|
India House
India House was a student residence that existed between 1905 and 1910 at Cromwell Avenue in Highgate, North London. With the patronage of lawyer Shyamji Krishna Varma, it was opened to promote nationalist views among Indian students in Britain. This institute used to grant scholarships to Indian youths for higher studies in England. The building rapidly became a hub for political activism, one of the most prominent for overseas revolutionary Indian nationalism. "India House" came to informally refer to the nationalist organisations that used the building at various times. Patrons of India House published an anti-colonialist newspaper, '' The Indian Sociologist'', which the British Raj banned as " seditious". A number of prominent Indian revolutionaries and nationalists were associated with India House, including Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, Bhikaji Cama, V.N. Chatterjee, Lala Har Dayal, V.V.S. Aiyar, M.P.T. Acharya and P.M. Bapat. In 1909, a member of India House, Madan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India House Today
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland Yard
Scotland Yard (officially New Scotland Yard) is the headquarters of the Metropolitan Police, the territorial police force responsible for policing Greater London's London boroughs, 32 boroughs. Its name derives from the location of the original Metropolitan Police headquarters at 4 Whitehall Place, which had its main public entrance on the Westminster street called Great Scotland Yard. The Scotland Yard entrance became the public entrance, and over time "Scotland Yard" came to be used not only as the common name of the headquarters building, but also as a metonym for the Metropolitan Police Service (MPS) itself and police officers, especially detectives, who serve in it. ''The New York Times'' wrote in 1964 that, just as Wall Street gave its name to New York's financial district, Scotland Yard became the name for police activity in London. The force moved from Great Scotland Yard in 1890, to a newly completed building on the Victoria Embankment, and the name "New Scotland Yard" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidency Of Madras
The Madras Presidency or Madras Province, officially called the Presidency of Fort St. George until 1937, was an Presidencies and provinces of British India, administrative subdivision (province) of British India and later the Dominion of India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including all of present-day Andhra Pradesh, almost all of Tamil Nadu and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, Odisha and Telangana in the modern day. The city of Madras was the winter capital of the presidency and Ooty (Udagamandalam) was the summer capital. The Madras State was neighboured by the Kingdom of Mysore to the northwest, the Kingdom of Cochin and Kingdom of Travancore to the southwest, the Pudukkottai State, Kingdom of Pudukkottai in the center, and the Kingdom of Hyderabad, Hyderabad State to the north. Some parts of the presidency were also flanked by Bombay Presidency, Bombay State (Konkan, Konkan Districts) and Central Provinces and Berar, Central States (mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the northwest. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India, the third most populous country subdivision in South Asia and the fourth-most populous in the world. The state is divided into 6 divisions and 36 districts. Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra due to its historical significance as a major trading port and its status as India's financial hub, housing key institutions and a diverse economy. Additionally, Mumbai's well-developed infrastructure and cultural diversity make it a suitable administrative center for the state, and the most populous urban are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
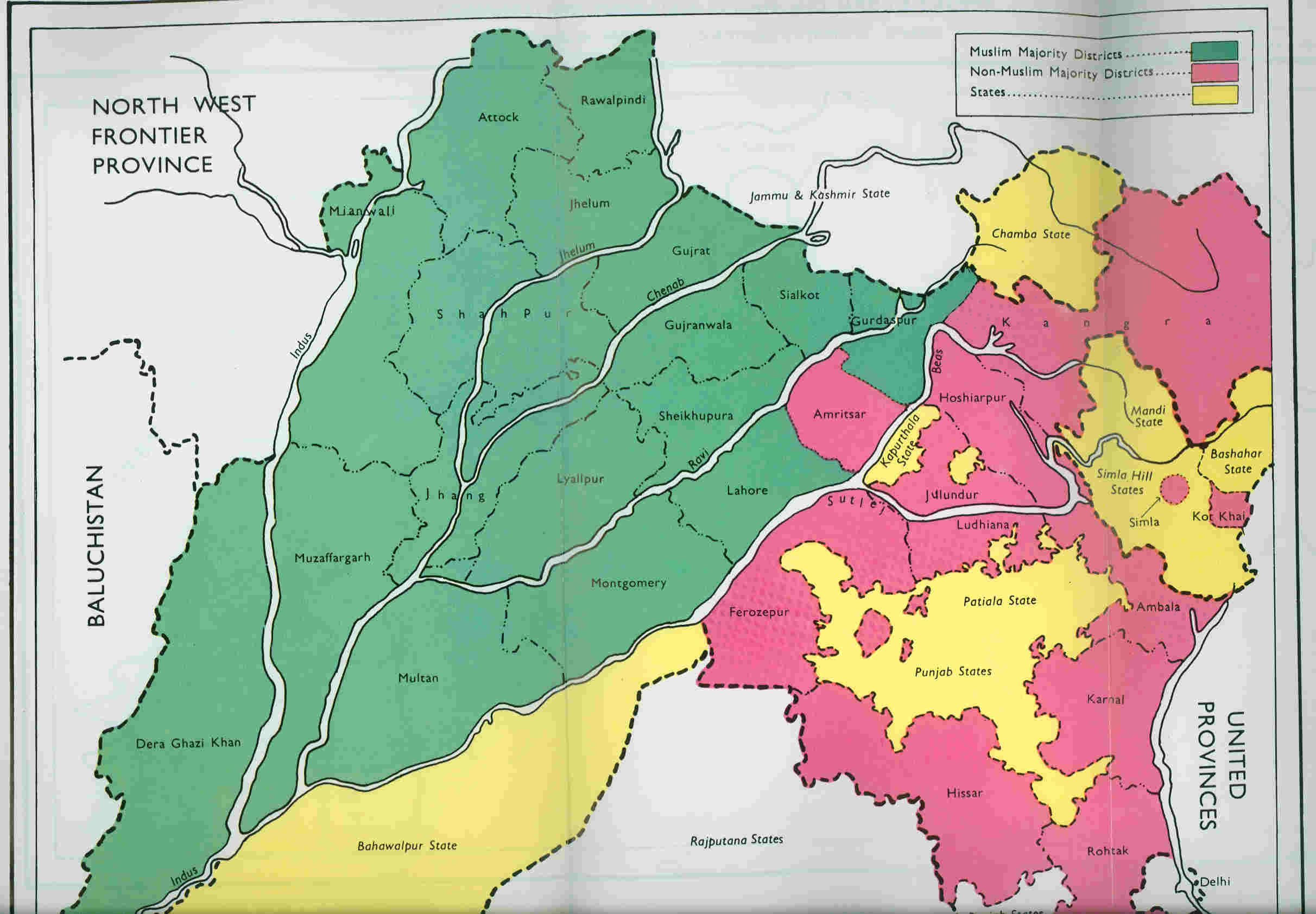
Punjab (British India)
The Punjab Province, officially the Province of the Punjab, was a province of British India, with its capital in Lahore and summer capitals in Murree and Simla. At its greatest extent, it stretched from the Khyber Pass to Delhi; and from the Babusar Pass and the borders of Tibet to the borders of Sind. Established in 1849 following Punjab's annexation, the province was partitioned in 1947 into West and East Punjab; and incorporated into Pakistan and India, respectively. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company on 29 March 1849 following the company's victory at the battle of Gujrat in northern Punjab, a month prior. The Punjab was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to fall to British imperialism. Immediately following its annexation, the Punjab was annexed into the Bengal Presidency and administered separately by a board of administration led by the head of province. After 1853, the board was replaced by a chief commissioner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Bengal proper is divided between the modern-day sovereign nation of Bangladesh and the States and union territories of India, Indian states of West Bengal, and Karimganj district of Assam. The ancient Vanga Kingdom is widely regarded as the namesake of the Bengal region. The Bengali calendar dates back to the reign of Shashanka in the 7th century CE. The Pala Empire was founded in Bengal during the 8th century. The Sena dynasty and Deva dynasty ruled between the 11th and 13th centuries. By the 14th century, Bengal was absorbed by Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent. An independent Bengal Sultanate was formed and became the eastern frontier of the Islamic world. During this period, Bengal's rule and influence spread to Assam, Arakan, Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Octavian Hume
Allan Octavian Hume, Order of the Bath, CB Indian Civil Service, ICS (4 June 1829 – 31 July 1912) was a British political reformer, ornithologist, civil servant and botanist who worked in British Raj, British India and was the founding spirit and key founder of the Indian National Congress. He was a proponent of Indian self-rule and strongly supported the idea of Indian independence. He supported the idea of self-governance by Indians. A notable ornithologist, Hume has been called "the Father of Indian Ornithology" and, by those who found him dogmatic, "the Pope of Indian Ornithology". As the collector of Etawah, he saw the Indian Rebellion of 1857 as a result of misgovernance and made great efforts to improve the lives of the common people. The district of Etawah was among the first to be returned to normality and over the next few years Hume's reforms led to the district being considered a model of development. Hume rose in the ranks of the Indian Civil Service (British India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a political parties in India, political party in India with deep roots in most regions of India. Founded on 28 December 1885, it was the first modern Nationalism, nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. The Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and significantly influenced other Decolonization, anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire. The INC is a "big tent" party that has been described as sitting on the Centrism, centre of the Indian politics, Indian political spectrum. The party held its first session in 1885 in Mumbai, Bombay where Womesh Chunder Bonnerjee, W.C. Bonnerjee presided over it. After Indian independence in 1947, Congress eme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Nationalism
Hindu nationalism has been collectively referred to as the expression of political thought, based on the native social and cultural traditions of the Indian subcontinent. "Hindu nationalism" is a simplistic translation of . It is better described as "Hindu polity". The native thought streams became highly relevant in Indian history when they helped form a distinctive identity about the Indian polityChatterjee Partha (1986) and provided a basis for questioning colonialism.Peter van der Veer, Hartmut Lehmann, Nation and religion: perspectives on Europe and Asia, Princeton University Press, 1999 p. 90 These also inspired Indian nationalism, Indian nationalists during the Indian independence movement, independence movement based on armed struggle,Li Narangoa, R. B. Cribb ''Imperial Japan and National Identities in Asia'', 1895–1945, Published by Routledge, 2003 p. 78 coercive politics,Bhatt, Chetan, ''Hindu Nationalism: Origins, Ideologies and Modern Myths'', Berg Publishers (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communism In India
Communism in India has existed as a social or political ideology as well as a political movement since 1920's. In its early years, communist ideology was harshly suppressed through legal prohibitions and criminal prosecutions. Eventually, communist parties became ensconced in national party politics, sprouting several political offshoots. Early history of communism in India Following the October Revolution, Bipin Chandra Pal and Bal Gangadhar Tilak were amongst the prominent Indians who expressed their admiration of Lenin and the new rulers in the USSR, now Russia. Abdul Sattar Khairi and Abdul Zabbar Khairi went to Moscow, immediately on hearing about the revolution. In Moscow, they met Lenin and conveyed their greetings to him. The Russian Revolution also affected émigré Indian revolutionaries, such as the Ghadar Party in North America.M.V.S. Koteswara Rao. ''Communist Parties and United Front – Experience in Kerala and West Bengal''. Hyderabad: Prajasakti Book House, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni
Alumni (: alumnus () or alumna ()) are former students or graduates of a school, college, or university. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for groups of women, and alums (: alum) or alumns (: alumn) as gender-neutral alternatives. The word comes from Latin, meaning nurslings, pupils or foster children, derived from "to nourish". The term is not synonymous with "graduates": people can be alumni without graduating, e.g. Burt Reynolds was an alumnus of Florida State University but did not graduate. The term is sometimes used to refer to former employees, former members of an organization, former contributors, or former inmates. Etymology The Latin noun means "foster son" or "pupil". It is derived from the Latin verb "to nourish". Separate, but from the same root, is the adjective "nourishing", found in the phrase '' alma mater'', a title for a person's home university. Usage in Roman law In Latin, is a legal term (Roman law) to describe a child placed in foster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |