|
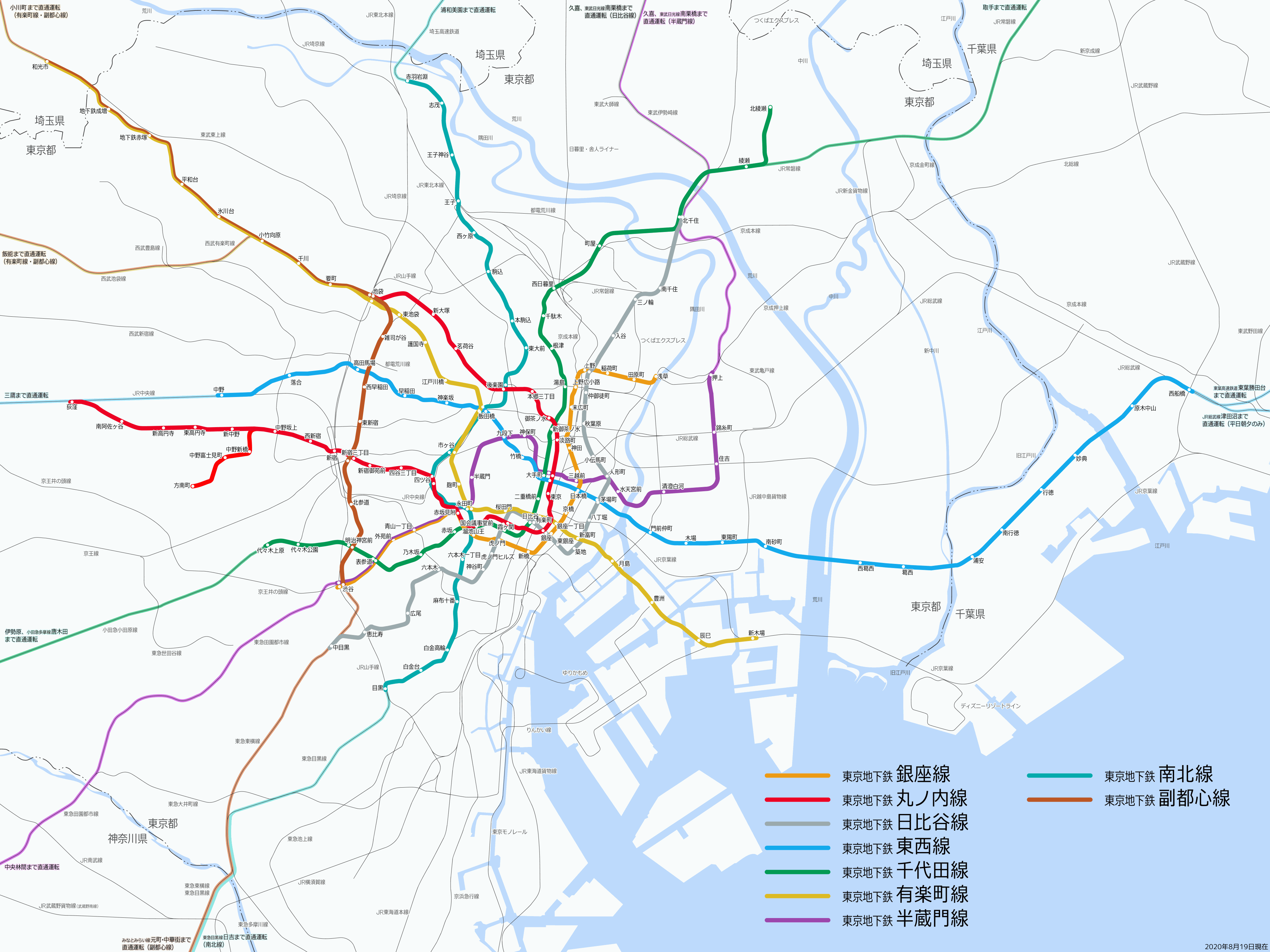
Iidabashi Station
is a major interchange railway station which straddles Tokyo's Chiyoda, Shinjuku and Bunkyō wards. It was originally built as Iidamachi Station (albeit in a slightly different location), terminus of the then Kōbu Railway, precursor to today's Chūō Line. The Ōedo Line addition to the station in 2000 was designed by architect Makoto Sei Watanabe. Lines Iidabashi Station is served by the following above-ground and subway lines. Above ground * Chūō-Sōbu Line (JB16) Subway lines * Tokyo Metro Tōzai Line (T-06) * Tokyo Metro Yūrakuchō Line (Y-13) * Tokyo Metro Namboku Line (N-10) * Toei Ōedo Line (E-06) Station layout The JR East station has one island platform, serving the up and down local lines; there is no platform for the parallel rapid double track (for longer-distance commuter and express Chūō Line trains). The station is located on the inside of the Outer Moat. It is elevated over Mejiro-dori, a major thoroughfare from the Imperial Palace towards Ikebuk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiyoda, Tokyo
, known as Chiyoda City in English, ." ''City of Chiyoda''. Retrieved on December 28, 2008. is a Special wards of Tokyo, special ward of Tokyo, Japan. Located in the heart of Tokyo's 23 special wards, Chiyoda consists of Tokyo Imperial Palace, the Imperial Palace and a surrounding radius of about a kilometer (1000 yards), and is known as the political and financial center of Japan. As of October 2020, the ward has a population of 66,680, and a population density of 5,709 people per km2 (14,786 per sq. mi.), making it by far the least populated of the special wards. The residential part of Chiyoda is at the heart of Yamanote and Shitamachi, Yamanote, Tokyo's traditional upper-class residential area, with Banchō, Kōjimachi, and Kioichō, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Kioichō considered the most exclusive neighbourhoods in the entire city. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagurazaka
is a neighbourhood in Tokyo, northwest of Iidabashi Station. It has a shopping street at its center, lined by numerous cafés and restaurants. It is served by Tokyo Metro Tozai Line and Toei Oedo Line. History The main road of Kagurazaka was once at the outer edge of Edo Castle, opposite the Ushigome bridge over the castle moat, and has always been busy because of this privileged location. In the early 20th century, the area was renowned for its numerous geisha houses, of which several remain today. Currently, Kagurazaka is experiencing a popularity boom due to its traditional atmosphere on the edge of modern Shinjuku ward, the existence of the original campus of Tokyo University of Science and its proximity to Waseda University. The area is also home to a number of publishing houses. While it retains a traditional Japanese atmosphere, Kagurazaka now has a significant French presence with many French expatriates living in the area due to the proximity of l'Institut Franco- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iidabashi
is a district of Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It was in the former ward of Kōjimachi, which existed in Tokyo until 1947. Etymology Iidabashi is named after a nearby bridge A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ... called Iida Bridge (, ''Iidabashi''), itself named after an Edo-period farmer, Iida Kihee (, ''Iida Kihee''). Places * Iidabashi Station *Iida Bridge * Kanda River Economy Several companies have their headquarters in Iidabashi, among them Japan Freight Railway Company, KDDI Nikken Sekkei, and Shohakusha. Education operates public elementary and junior high schools. Fujimi Elementary School (富士見小学校) is the zoned elementary school for Iidabashi 1-4 chōme. There is a freedom of choice system for junior high schools in Chiyoda Ward, and so there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koishikawa Kōrakuen Garden
is a district of Bunkyo, Tokyo. It consists of five sub-areas, . In Koishikawa are located two well regarded gardens: the Koishikawa Botanical Garden (operated by the University of Tokyo) in Hakusan, and the Koishikawa Korakuen Garden in Kōraku. Train stations for accessing this locality include , , , and Myōgadani Station. The Koishikawa Arsenal was an important military installation during the Meiji era. Education Bunkyo operates the local public elementary and middle schools. Zoned elementary schools are: Kanatomi ( 金富小学校), Kubomachi ( 窪町小学校), Rekisen ( 礫川小学校), and Yanagicho ( 柳町小学校). Zoned junior high schools are: No. 1 ( 第一中学校), No. 3 ( 第三中学校), and Meidai ( 茗台中学校). Koishikawa High School is operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education. In addition the metropolis operates the Koishikawa Secondary Education School. Image:Koishikawastreets.JPG, Residential street in Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platform Gap
A platform gap (also known technically as the platform train interface or PTI in some countries) is the space between a train car (or other Public transport, mass transit vehicle) and the edge of the station platform, often created by geometric constraints, historic legacies, or use of partially compatible equipment. Many high-quality bus rapid transit (BRT) systems also use high platforms at station stops to allow fast and efficient level boarding and alighting, but potentially leaving hazardous gaps between the platforms and the buses. Alignment setups such as Kassel curbs help to reduce platform gaps without requiring time-consuming manual alignment at each BRT station stop. Definition and measurement A platform gap has two component measurements: *vertical (difference between the platform height and train floor height) *horizontal (distance from the platform edge to the train step)Gareth Dennis, 'Time to "mind the gap" once and for all' in ''Railway Gazette International May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metro
The Tokyo Metro () is a major rapid transit system in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the #Organization, Tokyo Metro Co. With an average daily ridership of 6.52 million passengers (as of 2023), the Tokyo Metro is the larger of the Tokyo subway, two subway operators in the city, the other being the Toei Subway, with 2.85 million average daily rides. Organization Tokyo Metro is operated by , a joint-stock company jointly owned by the Government of Japan and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. The company, founded as a part of then-Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi's policy of converting statutory corporations into Joint-stock company, joint-stock companies, replaced the , commonly known as Eidan or TRTA, on April 1, 2004. TRTA was administered by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (Japan), Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, and jointly funded by the national and metropolitan governments. It was formed in 1941 as a part-nationalization of the Tokyo Undergrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotetsu Main Line
The , or , is a private railway company operating three lines in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of holding company Sōtetsu Holdings, Inc. Sōtetsu Holdings is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange; 6.58% of it is owned by the Odakyu Electric Railway Company. Overview Sagami Railway is one of the core companies of the Sōtetsu group. Sōtetsu focuses on railway operations, although formerly it had a more diversified set of holdings, such as bus lines and supermarkets. Sōtetsu is the smallest company of the "Big 15" private railways in Japan, as it has only short lines, but it succeeded in developing towns along its lines in the 1960s and 1970s, with many passengers riding this line. In May 1990, Sōtetsu joined the major railways. In 2010 it had a daily ridership of 623,500 Lines The company operates three passenger (commuter) lines and a freight-only line. All lines are electrified. All the railroads owned or operated by Sōtetsu are entirely wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shin-Yokohama Station
is a major interchange railway station in Yokohama, Japan, jointly operated by Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central), East Japan Railway Company (JR East), Yokohama City Transportation Bureau, Sagami Railway (Sotetsu), and Tokyu Railways (Tokyu). Lines Shin-Yokohama Station is served by the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, Yokohama Line, Yokohama Municipal Subway Blue Line, Sōtetsu Shin-Yokohama Line, and the Tōkyū Shin-Yokohama Line. Station layout The JR station consists of an island platform at ground level serving the Yokohama Line, with two elevated island platforms for the shinkansen tracks overhead. The shinkansen platforms 2 and 3 have safety fences, as some trains passed non-stop through the station prior to 2008. The JR Central portion of the station includes a ''Midori no Madoguchi'' staffed ticket office. Additionally, the JR East portion of the station includes reserved seat ticket vending machines. The Municipal Subway, Tōkyū Railways and Sagami Railway (S� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyu Shin-Yokohama Line
The , a contraction of and formerly until 2 September 2019, is a Japanese ''keiretsu'' or conglomerate headquartered in Shibuya, Tokyo. While a multinational corporation, its main operation is , a wholly-owned subsidiary operating railways in the Greater Tokyo Area. History The oldest predecessor of company was the , opened in 1908. The railway's operations were converted into a kabushiki gaisha (company) in 1910. Keita Gotō, now a notable Japanese industrialist, was appointed as the CEO in 1920 and he began a major expansion program. The most important predecessor was first registered on September 2, 1922, as the and is related to the construction of Den-en-chōfu. It was originally founded by the developers of Den-en-chōfu). It was acquired by the Musashi Electric Railway in 1924, shortly before Musashi was renamed into the , also known as the Toyoko, in the same year. After Musashi/Toyoko's acquisition, the Meguro-Kamata Electric Railway initially operated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meguro Line
The is a railway line operated by Japanese private railway company Tokyu Corporation. As a railway line, the name is for the section between and in southwest Tokyo, but nearly all trains run to on a quad-tracked section of the Tōyoko Line in Yokohama, Kanagawa. Additionally, the Meguro line interoperates with the Tokyo Metro Namboku Line and Toei Mita Line beyond Meguro. History *1923: **March 11: The line opens as the Meguro Line between Meguro and Maruko (now Numabe) (on the current Tamagawa Line). **October: Meguro-Fudōmae station is renamed to Fudōmae station. **November 1: The line is extended from Maruko to Kamata, and the line is renamed to the Mekama line. *1924, June 1: Koyama becomes Musashi-Koyama. *1926, January 1: Chōfu and Tamagawa stations are renamed to Den-en-Chōfu and Maruko-Tamagawa stations respectively. *1928, August 1: Nishi-Koyama station opens. *1931, January 1: Maruko-Tamagawa station is renamed again to Tamagawa-en-mae station. *1977, December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |