C, its glass transition temperature. It becomes rigid again when cooled. This te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Bottle
A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo or milk. They range in sizes, from very small bottles to large carboys. Consumer blow molded containers often have integral package handle, handles or are shaped to facilitate grasping. Plastic was invented in the nineteenth century and was originally used to replace common materials such as ivory, rubber, and shellac. Plastic bottles were first used commercially in 1947, but remained relatively expensive until the early 1950s when high-density polyethylene was introduced. They quickly became popular with both manufacturers and customers because compared to glass bottles, plastic bottles are lighter, cheaper and easier to transport. However, the biggest advantage plastic bottles have over their glass counterparts is their superior resistance to Structural integrity and failure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packaging And Labeling
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a coordinated system of preparing goods for transport, warehousing, logistics, sale, and end use. Packaging contains, protects, preserves, transports, informs, and sells. In many countries it is fully integrated into government, business, institutional, industrial, and for personal use. ''Package labeling'' (American English) or ''labelling'' (British English) is any written, electronic, or graphic communication on the package or on a separate but associated label. Many countries or regions have regulations governing the content of package labels. Merchandising, branding, and persuasive graphics are not covered in this article. History of packaging Ancient era The first packages used the natural materials available at the time: baskets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have some properties similar to animal wool. As an animal fiber, wool consists of protein together with a small percentage of lipids. This makes it chemically quite distinct from cotton and other plant fibers, which are mainly cellulose. Characteristics Wool is produced by follicles which are small cells located in the skin. These follicles are located in the upper layer of the skin called the epidermis and push down into the second skin layer called the dermis as the wool fibers grow. Follicles can be classed as either primary or secondary follicles. Primary follicles produce three types of fiber: kemp, medullated fibers, and true wool fibers. Secondary follicles only produce true wool fibers. Medullated fibers share nearly identical characteristics to hair and are long but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |