|
Impact (novel)
The American author Douglas Preston has released a number of novels and works, including a five-novel series set in the same universe. Private investigator, ex-monk, and ex-government agent Wyman Ford stars in three of them and has a major supporting role in a fourth. ''Jennie'' (1994) ''Jennie'' is a novel by American author Douglas Preston. The book was published on October 1, 1994, by St. Martin's Press. The work is set in the 1970s and is styled as an in-world nonfictional memoir looking back at the experiment. Naturalist Dr. Hugo Archibald delivers Jennie, a chimpanzee, from her dying mother in the Cameroons and brings her home to his American family. The Archibalds try raising Jennie as if she were a human child, dressing her and buying her toys and the like. His young son, Sandy, becomes extremely attached to Jennie, but Archibald's daughter, Sarah, resents the chimp. Jennie, through her learning of ASL (American Sign Language), starts to converse and interact with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Preston
Douglas Jerome Preston (born May 31, 1956) is an American journalist and author. Although he is best known for his thrillers in collaboration with Lincoln Child (including the '' Agent Pendergast'' series and ''Gideon Crew'' series), he has also written six solo novels, including the '' Wyman Ford'' series and a novel entitled ''Jennie'', which was made into a movie by Disney. He has authored a half-dozen nonfiction books on science and exploration and writes occasionally for ''The New Yorker'', '' Smithsonian'', and other magazines. Life and early career Preston was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts and grew up in Wellesley, Massachusetts. A graduate of the Cambridge School of Weston in Weston, Massachusetts, and Pomona College in Claremont, California, Preston began his writing career at the American Museum of Natural History in New York. From 1978 to 1985, Preston worked for the American Museum of Natural History as a writer, editor, and manager of publications. He served as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
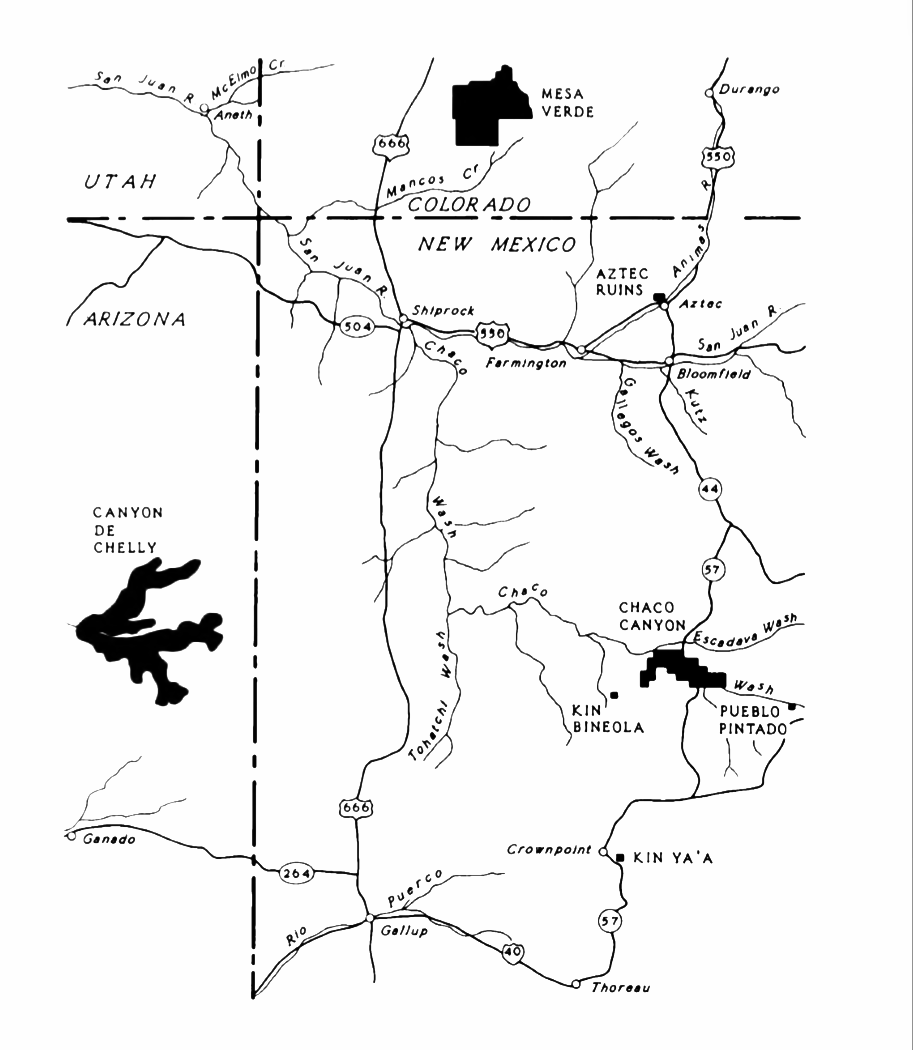
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also borders the state of Texas to the east and southeast, Oklahoma to the northeast, and shares Mexico-United States border, an international border with the Mexican states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua and Sonora to the south. New Mexico's largest city is Albuquerque, and its List of capitals in the United States, state capital is Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe, the oldest state capital in the U.S., founded in 1610 as the government seat of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, Nuevo México in New Spain. It also has the highest elevation of any state capital, at . New Mexico is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fifth-largest of the fifty states by area, but with just over 2.1 million residents, ranks List of U.S. states and terri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theological Fiction
Theological fiction is fictional writing which shapes or depicts people's attitudes towards theological beliefs. It is typically ''instructional'' or ''exploratory'' rather than descriptive, and it engages specifically with the theoretical ideas which underlie and shape typical responses to religion. Theological fiction, as a concept, is used by both theists and atheists, such as in fictional pantheons and cultures in theological fantasy literature. Theological and religious fiction The subject matter of theological novels often overlaps with philosophical novels, particularly when it deals with issues from natural theology (also called philosophy of religion). For example, Roger Olson notes that the problem of evil is a feature of some significant theological fiction. Theological fiction also overlaps with religious fiction or Christian novels (also called inspirational fiction), especially when dealing with complex ideas such as '' redemption,'' ''salvation'' and ''predestinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Fiction
Philosophical fiction is any fiction that devotes a significant portion of its content to the sort of questions addressed by philosophy. It might explore any facet of the human condition, including the function and role of society, the nature and motivation of human acts, the purpose of life, ethics or morals, the role of art in human lives, the role of experience or reason in the development of knowledge, whether there exists free will, or any other topic of philosophical interest. Philosophical fiction includes the ''novel of ideas'', which can also fall under the genre of science fiction, utopian and dystopian fiction, and bildungsroman. There is no universally accepted definition of philosophical fiction, but a sampling of notable works can help to outline its history. For example, a Platonic dialogue could be considered philosophical fiction. Some modern philosophers have written novels, plays, or short fiction in order to demonstrate or introduce their ideas. Common example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as Ancestral Pueblo peoples or the Basketmaker-Pueblo culture, were an ancient Native American culture of Pueblo peoples spanning the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition, which developed from the Picosa culture. The Ancestral Puebloans lived in a range of structures that included small family pit houses, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos, and cliff-sited dwellings for defense. They had a complex network linking hundreds of communities and population centers across the Colorado Plateau. They held a distinct knowledge of celestial sciences that found form in their architecture. The kiva, a congregational space that was used mostly for ceremonies, was an integral part of the community structure. Archaeologists continue to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicxulub Crater
The Chicxulub crater is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore, but the crater is named after the onshore community of Chicxulub Pueblo (not the larger coastal town of Chicxulub Puerto). It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when an asteroid, about in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be in diameter and in depth. It is believed to be the second largest impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring is intact and directly accessible for scientific research. The crater was discovered by Antonio Camargo and Glen Penfield, geophysicists who had been looking for petroleum in the Yucatán Peninsula during the late 1970s. Penfield was initially unable to obtain evidence that the geological feature was a crater and gave up his search. Later, through contact with Alan R. Hildebrand in 1990, Penfield obtained samples that suggested it was an impact feature. Evidence for the crater's imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Op
A covert operation or undercover operation is a military or police operation involving a covert agent or troops acting under an assumed cover to conceal the identity of the party responsible. US law Under US law, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) must lead covert operations unless the president finds that another agency should do so and informs Congress. The CIA's authority to conduct covert action comes from the National Security Act of 1947. President Ronald Reagan issued Executive Order 12333 titled ''United States Intelligence Activities'' in 1984. This order defined covert action as "special activities", both political and military, that the US Government could legally deny. The CIA was also designated as the sole authority under the 1991 Intelligence Authorization Act and in Title 50 of the United States Code Section 413(e). The CIA must have a "Presidential Finding" issued by the President in order to conduct these activities under the Hughes-Ryan amendment to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the director of national intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and processing of information and data for global intelligence and counterintelligence purposes, specializing in a discipline known as signals intelligence (SIGINT). The NSA is also tasked with the protection of U.S. communications networks and information systems. The NSA relies on a variety of measures to accomplish its mission, the majority of which are clandestine. The NSA has roughly 32,000 employees. Originating as a unit to decipher coded communications in World War II, it was officially formed as the NSA by President Harry S. Truman in 1952. Between then and the end of the Cold War, it became the largest of the U.S. intelligence organizations in terms of personnel and budget. Still, information available as of 2013 indicates that the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Museum Of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. Located in Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 21 interconnected buildings housing 45 permanent exhibition halls, in addition to a planetarium and a library. The museum collections contain about 32 million specimens of plants, animals, fungi, fossils, minerals, rocks, meteorites, human remains, and human cultural artifacts, as well as specialized collections for frozen tissue and genomic and astrophysical data, of which only a small fraction can be displayed at any given time. The museum occupies more than . AMNH has a full-time scientific staff of 225, sponsors over 120 special field expeditions each year, and averages about five million visits annually. The AMNH is a private 501(c)(3) organization. The naturalist Albert S. Bickmore devised the idea for the American Museum of Natural History in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' () is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The type species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' ( meaning 'king' in Latin), often shortened to ''T. rex'' or colloquially t-rex, is one of the best represented theropods. It lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. ''Tyrannosaurus'' had a much wider range than other tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of geological formations dating to the latest Campanian-Maastrichtian ages of the late Cretaceous period, 72.7 to 66 million years ago, with isolated specimens possibly indicating an earlier origin in the middle Campanian. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids and among the last non- avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' was a bipedal carnivore with a massive skull balanced by a long, heavy tail. Relative to its large and powerful hind limbs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-penetrating Radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables or masonry. This nondestructive method uses electromagnetic radiation in the microwave band ( UHF/ VHF frequencies) of the radio spectrum, and detects the reflected signals from subsurface structures. GPR can have applications in a variety of media, including rock, soil, ice, fresh water, pavements and structures. In the right conditions, practitioners can use GPR to detect subsurface objects, changes in material properties, and voids and cracks. GPR uses high-frequency (usually polarized) radio waves, usually in the range 10 MHz to 2.6 GHz. A GPR transmitter and antenna emits electromagnetic energy into the ground. When the energy encounters a buried object or a boundary between materials having different permittivities, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |