|
Ice–albedo Feedback
Ice–albedo feedback is a climate change feedback, where a change in the area of ice caps, glaciers, and sea ice alters the albedo and surface temperature of a planet. Because ice is very reflective, it reflects far more solar energy back to space than open water or any other land cover. It occurs on Earth, and can also occur on exoplanets. Since higher latitudes have the coolest temperatures, they are the most likely to have perennial snow cover, widespread glaciers and ice caps - up to and including the potential to form ice sheets. However, if warming occurs, then higher temperatures would decrease ice-covered area, and expose more open water or land. The albedo decreases, and so more solar energy is absorbed, leading to more warming and greater loss of the reflective parts of the cryosphere. Inversely, cooler temperatures increase ice cover, which increases albedo and results in greater cooling, which makes further ice formation more likely. Thus, ice–albedo feedback plays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
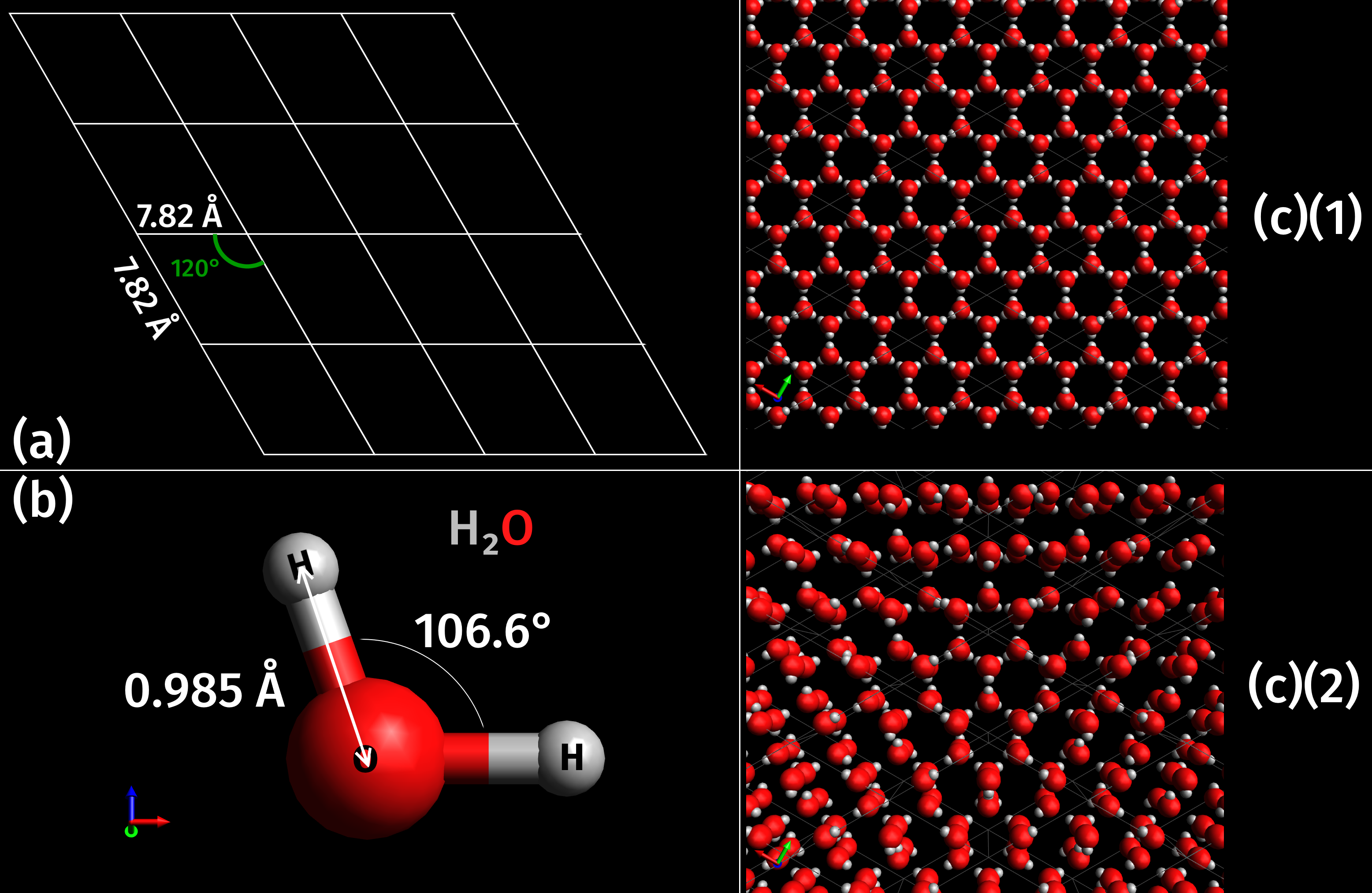
Ice Albedo Feedback
Ice is water that is freezing, frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 °Celsius, C, 32 °Fahrenheit, F, or 273.15 Kelvin, K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Depending on the presence of Impurity, impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less Opacity (optics), opaque bluish-white color. Virtually all of the ice on Earth is of a Hexagonal crystal system, hexagonal Crystal structure, crystalline structure denoted as ''ice Ih'' (spoken as "ice one h"). Depending on temperature and pressure, at least nineteen phases of ice, phases (Sphere packing, packing geometries) can exist. The most common phase transition to ice Ih occurs when liquid water is cooled below (, ) at standard atmospheric pressure. When water is coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deglaciation
Deglaciation is the transition from full glacial conditions during ice ages, to warm interglacials, characterized by global warming and sea level rise due to change in continental ice volume. Thus, it refers to the retreat of a glacier, an ice sheet or frozen surface layer, and the resulting exposure of the Earth's surface. The decline of the cryosphere due to ablation can occur on any scale from global to localized to a particular glacier. After the Last Glacial Maximum (ca. 21,000 years ago), the last deglaciation begun, which lasted until the early Holocene. Around much of Earth, deglaciation during the last 100 years has been accelerating as a result of climate change, partly brought on by anthropogenic changes to greenhouse gases. The previous deglaciation took place from approximately 22 ka until 11.5 ka. This occurred when there was an annual mean atmospheric temperature on the earth that increased by roughly 5 °C, which was also accompanied by regional hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Brief
Carbon Brief is a UK-based website specialising in the science and policy of climate change. It has won awards for investigative journalism and data visualisation. Leo Hickman is the director and editor for Carbon Brief. Founding Carbon Brief is funded by the European Climate Foundation, and has their office located in London. The website was established in response to the Climategate controversy. Reception Carbon Brief's climate-and-energy coverage is often cited by news outlets and climate related websites. Awards The Royal Statistical Society gave Carbon Brief a ''Highly Commended'' award for investigative journalism in 2018, for the article ''Mapped: How UK foreign aid is spent on climate change'', authored by Leo Hickman and Rosamund Pearce, and in 2020 in the category data visualisation for ''How the UK transformed its electricity supply in just a decade''. In 2017, Carbon Brief won ''The Drum Online Media Award'' for "Best Specialist Site for Journalism". Carbon Brief' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
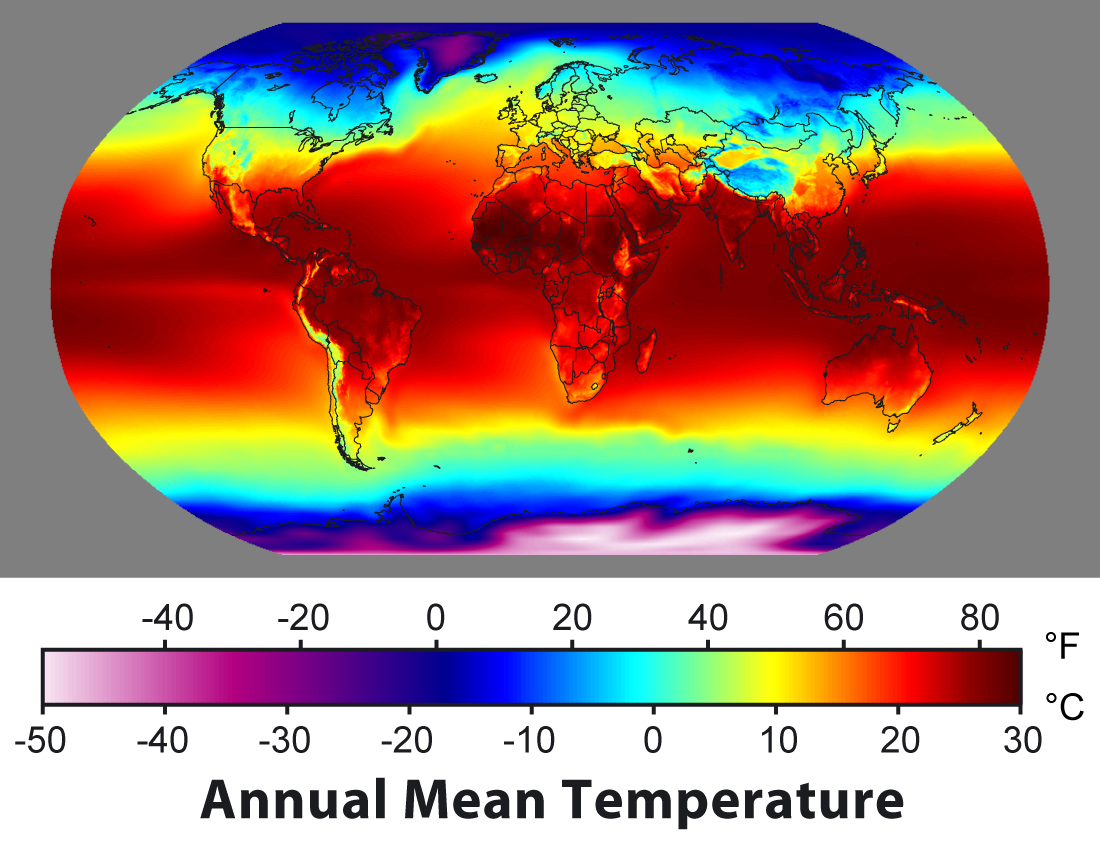
Earth's Energy Budget
Earth's energy budget (or Earth's energy balance) is the balance between the energy that Earth receives from the Sun and the energy the Earth loses back into outer space. Smaller energy sources, such as Earth's internal heat, are taken into consideration, but make a tiny contribution compared to solar energy. The energy budget also takes into account how energy moves through the climate system. The Sun heats the equatorial tropics more than the polar regions. Therefore, the amount of solar irradiance received by a certain region is unevenly distributed. As the energy seeks equilibrium across the planet, it drives interactions in Earth's climate system, i.e., Earth's water, ice, atmosphere, rocky crust, and all living things. The result is Earth's climate. Earth's energy budget depends on many factors, such as atmospheric aerosols, greenhouse gases, surface albedo, clouds, and land use patterns. When the incoming and outgoing energy fluxes are in balance, Earth is in radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syukuro Manabe
is a Japanese– American physicist, meteorologist, and climatologist, who pioneered the use of computers to simulate global climate change and natural climate variations. He was awarded the 2021 Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Klaus Hasselmann and Giorgio Parisi, for his contributions to the physical modeling of Earth's climate, quantifying its variability, and predictions of climate change. Early life and education Born in 1931 in Shinritsu Village, Uma District, Ehime Prefecture, Japan. Both his grandfather and his father were physicians, who operated the only clinic in the village. A classmate recalled that, even in elementary school, he was already "interested in the weather, making comments such as 'If Japan didn't have typhoons, we wouldn't have so much rain.'" Easier to access at ahoo mirror site https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/04e7a8f6d96a5694121d438ec1d19c86a3ec6eeb Manabe attended Ehime Prefectural Mishima High School. When he was accepted into the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climatologist
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "slope"; and , ''-logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. Climate concerns the atmospheric condition during an extended to indefinite period of time; weather is the condition of the atmosphere during a relative brief period of time. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. This topic of study is regarded as part of the atmospheric sciences and a subdivision of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology includes some aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry. The main methods employed by climatologists are the analysis of observations and modelling of the physical processes that determine climate. Short term weather forecasting can be interpreted in terms of knowledge of longer-term phenomena of climate, for instance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenland are full Danish nationality law, citizens of Denmark and European Union citizenship, of the European Union. Greenland is one of the Special territories of members of the European Economic Area#Overseas countries and territories, Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union and is part of the Council of Europe. It is the List of islands by area, world's largest island, and lies between the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is the location of the northernmost point of land in the world; Kaffeklubben Island off the northern coast is the world's Northernmost point of land, northernmost undisputed point of land—Cape Morris Jesup on the mainland was thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land“Glacier, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Accessed 25 Jan. 2025. and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Model
Numerical climate models (or climate system models) are mathematical models that can simulate the interactions of important drivers of climate. These drivers are the atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. Scientists use climate models to study the dynamics of the climate system and to make projections of future climate and of climate change. Climate models can also be qualitative (i.e. not numerical) models and contain narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures. Climate models take account of incoming energy from the Sun as well as outgoing energy from Earth. An imbalance results in a change in temperature. The incoming energy from the Sun is in the form of short wave electromagnetic radiation, chiefly visible and short-wave (near) infrared. The outgoing energy is in the form of long wave (far) infrared electromagnetic energy. These processes are part of the greenhouse effect. Climate models vary in complexity. For example, a simple radiant heat transfer model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Sea Ice Decline
Sea ice in the Arctic region has declined in recent decades in area and volume due to climate change. It has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in winter. Global warming, caused by Radiative forcing#Forcing due to changes in atmospheric gases, greenhouse gas forcing is responsible for the decline in Arctic sea ice. The decline of sea ice in the Arctic has been accelerating during the early twenty-first century, with a decline rate of 4.7% per decade (it has declined over 50% since the first satellite records). Summertime sea ice will likely cease to exist sometime during the 21st century. The region is at its warmest in at least 4,000 years. Furthermore, the Arctic-wide melt season has lengthened at a rate of five days per decade (from 1979 to 2013), dominated by a later autumn freeze-up. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (2021) stated that Arctic sea ice area will likely drop below 1 million km2 in at least some Septembers before 2050.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effects Of Climate Change
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an Instrumental temperature record, overall warming trend, Effects of climate change on the water cycle, changes to precipitation patterns, and more extreme weather. As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification. These changes impact ecosystems and societies, and can become irreversible once Tipping points in the climate system, tipping points are crossed. Climate activists are engaged in a range of activities around the world that seek to ameliorate these issues or prevent them from happening. The effects of climate change vary in timing and location. Up until now the polar amplification, Arctic has warmed faster than most other regions due to climate change feedbacks. Surface air temperatures over land have also increased at ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |