|
Inferior Epigastric Artery
In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold (which represents the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude.) The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath. Structure Origin The inferior epigastric artery arises from the external iliac artery, immediately superior to the inguinal ligament. Course and relations It curves forward in the subperitoneal tissue, and then ascends obliquely along the medial margin of the abdominal inguinal ring; continuing its course upward, it pierces the transversalis fascia, and, passing in front of the linea semicircularis, ascends betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Iliac Artery
The external iliac arteries are two major Artery, arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis. Structure The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles. They exit the Pelvis, pelvic girdle posterior and inferior to the inguinal ligament. This occurs about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the pubic tubercle. At this point they are referred to as the femoral arteries. Branches Function The external iliac artery provides the main blood supply to the legs. It passes down along the brim of the pelvis and gives off two large branches - the "inferior epigastric artery" and a "deep circumflex artery." These vessels supply blood to the muscles and skin in the lower abdominal wall. The external iliac artery passes beneath the inguinal ligament in the lower part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linea Semicircularis
The arcuate line of rectus sheath (the arcuate line or the semicircular line of Douglas) is a line of demarcation corresponding to the free inferior margin of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath inferior to which only the anterior layer of the rectus sheath is present and the rectus abdominis muscle is therefore in direct contact with the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line is concave inferior-wards. The arcuate line is visible upon the inner surface of the abdominal wall. The arcuate line may be a well-defined, or may be represented by a gradual waning of the aponeurotic fibres with concomitant increasing prominence of the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line occurs about midway between the umbilicus and pubic symphysis, however, this varies from person to person. The inferior epigastric artery and vein pass across the arcuate line to enter the rectus sheath. Anatomy Superior to the arcuate line, the internal oblique muscle aponeurosis splits to envelop the rectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
The rectus abdominis muscle, () also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply better known as the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th–7th ribs superiorly. The rectus abdominis muscle is contained in the rectus sheath, which consists of the aponeuroses of the lateral abdominal muscles. Each rectus abdominus is traversed by bands of connective tissue called the tendinous intersections, which interrupt it into distinct muscle bellies. Structure The rectus abdominis is a very long flat muscle, which extends along the whole length of the front of the abdomen, and is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdomen#Contents, abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intrape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body. This terminology incorporates a range of unique terms, prefixes, and suffixes derived primarily from Ancient Greek and Latin. While these terms can be challenging for those unfamiliar with them, they provide a level of precision that reduces ambiguity and minimizes the risk of errors. Because anatomical terminology is not commonly used in everyday language, its meanings are less likely to evolve or be misinterpreted. For example, everyday language can lead to confusion in descriptions: the phrase "a scar above the wrist" could refer to a location several inches away from the hand, possibly on the forearm, or it could be at the base of the hand, either on the palm or dorsal (back) side. By using precise anatomical terms, such as "proximal," "distal," "palmar," or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Hernia
An inguinal hernia or groin hernia is a hernia (protrusion) of abdominal cavity contents through the inguinal canal. Symptoms, which may include pain or discomfort especially with or following coughing, exercise, or bowel movements, are absent in about a third of patients. Symptoms often get worse throughout the day and improve when lying down. A bulging area may occur that becomes larger when bearing down. Inguinal hernias occur more often on the right than the left side. The main concern is strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the intestine is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness of the area. Risk factors for the development of a hernia include: smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease, and previous open appendectomy, among others. Predisposition to hernias is genetic and they occur more often in certain families. Deleterious mutations causing predisposition to he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anastomosis
An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (such as the foramen ovale in a fetus' heart) or abnormal (such as the patent foramen ovale in an adult's heart); it may be acquired (such as an arteriovenous fistula) or innate (such as the arteriovenous shunt of a metarteriole); and it may be natural (such as the aforementioned examples) or artificial (such as a surgical anastomosis). The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology, geology, and geography. Etymology Anastomosis: medical or Modern Latin, from Greek ἀναστόμωσις, anastomosis, "outlet, opening", Greek ana- "up, on, upon", stoma "mouth" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
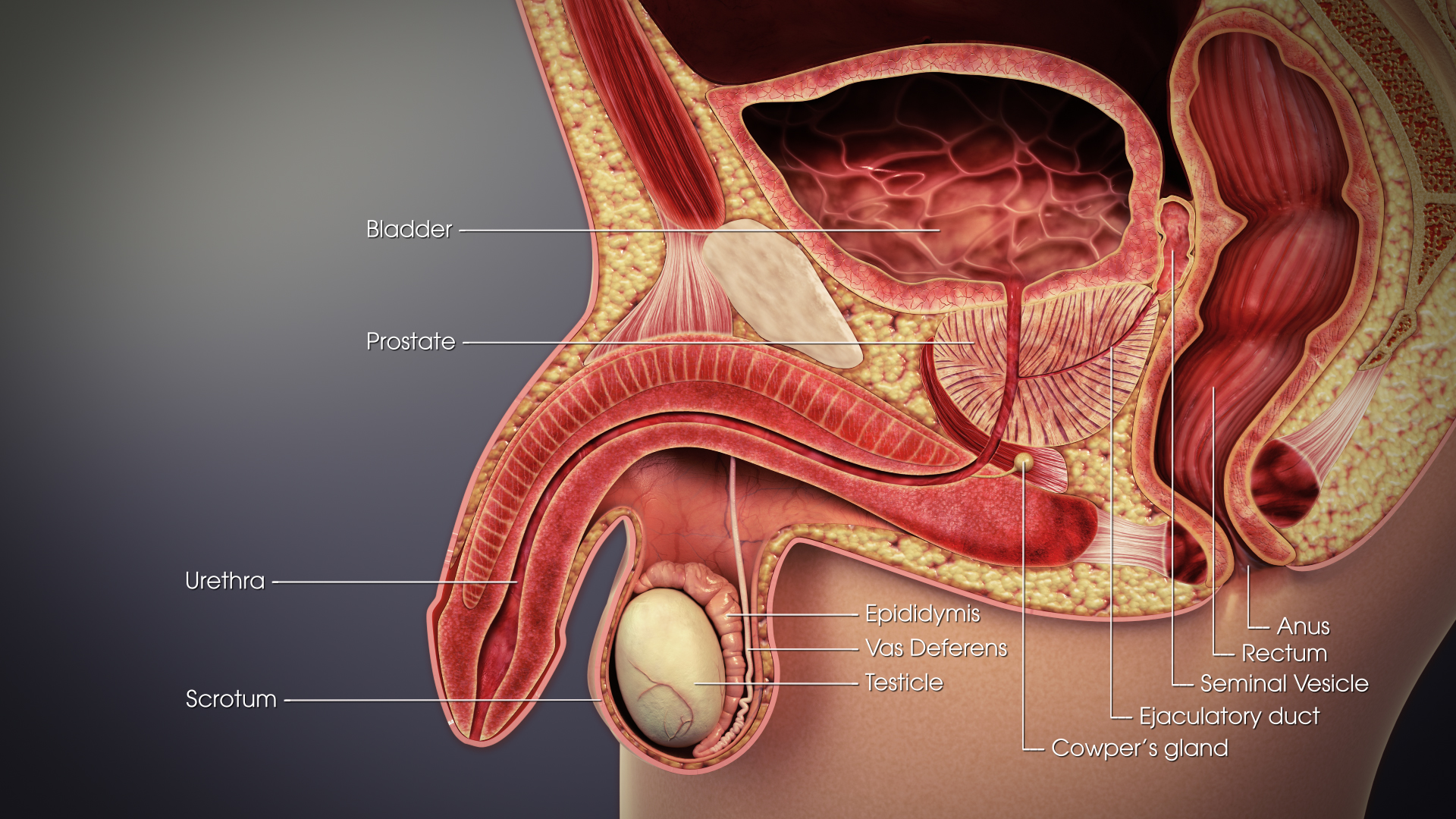
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididymal duct. The end of the epididymis is connected to the vas deferens. The vas deferens ends with an opening into the ejaculatory duct at a point where the duct of the seminal vesicle also joins the ejaculatory duct. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel" while ''ductus deferens'', also Latin, means "carrying-away duct". Structure The human vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis, and exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms a dilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side. Structure The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: * '' external spermatic fascia'', an extension of the innominate fascia that overlies the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. * '' cremasteric muscle and fascia'', formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia. * '' internal spermatic fascia'', continuous with the transversalis fascia. The normal diameter of the spermatic cord is about 16 mm (range 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Intercostal Arteries
The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space (the space between two adjacent ribs). There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branchthe musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta. Each anterior intercostal artery anastomoses with the corresponding posterior intercostal artery arising from the thoracic aorta. Anterior intercostal arteries Origin The upper six anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery (anterior intercostal branches of internal thoracic artery). The internal thoracic artery then divides into its two terminal branches, one of which - the musculophrenic artery - proceeds to issue anterior intercostal arteries to the remaining 7th, 8th, and 9th intercostal spaces; these dimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |