|
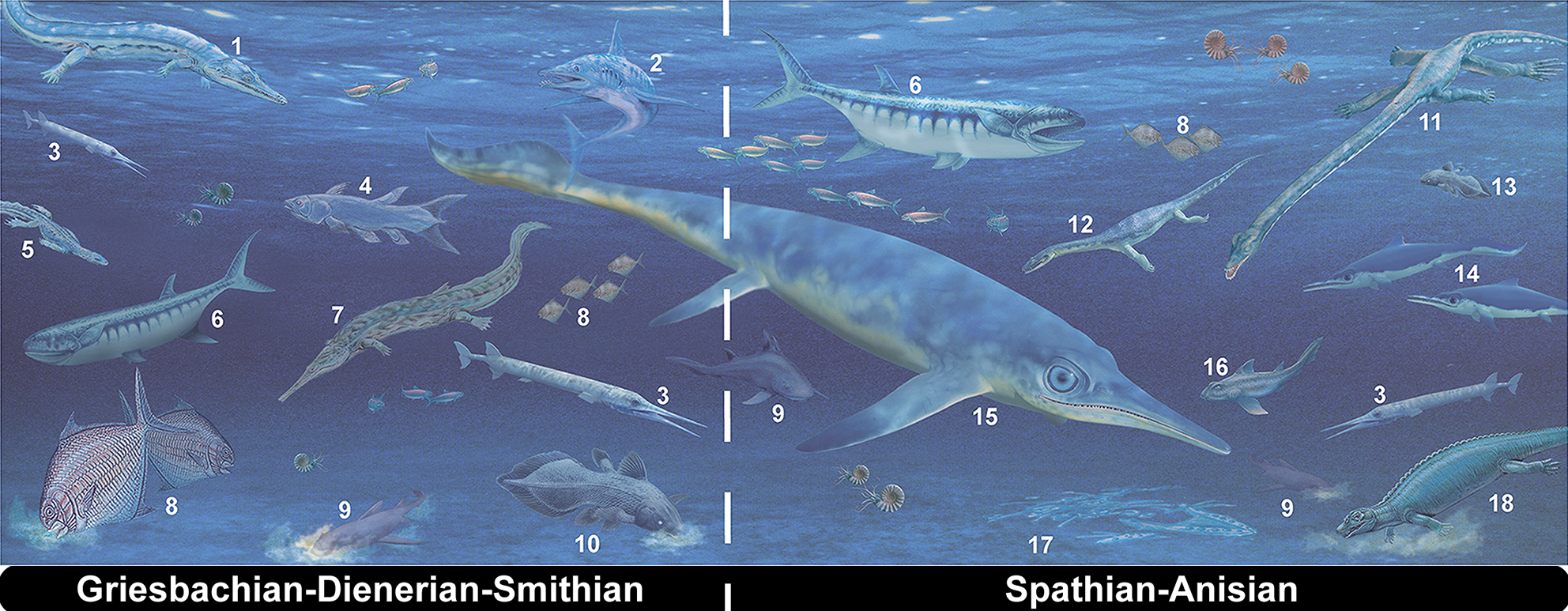
Ichthyosauriform
The Ichthyosauriformes are a group of marine reptiles, belonging to the Ichthyosauromorpha, that lived during the Mesozoic. The stem clade Ichthyosauriformes was in 2014 defined by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues as the group consisting of all ichthyosauromorphs that are more closely related to ''Ichthyosaurus communis'' than to ''Hupehsuchus nanchangensis''. Their synapomorphies include the possession of a long nasal bone, stretching to the front beyond the nostril; large scleral rings, filling the eye sockets; a narrow snout in top view; and converging digits with little space between them. The Ichthyosauriformes probably split off in the Early Triassic, about 250 million years ago; the last known forms lived in the middle Cretaceous. A basal ichthyosauriform is ''Cartorhynchus''; more derived species are part of the Ichthyopterygia which again include the Ichthyosauria Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartorhynchus
''Cartorhynchus'' (meaning "shortened snout") is an extinct genus of basal (phylogenetics), early ichthyosauriformes, ichthyosauriform marine reptile that lived during the Early Triassic epoch (geology), epoch, about 248 million years ago. The genus contains a single species, ''Cartorhynchus lenticarpus'', named in 2014 by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues from a single nearly-complete skeleton found near Chaohu, Anhui Province, China. Along with its close relative ''Sclerocormus'', ''Cartorhynchus'' was part of a diversification of marine reptiles that occurred suddenly (over about one million years) during the Olenekian, Spathian stage (geology), substage, soon after the devastating Permian-Triassic extinction event, but they were subsequently driven to extinction by volcanism and sea level changes by the Middle Triassic. Measuring about long, ''Cartorhynchus'' was a small animal with a lizard-like body and a short torso; it probably swam in an eel-like manner at slow speeds. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauromorpha
The Ichthyosauromorpha are an extinct clade of Mesozoic marine reptiles consisting of the Ichthyosauriformes and the Hupehsuchia. The node clade Ichthyosauromorpha was first defined by Ryosuke Motani ''et al.'' in 2014 as the group consisting of the last common ancestor of '' Ichthyosaurus communis'' and '' Hupehsuchus nanchangensis'', and all its descendants. Their synapomorphies, unique derived traits, include: the presence of an anterior flange on the humerus and radius; the lower end of the ulna being as wide as or wider than the upper end, the forelimb being as long as or longer than the hindlimb, the hand having at least three quarters of the length of the upper arm and lower arm combined, the fibula extending behind the level of the thighbone, and the transverse process of the vertebral neural arch being reduced or absent. The Ichthyosauromorpha were previously thought to have likely originated in China during the upper Lower Triassic period, about 248 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaohusaurus
''Chaohusaurus'' is an extinct genus of basal ichthyosauriform, depending on definition possibly ichthyosaur, from the Early Triassic of Chaohu and Yuanan, China. Discovery and naming The type species ''Chaohusaurus geishanensis'' was named and described by Yang Zhongjian and Dong Zhiming in 1972, based on a fossil found during the construction of a railway. The generic name refers to lake Chao Hu. The specific name refers to the Geishan location. The holotype, IVPP V 4001, was uncovered in a layer of the Majianshan Limestone Formation dating from the Anisian. It consists of a partial skeleton, containing the skull and the front torso. In 1985 Chen Lizhu named two additional species based on fossils found in the same formation: ''Anhuisaurus chaoxianensis'' and ''Anhuisaurus faciles''. However, the generic name had already been preoccupied by the lizard '' Anhuisaurus'' Hou 1974. Therefore, ''Anhuisaurus'' Chen 1985 was in 1991 renamed into ''Chensaurus'' by Jean-Michel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauria
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides. Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurians were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods, until they were replaced as the top aquatic predators by another marine reptilian group, the Plesiosauria, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utatsusaurus
''Utatsusaurus hataii'' is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period (c. 245–250 million years ago). It was nearly long with a slender body. The first specimen was found in Utatsu-cho (now part of Minamisanriku-cho), Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is the only described species in the genus ''Utatsusaurus'' and the only member of the family Utatsusauridae. The name ''Utatsusaurus'' was given after the city. The fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Osawa Formation of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. ''Utatsusaurus'' is one of the most primitive grades of ichthyosaurs, a basal ichthyosaur. Description ''Utatsusaurus'' was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Unlike the more advanced ichthyosaurs, ''Utatsusaurus'' has no dorsal fin and has a broad skull. The snout gently tapers, compared to the more rounded one of more derived ichthyopterygians. The postorbital underlaps the elon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olenekian First Appearances
In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian (Middle Triassic). The Olenekian saw the deposition of a large part of the Buntsandstein in Europe. The Olenekian is roughly coeval with the regional Yongningzhenian Stage used in China. Stratigraphic definitions The Olenekian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian stratigraphers in 1956. The stage is named after Olenëk in Siberia. Before the subdivision in Olenekian and Induan became established, both stages formed the Scythian Stage, which has since disappeared from the official timescale. The base of the Olenekian is at the lowest occurrence of the ammonoids '' Hedenstroemia'' or '' Meekoceras graci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic Reptiles
The Mesozoic Era is the era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and araucarian conifers; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, mosasaurs, and plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, and evolutionary activity. The supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart into separate landmasses. The climate of the Mesozoic was varied, alternating between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleral Ring
The scleral ring or sclerotic ring is a hardened ring of plates, often derived from bone, that is found in the eyes of many animals in several groups of vertebrates. Some species of mammals, amphibians, and crocodilians lack scleral rings. The ring is in the fibrous outer layer of the eye, called the sclera. The structure is commonly referred to as the sclerotic ring; but, because the word ''sclerotic'' often implies pathology of the sclera (''see'' " sclerosis", an unrelated medical condition), recent authors have urged avoiding the use of this term, to avoid confusion and to increase the utility of character comparisons. Scleral rings can be made of cartilaginous material (scleral cartilage) or bony material (scleral ossicles), or often a combination of both, that comes together to form a ring. The arrangement, size, shape, and number of ossicles vary by group. They are believed to have a role in supporting the eye, especially in animals whose eyes are not spherical, or which live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure There is heavy variation in the structure of the nasal bones, accounting for the differences in sizes and shapes of the nose seen across different people. Angles, shapes, and configurations of both the bone and cartilage are heavily varied between individuals. Broadly, most nasal bones can be categorized as "V-shaped" or "S-shaped" but these are not scientific or medical categorizations. When viewing anatomical drawings of these bones, consider that they are unlikely to be accurate for a majority of people. The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |