|
Idiognathodontidae
Idiognathodontidae is an extinct conodont family.New Pennsylvanian conodonts from Oklahoma. RW Harris and RV Hollingsworth, American Journal of Science, March 1933, Series 5, Vol. 25, no. 147, pages 193-204, Genera are ''Gnathodus'', ''Idiognathodus'', and ''Protognathodus''. References External links Idiognathodontidaeat fossilworks Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was cre ....org (retrieved 30 April 2016) Ozarkodinida families {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathodus
''Gnathodus'' is an extinct conodont genus in the family Idiognathodontidae. Use in stratigraphy The Tournaisian, the oldest age of the Mississippian (also known as Lower Carboniferous), contains eight conodont biozones, 3 of which are defined by ''Gnathodus species'': * the zone of ''Gnathodus pseudosemiglaber'' and ''Scaliognathus anchoralis'' * the zone of ''Gnathodus semiglaber'' and ''Polygnathus communis'' * the zone of ''Gnathodus typicus'' and ''Siphonodella isosticha'' The Visean, the second age of the Mississippian, contains four conodont biozones, two of which are defined by ''Gnathodus'' species: * the ''Gnathodus bilineatus'' Zone * the ''Gnathodus texanus'' Zone The Serpukhovian, the third or youngest age of the Mississippian, includes four conodont biozones, two of which are defined by ''Gnathodus'' species: * the ''Gnathodus postbilineatus'' Zone * the ''Gnathodus bollandensis'' Zone References * Proposal of Gnathodus bilineatus (Roundy, 1926) as type s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiognathodus
''Idiognathodus'' is an extinct conodont genus in the family Idiognathodontidae. Use in stratigraphy The species ''Idiognathodus simulator'' made its first appearance during the Gzhelian, the youngest age of the Pennsylvanian (late Carboniferous). Two species (''Idiognathodus toretzianus'' and ''Idiognathodus sagittatus'') are amongst the three conodonts forming the biozones of the Kasimovian, the third stage in the Pennsylvanian. One species (''Idiognathodus sinuosus'') is an index fossil of a biozone of the Bashkirian, the oldest age of the Pennsylvanian, amongst six biozones based on conodonts. See also * List of Global Boundary Stratotype Sections and Points References External links ''Idiognathodus''at fossilworks Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protognathodus
''Protognathodus'' is an extinct conodont Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which ... genus in the family Idiognathodontidae. References * The stratigraphical significance of the Protognathodus fauna from Stockum (Devonian/Carboniferous boundary, Rhenish Schiefergebirge). Alberti H, Groos-Uffenorde H, Streel M, Uffenorde H and Walliser OH, Newsletters on Stratigraphy, 1 Oct. 1974, Volume 3, Number 4, pages 263-276 External links * Ozarkodinida genera Carboniferous conodonts Devonian conodonts Fossil taxa described in 1969 {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
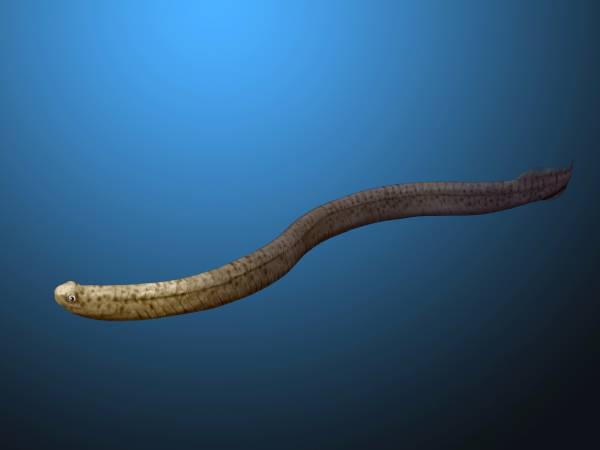
Conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', " tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozarkodinida
Ozarkodinida is an extinct conodont order. It is part of the clade Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts". Name Ozarkodinida is named after the Ozark Mountains of Missouri Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ..., United States. Elements The feeding apparatus of ozarkodinids is composed at the front of an axial Sa element, flanked by two groups of four close-set elongate Sb and Sc elements which were inclined obliquely inwards and forwards. Above these elements lay a pair of arched and inward pointing (makellate) M elements. Behind the S-M array lay transversely oriented and bilaterally opposed (pectiniform, i.e. comb-shaped) Pb and Pa elements. References External links * * Prehistoric jawless fish orders {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', " tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RW Harris
RW or rw may refer to: In arts and entertainment * ''The Real World'' (TV series), an American reality television show * ''Road Wild'', a World Championship Wrestling pay-per-view event * Robbie Williams, a British pop star * Robin Williams, an American actor * Roger Waters, British musician * Robot Wars (other) In mathematics, science and technology In computing * Read-write access to files or directories, in file system permissions * Read-write memory * Rewritable media * RenderWare, a 3-D rendering engine produced by Criterion Software Other uses in mathematics, science, and technology * Random walk, a mathematical process that can be used to explain phenomena in several disciplines * Reaction wheel, a type of flywheel used primarily by spacecraft for attitude control * Robertson–Walker metric, in cosmology * Robin Wight, botanist, noted as R.W. * RW is the designation for the 15th variable star named in a constellation: ** RW Andromedae, a Mira variable locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RV Hollingsworth
A recreational vehicle, often abbreviated as RV, is a motor vehicle or trailer that includes living quarters designed for accommodation. Types of RVs include motorhomes, campervans, coaches, caravans (also known as travel trailers and camper trailers), fifth-wheel trailers, popup campers, and truck campers. Features Typical amenities of an RV include a kitchen, a bathroom, and one or more sleeping facilities. RVs can range from utilitarian – containing only sleeping quarters and basic cooking facilities – to luxurious, with features like air conditioning (AC), water heaters, televisions and satellite receivers, and quartz countertops, for example. RVs can either be trailers (which are towed behind motor vehicles) or self-propelled vehicles. Most RVs are single-deck; however, double-deck RVs also exist. To allow a more compact size while in transit, larger RVs often have expandable sides (called slide-outs) or canopies that are deployed when stationary. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Journal Of Science
The ''American Journal of Science'' (''AJS'') is the United States of America's longest-running scientific journal, having been published continuously since its conception in 1818 by Professor Benjamin Silliman, who edited and financed it himself. Until 1880, it was also known as the ''American Journal of Science and Arts'', but its focus was always on natural sciences and especially on geology and related subjects. In early years, the journal was often referred to as "Silliman's Journal", and the publication became associated with Yale University due to his long tenure there (1804–1853). The editorship long remained in the family of Professor Silliman, as he was assisted by his son, Benjamin Silliman Jr., from 1838. On the death of the elder Silliman in 1864, he was succeeded as chief editor by his son-in-law, James Dwight Dana, and then from 1895 till 1926 by Dana's son Edward Salisbury Dana. Associate editors included the botanist Asa Gray and the zoologist Louis Agassiz. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossilworks
Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was created in 1998 by John Alroy and is housed at Macquarie University. It includes many analysis and data visualization tools formerly included in the Paleobiology Database.{{cite web, title=Frequently asked questions, url=http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, publisher=Fossilworks, access-date=17 December 2021 References {{Reflist External links {{Wikidata property, P842 * [Baidu] |