|
Ibn Bayṭār
Diyāʾ al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Aḥmad al-Mālaqī, commonly known as Ibn al-Bayṭār () (1197–1248 AD) was an Andalusian Arab physician, botanist, pharmacist and scientist. His main contribution was to systematically record the additions made by Islamic physicians in the Middle Ages, which added between 300 and 400 types of medicine to the one thousand previously known since antiquity. He was a student of Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati. Life Ibn al-Baitar was born in the city of Málaga in al-Andalus (Muslim Spain) at the end of the twelfth century, hence his '' nisba'' "al-Mālaqī". His name "Ibn al-Baitar" is Arabic for "son of the veterinarian", which was his father's profession. Ibn al-Bayṭār learned botany from the Málagan botanist Abū al-ʿAbbās al-Nabātī with whom he started collecting plants in and around Spain. In 1219, Ibn al-Bayṭār left Málaga, travelling to the coast of North Africa and as far as Anatolia, to collect plants. The major sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
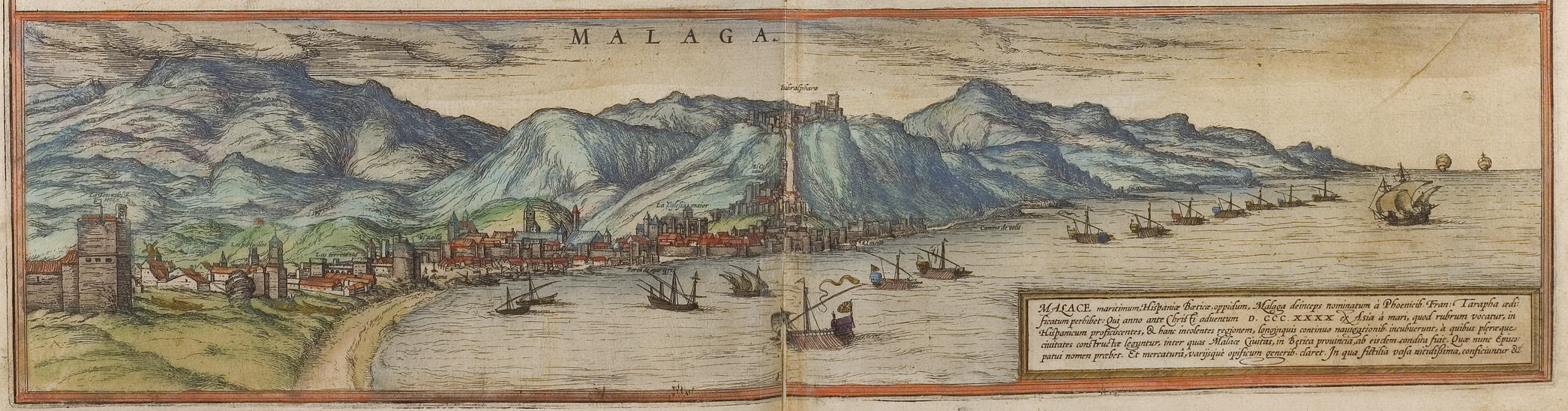
Málaga
Málaga (; ) is a Municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 591,637 in 2024, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia and the Ranked lists of Spanish municipalities#By population, sixth most populous in the country. It lies in Southern Iberian Peninsula, Iberia on the Costa del Sol ("Coast of the Sun") of the Mediterranean, primarily in the left bank of the Guadalhorce. The urban core originally developed in the space between the Gibralfaro, Gibralfaro Hill and the Guadalmedina. Málaga's history spans about 2,800 years, making it one of the List of cities by time of continuous habitation#Europe, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe. According to most scholars, it was founded about 770BC by the Phoenicians from Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre as ''Malaka''. From the 6th centuryBC the city was under the hegemony of Ancient Cartha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula as well as Septimania under Umayyad rule. These boundaries changed through a series of conquests Western historiography has traditionally characterized as the ''Reconquista'',"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalidad de las zonas conquistadas – siquiera temporalmente – por tropas arabo-musulmanas en territorios actualmente pertenecientes a Portugal, España y Francia" ("For medieval Arab authors, Al-Andalus designated all the conquered areas – even temporarily – by Arab-Muslim troops in territories now belonging to Spain, Portugal and France"), García de Cortázar, José Ángel. ''V Semana de Estudios Medievales: Nájera, 1 al 5 de agosto de 1994'', Gobie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacopoeia
A pharmacopoeia, pharmacopeia, or pharmacopoea (or the typographically obsolete rendering, ''pharmacopœia''), meaning "drug-making", in its modern technical sense, is a reference work containing directions for the identification of compound medicines. These are published or sanctioned by a government or a medical or pharmaceutical society, giving the work legal authority within a specified jurisdiction. In a broader sense it is a collection of pharmaceutical drug specifications. Descriptions of the individual preparations are called monographs. Etymology The term derives from "making of (healing) medicine, drug-making", a compound of "medicine, drug, poison" (), with the verb "to make" (), and the abstract noun suffix -ία ''-ia''. In early modern editions of Latin texts, the Greek diphthong οι (''oi'') is latinized to its Latin equivalent ''oe'' which is in turn written with the ligature ''œ'', giving the spelling ''pharmacopœia''; in modern UK English, ''œ'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltpetre
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or ''nitre'' outside the United States). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpetre (or saltpeter in the United States). Major uses of potassium nitrate are in fertilizers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants and fireworks. It is one of the major constituents of traditional gunpowder (black powder). In processed meats, potassium nitrate reacts with hemoglobin and myoglobin generating a red color. Etymology Nitre, or potassium nitrate, because of its early and global use and production, has many names. As for nitrate, Egyptian and Hebrew words for it had the consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Kamil
Al-Malik al-Kamil Nasir ad-Din Muhammad (; – 6 March 1238), titled Abu al-Maali (), was an Egyptian ruler and the fourth Ayyubid sultan of Egypt. During his tenure as sultan, the Ayyubids defeated the Fifth Crusade. He was known to the Frankish crusaders as Meledin, a name by which he is referred to in some older western sources. As a result of the Sixth Crusade, he ceded West Jerusalem to the Christians and is known to have met with Saint Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis. Biography Jazira campaign Al-Kamil was the son of the Kurds, Kurdish sultan al-Adil ("Saphadin"), a brother of Saladin. Al-Kamil's father was laying siege to the city of Mardin (in modern-day Turkey) in 1199 when he was called away urgently to deal with a security threat in Damascus. Al-Adil left al-Kamil to command the forces around Mardin continuing the siege. Taking advantage of the Sultan's absence, the combined forces of Mosul, Sinjar and Cizre, Jazirat ibn Umar appeared at Mardin when it was on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayyubid
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurds, Kurdish origin, Saladin had originally served the Zengid dynasty, Zengid ruler Nur al-Din Zengi, Nur al-Din, leading the latter's army against the Crusader invasions of Egypt, Crusaders in Fatimid Egypt, where he was made vizier (Fatimid Caliphate), vizier. Following Nur al-Din's death, Saladin was proclaimed as the first Sultan of Egypt by the Abbasid Caliphate, and rapidly expanded the new sultanate beyond Lower Egypt, Egypt to encompass most of Syria (region), Syria, in addition to Hijaz, Southern Arabia, Yemen, northern Nubia, Tripolitania and Upper Mesopotamia. Saladin's military campaigns set the general borders and sphere of influence of the sultanate of Egypt for the almost 350 years of its existence. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antalya
Antalya is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey and the capital of Antalya Province. Recognized as the "capital of tourism" in Turkey and a pivotal part of the Turkish Riviera, Antalya sits on Anatolia's southwest coast, flanked by the Taurus Mountains. The urban population of the city is 1,335,002 (Konyaalti, Kepez, Muratpasa), with a metropolitan population of 2,722,103.2011 Census Turkish Statistical Institute (Büyükşehir belediyeleri ve bağlı belediyelerin nüfusları) – 2011 The city was formerly known as Attalia and was founded in around 200 BC by King [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barqa
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, also known as ''Pentapolis'' ("Five Cities") in antiquity, was part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into ''Libya Pentapolis'' and ''Libya Sicca''. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as ''Barqa'', after the city of Barca. Cyrenaica became an Italian colony in 1911. After the 1934 formation of Italian Libya, the Cyrenaica province was designated as one of the three primary provinces of the country. During World War II, it fell under British military and civil administration from 1943 until 1951, and finally in the Kingdom of Libya from 1951 until 1963. The region that used to be Cyrenaica officially until 1963 has formed several shabiyat, the administrative divisions of Libya, since 1995. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripoli, Libya
Tripoli, historically known as Tripoli-of-the-West, is the capital city, capital and largest city of Libya, with a population of about 1.317 million people in 2021. It is located in the northwest of Libya on the edge of the desert, on a point of rocky land projecting into the Mediterranean Sea and forming a bay. It includes the port of Tripoli and the country's largest commercial and manufacturing center. It is also the site of the University of Tripoli. Tripoli was founded in the 7th century BC by the Phoenicians, who gave it the Libyco-Berber name (), before passing into the hands of the Greek rulers of Cyrenaica as Oea (). Due to the city's long history, there are many sites of archeological significance in Tripoli. ''Tripoli'' may also refer to the (top-level administrative division in the Libyan system), the Tripoli District, Libya, Tripoli District. Name In the Arab world, Tripoli is also known as "Tripoli-of-the-West" (), to distinguish it from Tripoli, Lebanon, known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casablanca and Algiers) and the List of largest cities in the Arab world, eleventh-largest in the Arab world. Situated on the Gulf of Tunis, behind the Lake of Tunis and the port of La Goulette (Ḥalq il-Wād), the city extends along the coastal plain and the hills that surround it. At its core lies the Medina of Tunis, Medina, a World Heritage Site. East of the Medina, through the Sea Gate (also known as the ''Bab el Bhar'' and the ''Porte de France''), begins the modern part of the city called "Ville Nouvelle", traversed by the grand Avenue Habib Bourguiba (often referred to by media and travel guides as "the Tunisian Champs-Élysées"), where the colonial-era buildings provide a clear contrast to smaller, older structures. Further east by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |