|
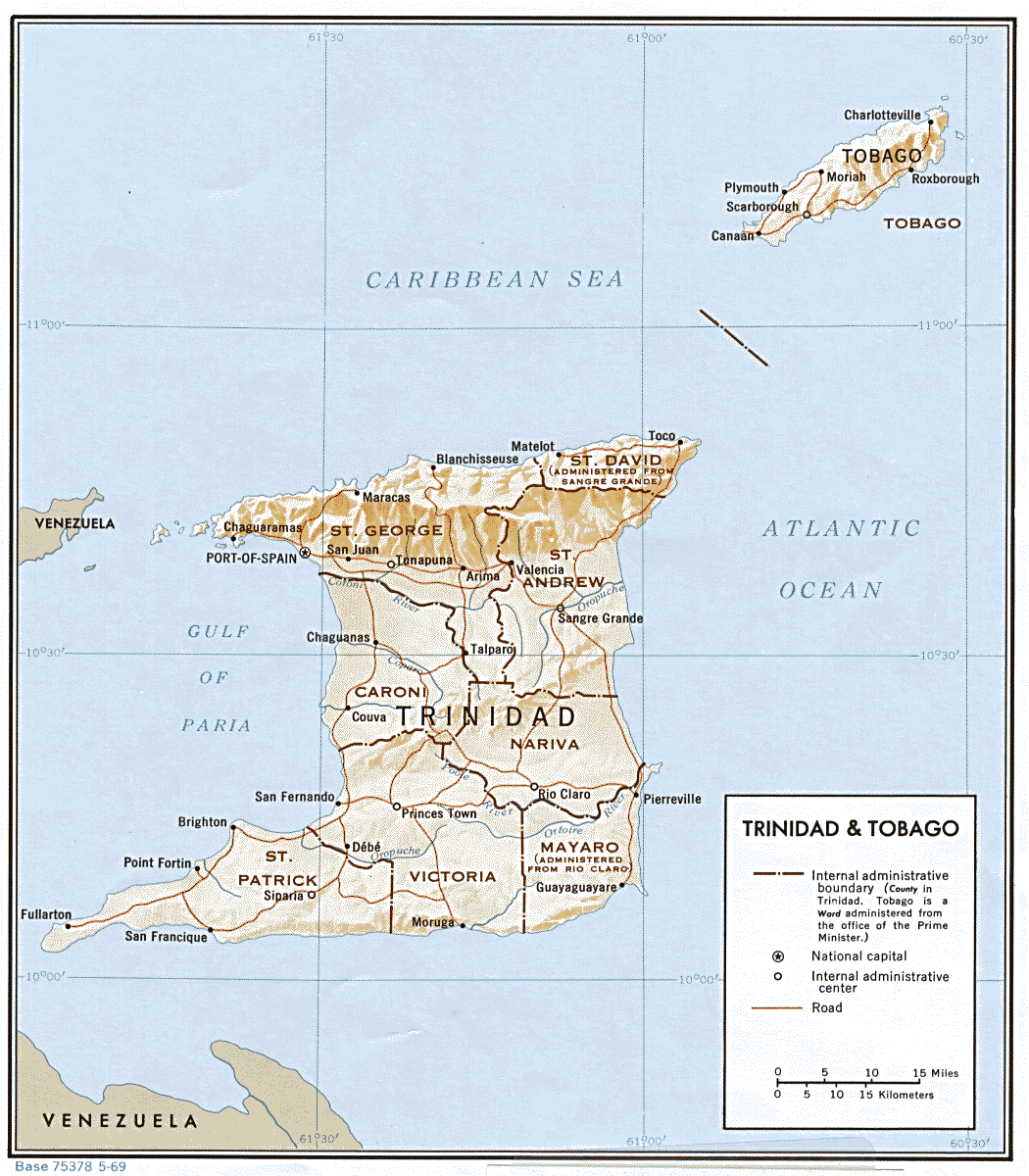
Icacos Point
Icacos Point is the southwesternmost point in Trinidad and Tobago. It is at the end of a long peninsula that forms Saint Patrick County. A channel called the Serpent's Mouth separates Icacos Point from the coast of Venezuela, only 11 kilometers away. A good image of the Serpent's mouth is seen in Travelling Luck's link which provides additional detail on the area "Although Icacos is referred to as a Point which suggests a narrow piece of land, parts of the area are also been referred to as a village in Teneil Nurse's blog where Ms Nurse writes on the history of Icacos. Activity & Places of Interest Icacos Beach The Icacos Beach which is photographed in the link, is identified as being after Icacos. While this may be so, given that Icacos is an area which is exposed to the sea on many sides, there may be other beaches worth exploring, however the state of the road may need to be taken into account in planning a visit to the beach in Icacos. Primary school In 2008, a new primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller islands, it is situated south of Grenada and off the coast of northeastern Venezuela. It shares maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Barbados to the northeast, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous city is San Fernando, Trinidad and Tobago, San Fernando. The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Patrick County
Saint Patrick was a county in Trinidad and Tobago that occupied an area of . It occupied the southwestern peninsula of the island of Trinidad, bounded by the Columbus Channel to the south, the Gulf of Paria to the west, and Victoria to the north. It included the towns of Point Fortin, La Brea, Siparia, Cedros, Fyzabad and Penal. Saint Patrick was divided into four Wards: Cedros, La Brea, Erin and Siparia. Prior to 1990, local government was administered by the Saint Patrick County Council and the Point Fortin Borough Corporation. After 1990, areas formerly administered by the Saint Patrick County Council were divided between Penal–Debe Regional Corporation Penal–Debe region is a region of Trinidad. The local government body is Penal–Debe Regional Corporation, a Regional Corporation of Trinidad and Tobago. The region has a land area of 246.91 km². Urban areas within Penal–Debe include ... and Siparia Regional Corporation. References * Counties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpent's Mouth
The Columbus Channel or Serpent's Mouth ( es, Boca de la Serpiente), is a strait lying between Icacos Point in southwest Trinidad and Tobago and the north coast of Venezuela. It leads from the Atlantic Ocean to the Gulf of Paria The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries .... The channel is about wide at its narrowest point. History The passage was named by Christopher Columbus on his third voyage. References Gulf of Paria Straits of Venezuela Bodies of water of Trinidad and Tobago International straits Trinidad and Tobago–Venezuela border {{Trinidad-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TnT Icacos Three Sisters 1
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts. History TNT was first prepared in 1863 by German chemist Julius Wilbrand and originally used as a yellow dye. Its potential as an explosive was not recognized for three decades, mainly because it was too difficult to detonate because it was less sensitive than alternatives. Its explosive properties were first discovered in 1891 by another German chemist, Carl Häussermann. TNT can be safely poured when liquid into shell cases, and is so insensitive that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Ibis
The scarlet ibis (''Eudocimus ruber'') is a species of ibis in the bird family Threskiornithidae. It inhabits tropical South America and part of the Caribbean. In form, it resembles most of the other twenty-seven extant species of ibis, but its remarkably brilliant scarlet coloration makes it unmistakable. It is one of the two national birds of Trinidad and Tobago, and its Tupi–Guarani name, guará, is part of the name of several municipalities along the coast of Brazil. This medium-sized wader is a hardy, numerous, and prolific bird, and it has protected status around the world. Its IUCN status is Least Concern. The legitimacy of ''Eudocimus ruber'' as a biological classification, however, is in dispute. Traditional Linnaean taxonomy classifies it as a unique species, but some scientists have moved to reclassify it as a subspecies of a more general American ibis species, along with its close relative, the American white ibis (''Eudocimus albus''). Taxonomy The species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TnT Icacos Coral Point 2
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts. History TNT was first prepared in 1863 by German chemist Julius Wilbrand and originally used as a yellow dye. Its potential as an explosive was not recognized for three decades, mainly because it was too difficult to detonate because it was less sensitive than alternatives. Its explosive properties were first discovered in 1891 by another German chemist, Carl Häussermann. TNT can be safely poured when liquid into shell cases, and is so insensitive that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |