|
Indo-1
Indo-1 is a popular dye that is used as a ratiometric calcium indicator similar to Fura-2. In contrast to Fura-2, Indo-1 has a dual emissions peak and a single excitation. The main emission peak in calcium-free solution is 475 nm while in the presence of calcium the emission is shifted to 400 nm. It is widely used in flow cytometry and laser scanning microscopy, due to its single excitation property. However, its use for confocal microscopy is limited due to its photo-instability caused by photobleaching. Indo-1 is also able to keep possession of its ratiometric emission, dissimilar to Fura-2. The penta potassium salt is commercially available and preferred to the free acid because of its higher solubility in water. While Indo-1 is not cell permeable the penta acetoxymethyl ester Indo-1 AM enters the cell where it is cleaved by intracellular esterases to Indo-1. The synthesis and properties of Indo-1 were presented in 1985 by the group of Roger Y Tsien. In intact h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Indicator
Calcium imaging is a microscopy technique to optically measure the calcium (Ca2+) status of an isolated cell, tissue or medium. Calcium imaging takes advantage of calcium indicators, fluorescent molecules that respond to the binding of Ca2+ ions by fluorescence properties. Two main classes of calcium indicators exist: chemical indicators and genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECI). This technique has allowed studies of calcium signalling in a wide variety of cell types, and can be used to measure electrical activity in hundreds of neurons in cell culture, or in living animals during ongoing behavior. Chemical indicators Chemical indicators are small molecules that can chelate calcium ions. All these molecules are based on an EGTA homologue called BAPTA, with high selectivity for calcium (Ca2+) ions versus magnesium (Mg2+) ions. This group of indicators includes fura-2, indo-1, fluo-3, fluo-4, Calcium Green-1. These dyes are often used with the chelator carboxyl groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-1 AM
Indo-1 is a popular dye that is used as a ratiometric calcium indicator similar to Fura-2. In contrast to Fura-2, Indo-1 has a dual emissions peak and a single excitation. The main emission peak in calcium-free solution is 475 nm while in the presence of calcium the emission is shifted to 400 nm. It is widely used in flow cytometry and laser scanning microscopy, due to its single excitation property. However, its use for confocal microscopy is limited due to its photo-instability caused by photobleaching In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between .... Indo-1 is also able to keep possession of its ratiometric emission, dissimilar to Fura-2. The penta potassium salt is commercially available and preferred to the free acid because of its higher solubility in water. Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescent Dyes
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to macromolecules, serving as a markers (or dyes, or tags, or reporters) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, such as fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents
Chelation () is a type of bonding of ions and their molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity. The word ''chelation'' is derived from Greek χηλή, ''chēlē'', meaning "claw"; the ligands lie around the central atom like the claws of a crab. The term ''chelate'' () was first applied in 1920 by Sir Gilbert T. Morgan and H. D. K. Drew, who stated: "The adjective chelate, derived from the great claw or ''chele'' (Greek) of the crab or other crustaceans, is suggested for the caliperlike groups which function as two associating units and fasten to the central atom so as to produce heterocyclic rings." Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
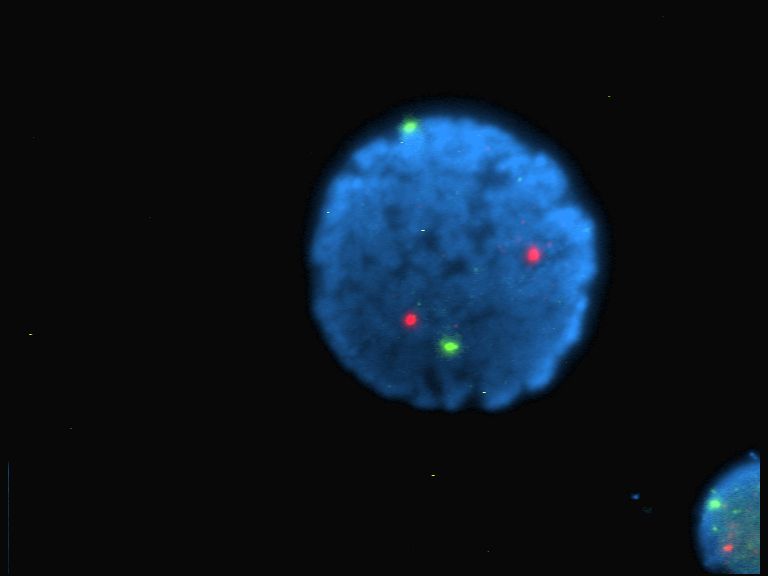
Cell Imaging
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life * Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network * Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Electrochemical cell, a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Cell may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Cell (comics), a Marvel comic book character * Cell (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the manga series ''Dragon Ball'' Literature * ''Cell'' (novel), a 2006 horror novel by Stephen King * "Cells", poem, about a hungover soldier in gaol, by Rudyard Kipling * ''The Cell'' (play), an Australian play by Robert Wales Music * Cell (music), a small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a thematic context * Cell (American band) * Cell (Japanese band) * ''Cell'' (album), a 2004 album by Plastic Tree * ''Cells'', a 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry Methods
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to biochemistry: Biochemistry – study of chemical processes in living organisms, including living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes. Applications of biochemistry * Testing ** Ames test – salmonella bacteria is exposed to a chemical under question (a food additive, for example), and changes in the way the bacteria grows are measured. This test is useful for screening chemicals to see if they mutate the structure of DNA and by extension identifying their potential to cause cancer in humans. ** Pregnancy test – one uses a urine sample and the other a blood sample. Both detect the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone is produced by the placenta shortly after implantation of the embryo into the uterine walls and accumulates. ** Breast cancer screening – identification of risk by testing for mutations in two genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aequorin
Aequorin is a calcium-activated photoprotein isolated from the hydrozoan ''Aequorea victoria''. Its bioluminescence was studied decades before the protein was isolated from the animal by Osamu Shimomura in 1962. In the animal, the protein occurs together with the green fluorescent protein to produce green light by resonant energy transfer, while aequorin by itself generates blue light. Discussions of "jellyfish DNA" that can make "glowing" animals often refer to transgenic animals that express the green fluorescent protein, not aequorin, although both originally derive from the same animal. Apoaequorin, the protein portion of aequorin, is an ingredient in the dietary supplement Prevagen. The US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has charged the maker with false advertising for its memory improvement claims. Discovery Work on aequorin began with E. Newton Harvey in 1921. Though Harvey was unable to demonstrate a classical luciferase-luciferin reaction, he showed that water cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Y
Roger is a masculine given name, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic languages">Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") and ', ' ("spear", "lance") (Hrōþigēraz). The name was introduced into England by the Normans. In Normandy, the Franks, Frankish name had been reinforced by the Old Norse cognate '. The name introduced into England replaced the Old English cognate '. ''Roger'' became a very common given name during the Middle Ages. A variant form of the given name ''Roger'' that is closer to the name's origin is '' Rodger''. Slang and other uses From up to , Roger was slang for the word "penis". In ''Under Milk Wood'', Dylan Thomas writes "jolly, rodgered" suggesting both the sexual double entendre and the pirate term "Jolly Roger". In 19th-century England, Roger was slang for another term, the cloud of toxic green gas that swept through the chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esterases
In biochemistry, an esterase is a class of enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis (and as such, it is a type of hydrolase). A wide range of different esterases exist that differ in their substrate specificity, their protein structure, and their biological function. EC classification/list of enzymes * ''EC 3.1.1'': Carboxylic ester hydrolases ** Acetylesterase (EC 3.1.1.6), splits off acetyl groups *** Cholinesterase **** Acetylcholinesterase, inactivates the neurotransmitter acetylcholine **** Pseudocholinesterase, broad substrate specificity, found in the blood plasma and in the liver ** Pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11), clarifies fruit juices * ''EC 3.1.2'': Thiolester hydrolases ** Thioesterase *** Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 * ''EC 3.1.3'': Phosphoric monoester hydrolases ** Phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.x), hydrolyses phosphoric acid monoesters into a phosphate ion and an alcohol *** Alkaline phosphata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |