|
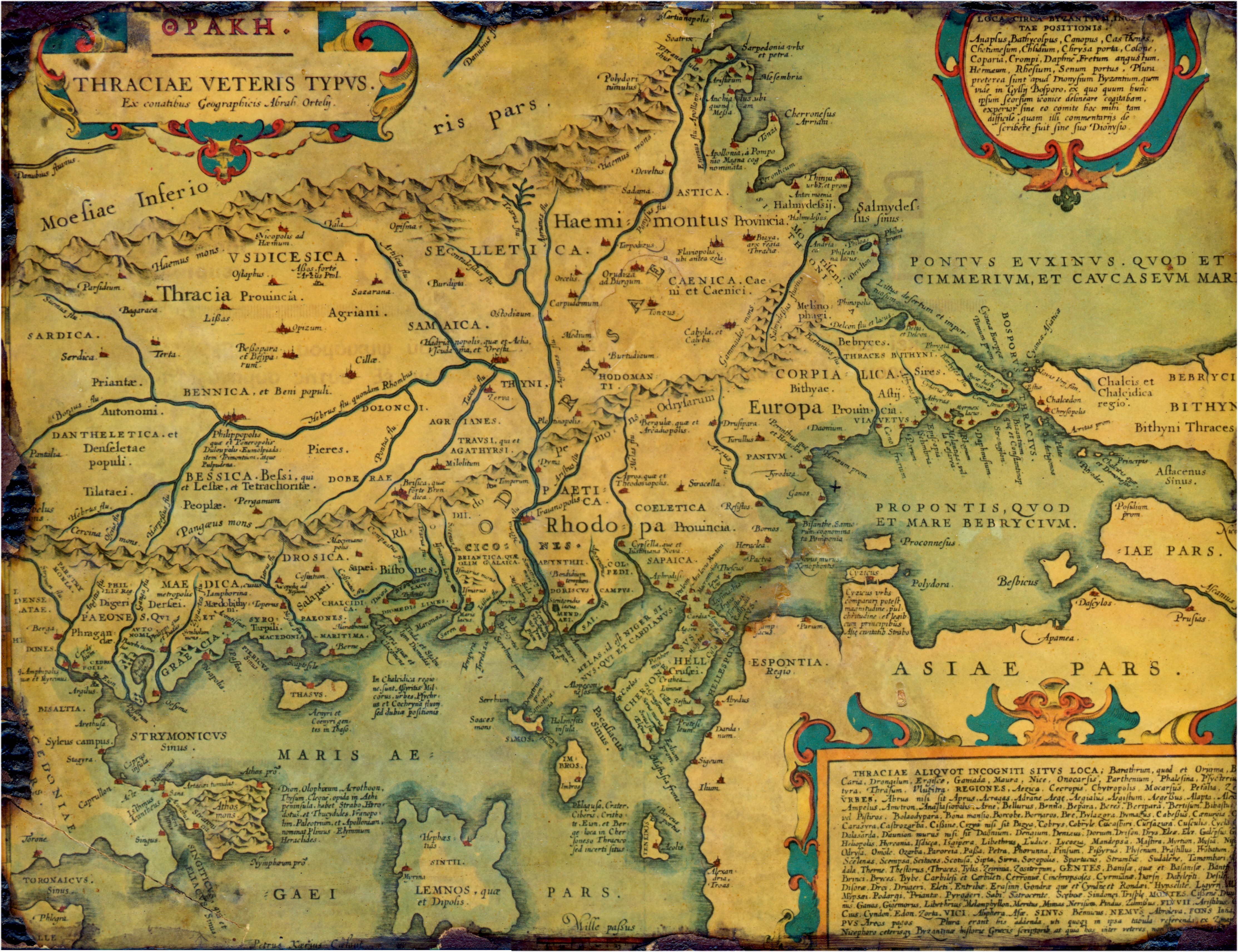
Iamphorynna
Iamphorina or Iamphorynna was the capital of the Maedi, a Thracian tribe in ancient Macedonia. It was taken by Philip V of Macedon in 211 BCE. Writing in the 19th century, William Martin Leake placed it at Ivorina (Vrania), in the upper valley of the Morava River. Modern scholars treat it as unlocated. Stephanus of Byzantium, citing Diodorus Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, b ..., has the name as Phorunna or Phorounna (). References Populated places in ancient Macedonia Former populated places in the Balkans Thracian towns Lost ancient cities and towns {{AncientMacedonia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian Towns
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Thracian and Dacian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Thrace and Dacia were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maedi
The Maedi (also ''Maidans'', ''Maedans'', or ''Medi''; ) were a Thracian tribe in antiquity. Their land was called Maedica (Μαιδική). In historic times, they occupied the area between Paionia and Thrace, on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along the middle course of the Strymon, between the Kresna Gorge and the Rupel Pass (present-day southwestern Bulgaria). Strabo says that the Maedi bordered eastward on the Thunatae of Dardania, and that the Axius flowed through their territory. Their capital city was Iamphorynna, which lay somewhere in the southwest corner of what is now Bulgaria. Some archaeologists posit it in the area between the cities of Petrich and Sandanski, but its exact location remains unknown. They were an independent tribe through much of their history, and the Thracian king Sitalkes recognized their independence, along with several other warlike "border" tribes such as the Dardani, Agrianes, and Paeonians, whose lands formed a buffer z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, Romania, and north-western Turkey. They shared the same language and culture. There may have been as many as a million Thracians, divided among up to 40 tribes." Thracians resided mainly in Southeast Europe in modern-day Bulgaria, Romania, North Macedonia, northern Greece and European Turkey, but also in north-western Anatolia (Asia Minor) in Turkey. The exact origin of the Thracians is uncertain, but it is believed that Thracians like other Indo-European speaking groups in Europe descended from a mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers. Around the 5th millennium BC, the inhabitants of the eastern region of the Balkans became organized in different groups of indigenous people that were later named by the ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Macedonia
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the southwest, Illyria to the northwest, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip V Of Macedon
Philip V (; 238–179 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War (220–217 BC), Social War in Greece (220-217 BC) and a struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First Macedonian War, First (212-205 BC) and Second Macedonian War, Second (200-196 BC) Macedonian Wars. While he lost the latter, Philip later allied with Rome against Antiochus III the Great, Antiochus III in the Roman–Seleucid war, Roman-Seleucid War. He died in 179 BC from illness after efforts to recover the military and economic condition of Macedonia and passed the throne onto his elder son, Perseus of Macedon. Early life Philip was the son of Demetrius II of Macedon, and either Phthia of Macedon or Chryseis. Philip was nine years old when his father died in 229 BC. His elder paternal half-sister was Apama III. Philip's grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Martin Leake
William Martin Leake FRS (14 January 17776 January 1860) was an English soldier, spy, topographer, diplomat, antiquarian, writer, and Fellow of the Royal Society. He served in the British Army, spending much of his career in the Mediterranean seaports. He developed an interest in geography and culture of the regions visited, and authored a number of works, mainly about Greece. Life Leake was born in London to John Martin Leake and Mary Calvert Leake. Following a family tradition, he joined the British Royal Regiment of Artillery as an officer; he completed his training at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich in 1794 and was commissioned as a second lieutenant. Having spent four years in the West Indies as lieutenant of marine artillery, he was promoted to captain, and was sent in 1799 by the government to Constantinople to train the forces of the Ottoman Empire in the use of artillery. The British Empire had decided to support the Ottoman in its defence against Napoleonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morava (river)
The Morava () is a river in Central Europe, a left tributary of the Danube. It is the main river of Moravia historical region in the Czech Republic, which derives its name from the river. The Morava originates on the Králický Sněžník mountain in the north-eastern corner of Pardubice Region, near the border between the Czech Republic and Poland and has a vaguely southward trajectory. The lower part of the river's course forms the border between the Czech Republic and Slovakia and then between Austria and Slovakia. Etymology The root of the river's name, ''mor-'', is derived from the Proto-Indo-European word for 'water', 'marsh', from which the Latin word ''mare'' arose. The suffix ''-ava'' is a Slavic form of the Proto-Germanic word ''ahwa'', meaning 'water', 'river'. The name of the river was first documented as ''Maraha'' in an 892 deed. The river gave its name to the entire historical land of Moravia, yet the oldest surviving record of the land (from 822) is older than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanus Of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephen of Byzantium (; , ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD) was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epitome is extant, compiled by one Hermolaus, not otherwise identified. Life Nothing is known about the life of Stephanus, except that he was a Greek grammarian who was active in Constantinople, and lived after the time of Arcadius and Honorius, and before that of Justinian II. Later writers provide no information about him, but they do note that the work was later reduced to an epitome by a certain Hermolaus, who dedicated his epitome to Justinian; whether the first or second emperor of that name is meant is disputed, but it seems probable that Stephanus flourished in Byzantium in the earlier part of the sixth century AD, under Justinian I. The ''Ethnica'' Stephanos' work, originally written in Greek, takes the form of an alphabetical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, between 60 and 30 BC. The history is arranged in three parts. The first covers mythic history up to the destruction of Troy, arranged geographically, describing regions around the world from Egypt, India and Arabia to Europe. The second covers the time from the Trojan War to the death of Alexander the Great. The third covers the period to about 60 BC. ''Bibliotheca'', meaning 'library', acknowledges that he was drawing on the work of many other authors. Life According to his own work, he was born in Agyrium in Sicily (now called Agira). With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about his life and doings beyond his written works. Only Jerome, in his '' Chronicon'' under the "year of Abraham 1968" (49 BC), writes, "D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Macedonia
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In The Balkans
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third ed ..., typically perpendicular to the Flight control surfaces#Longitudinal_axis, longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |