|
Inclusion (mineral)
In mineralogy, an inclusion is any material trapped inside a mineral during its formation. In gemology, it is an object enclosed within a gemstone or reaching its surface from the interior. According to James Hutton's law of inclusions, fragments included in a host rock are older than the host rock itself. Mineralogy Inclusions are usually rock (geology), rocks or other minerals, less often water, gas or petroleum. Liquid and vapor create fluid inclusions. In amber, insects and plants are common inclusions. The analysis of atmospheric gas Bubble (physics), bubbles as inclusions in ice cores is an important tool in the study of climate change (general concept), climate change. A xenolith is a preexisting rock which has been picked up by a lava flow. Melt inclusions form when bits of melt become trapped inside crystals as they form in the melt. Gemology Inclusions are one of the most important factors when it comes to gem valuation. They diminish the diamond clarity, clarity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Phase In Rock Crystal Quartz, Pakistan
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Inclusions
Diamond inclusions are the non-diamond materials that get encapsulated inside diamond during its formation process in the Mantle (geology), mantle. The trapped materials can be other minerals or fluids like water. Since diamonds have high Strength of materials, strength and low Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity with either the inclusion or the volcanic host rocks which carry the diamond to the Earth's surface, the diamond serves as a container that preserves the included material intact under the changing conditions from the mantle to the surface. Although diamonds can only place a lower bound on the pressure of their formation, many inclusions provide additional constraints on the pressure, temperature and even age of formation. Inclusion types Mineral inclusions Mineral inclusions, especially the silicate inclusions in Lithosphere, lithospheric diamonds, can be classified into two dominant types depending on the mantle Parent rock, parental rocks of the host diamond: eclo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new Phase (matter), thermodynamic phase or Crystal structure, structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled (at atmospheric pressure) significantly below 0°C, it will tend to Freezing, freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0°C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay. Nucleation is a common mechanism which generates first-order phase transitions, and it is the start of the process of forming a new thermodynamic phase. In contrast, new phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral, silicate mineral group in which boron is chemical compound, compounded with chemical element, elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. This gemstone comes in a wide variety of colors. The name is derived from the Sinhala language, Sinhalese (), which refers to the carnelian gemstones. History Brightly colored Ceylonese gem tourmalines were brought to Europe in great quantities by the Dutch East India Company to satisfy a demand for curiosities and gems. Tourmaline was sometimes called the "Ceylonese Magnet" because it could attract and then repel hot ashes due to its Pyroelectricity, pyroelectric properties. Tourmalines were used by chemists in the 19th century to Polarization (waves), polarize light by shining rays onto a cut and polished surface of the gem. Species and varieties Commonly encountered species and varieties of tourmaline include the following: * Schorl species ** Brownish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
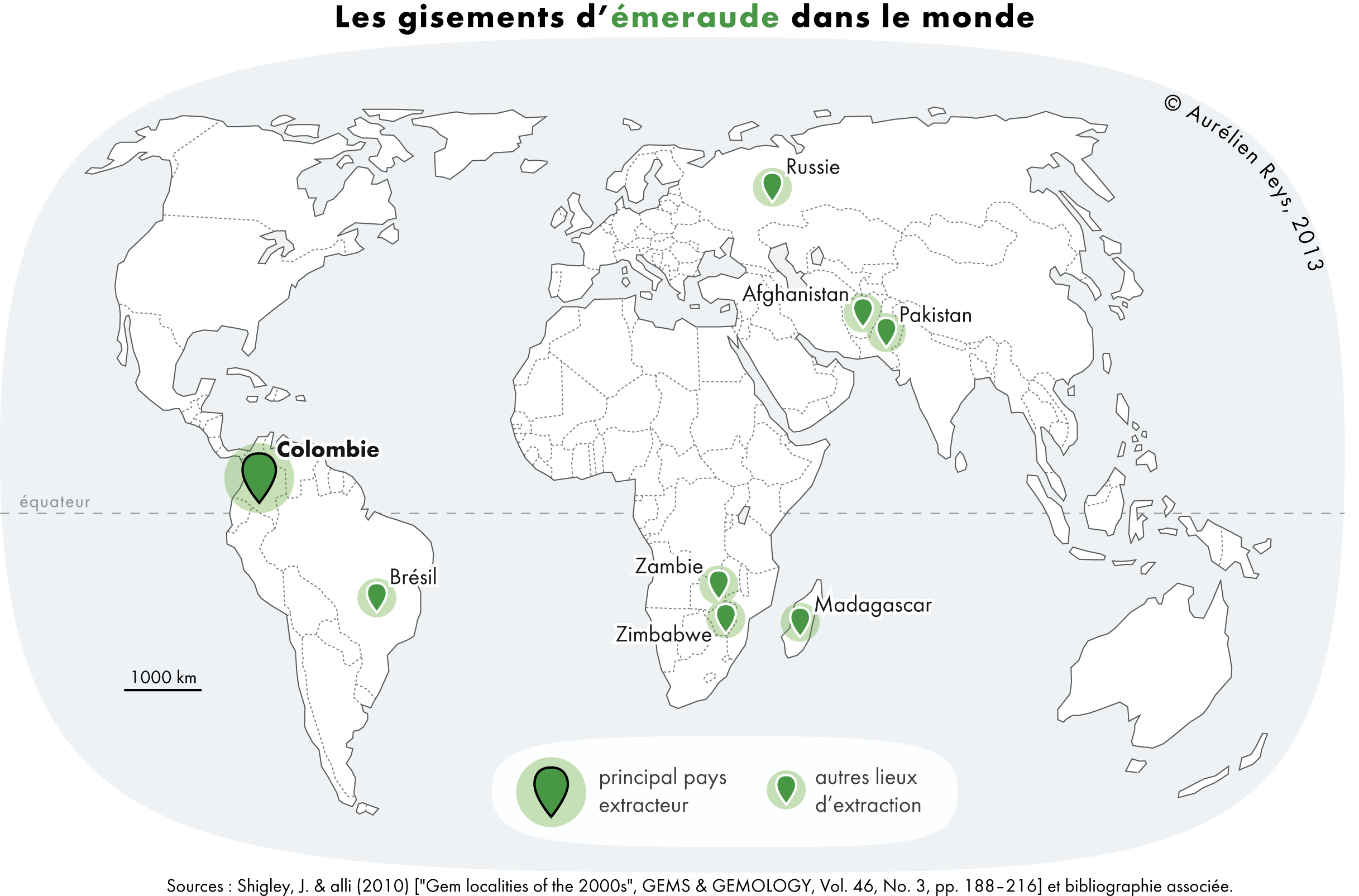
Emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 203, . Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds have many inclusions, so their toughness (resistance to breakage) is classified as generally poor. Emerald is a cyclosilicate. Etymology The word "emerald" is derived (via and ), from Vulgar Latin: ''esmaralda/esmaraldus'', a variant of Latin ''smaragdus'', which was via (smáragdos; "green gem"). The Greek word may have a Semitic, Sanskrit or Persian origin. According to ''Webster's Dictionary'' the term emerald was first used in the 14th century. Properties determining value Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters known as "the four ''C''s": ''color'', ''clarity,'' ''cut'' and ''carat weight''. Normally, in grading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinel
Spinel () is the magnesium/aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula in the cubic crystal system. Its name comes from the Latin word , a diminutive form of ''spine,'' in reference to its pointed crystals. Properties Spinel crystallizes in the isometric system; common crystal forms are octahedron, octahedra, usually Crystal twinning, twinned. It has no true Cleavage (crystal), cleavage, but shows an octahedral Parting (crystal), parting and a conchoidal fracture. Its Mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness is 8, its specific gravity is 3.5–4.1, and it is transparent to opaque with a vitreous to dull Lustre (mineralogy), luster. It may be colorless, but is usually various shades of red, lavender (color), lavender, blue, green, brown, black, or yellow. Chromium(III) causes the red color in spinel from Burma. Some spinels are among the most famous gemstones; among them are the Black Prince's Ruby and the "Timur ruby" in the British Crown Jewels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. Garnet minerals, while sharing similar physical and crystallographic properties, exhibit a wide range of chemical compositions, defining distinct species. These species fall into two primary solid solution series: the pyralspite series (pyrope, almandine, spessartine), with the general formula [Mg,Fe,Mn]3Al2(SiO4)3; and the ugrandite series (uvarovite, grossular, andradite), with the general formula Ca3[Cr,Al,Fe]2(SiO4)3. Notable varieties of grossular include Grossular#Hessonite, hessonite and tsavorite. Etymology The word ''garnet'' comes from the 14th-century Middle English word ''gernet'', meaning 'dark red'. It is borrowed from Old French ''grenate'' from Latin language, Latin ''granatus,'' from ''granum'' ('grain, seed'). This is possibly a reference to ''mela granatum'' or even ''pomum granatum'' ('pomegranate', ''Punica granatum''), a plant whose fruits conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
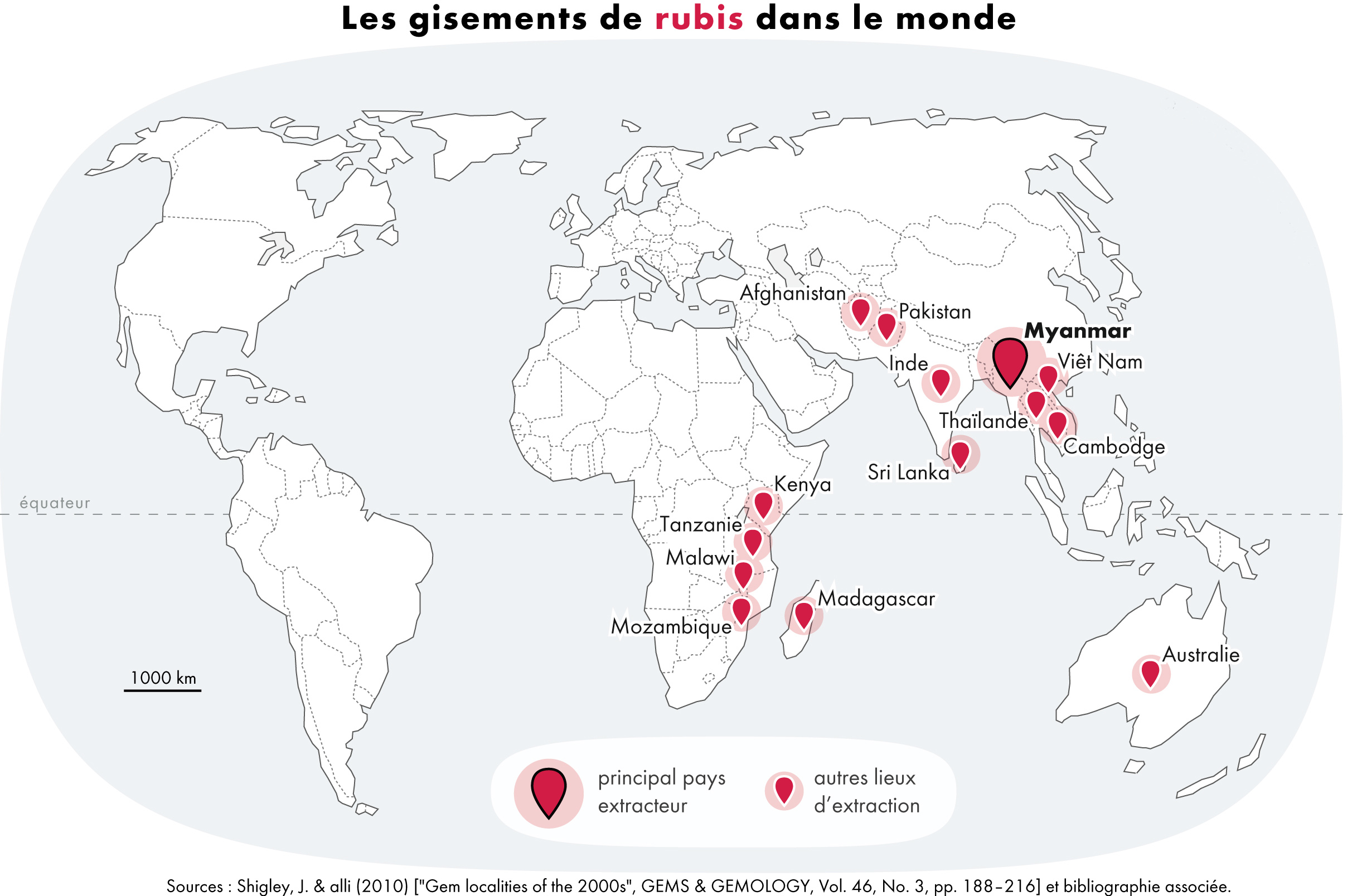
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr1–y, REEy)(SiO4)1–x(OH)4x–y. Zircon precipitates from silicate melts and has relatively high concentrations of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green. The name derives from the Persian ''zargun'', meaning "gold-hued". This word is changed into " jargoon", a term applied to light-colored zircons. The English word "zircon" is derived from ''Zirkon'', which is the German adaptation of this word. Yellow, orange, and red zircon is also known as " hyacint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral made of aluminium, aluminum and fluorine with the chemical formula aluminium, Alsilicon, Sioxygen, O(fluorine, F, hydroxide, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can make it pale blue or golden-brown to yellow-orange. Topaz is often treated with heat or radiation to make it a deep blue, reddish-orange, pale green, pink, or purple. Topaz is a nesosilicate mineral, and more specifically, an aluminosilicate mineral. It is one of the hardest naturally occurring minerals and has a relatively low index of refraction. It has the orthorhombic crystal system and a dipyramidial crystal class. It occurs in many places in the world. Some of the most popular places where topaz is sourced are Brazil and Russia. Topaz is often mined in open pit or alluvial settings. Etymology The word "topaz" is usually believed to be derived (via Old French: Topace and Latin: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hexagonal crystal system, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several meters in size, but double terminated crystal, terminated crystals are relatively rare. Pure beryl is colorless, but it is frequently tinted by impurities; possible colors are green, blue, yellow, pink, and red (the rarest). It is an ore source of beryllium. Etymology The word ''beryl'' – – is borrowed, via and , from Ancient Greek βήρυλλος ''bḗryllos'', which referred to various blue-green stones, from Prakrit ''veruḷiya'', ''veḷuriya'' 'beryl' which is ultimately of Dravidian languages, Dravidian origin, maybe from the name of Belur, Karnataka, Belur or ''Velur'', a town in Karnataka, southern India. The term was later adopted for the mineral ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |