|
IWI Tavor 7
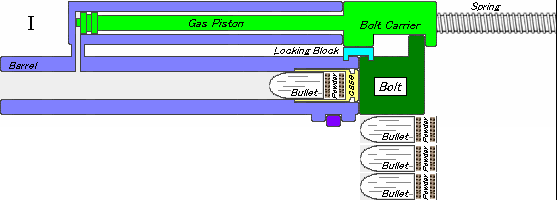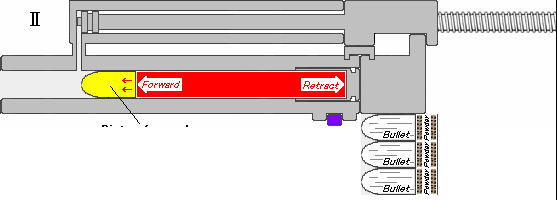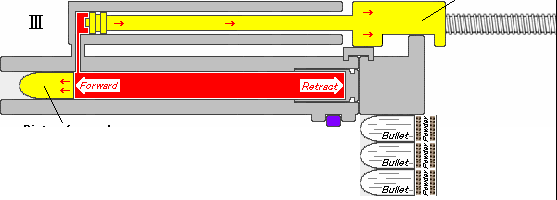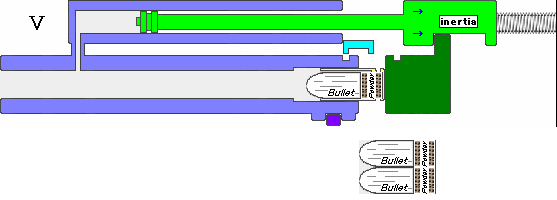
The IWI Tavor 7 is an Israeli bullpup battle rifle chambered in 7.62×51mm NATO cartridge designed and produced by Israel Weapon Industries (IWI) as part of the Tavor rifle family. It is a fully ambidextrous rifle. Design The Tavor 7 is in a bullpup configuration, the same as all the other rifles in the family. It uses a short-stroke gas piston system, unlike the two previous rifles, which utilized a long-stroke gas piston system, similar to the Galil and Kalashnikov rifles. This decreases recoil, as there is not as much mass cycling with each shot. The Tavor 7 also has a gas regulator with four positions: regular (R), adverse/extreme (A), suppressed/suppressor (S), and off/closed, intended for special operations. It has a hammer-forged, chrome-lined and free-floating barrel, with four RH grooves with a 1:12" right hand rifling twist. The Tavor 7 is fed by SR-25 pattern magazines. The Tavor 7's external aesthetics are very similar to the original Tavor TAR-21, while the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullpup
A bullpup firearm is one with its firing grip located in front of the breech of the weapon, instead of behind it. This creates a weapon with a shorter overall length for a given barrel length, and one that is often lighter, more compact, concealable and more maneuverable than a conventionally configured firearm. Where it is desirable for troops to be issued a more compact weapon, the use of a bullpup configuration allows for barrel length to be retained, thus preserving muzzle velocity, range and ballistic effectiveness. The bullpup concept was first tested militarily in 1901 with the British Thorneycroft carbine, but it was not until the Cold War that more successful designs and improvements led to wider adoption. In 1977, the Austrian Army became the first military force in the world to adopt a bullpup rifle, the Steyr AUG, as a principal combat weapon. Since then the militaries in many countries have followed suit with other bullpup designs, such as the Chinese QBZ-95, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullpup Rifles
A bullpup firearm is one with its firing grip located in front of the breech of the weapon, instead of behind it. This creates a weapon with a shorter overall length for a given barrel length, and one that is often lighter, more compact, concealable and more maneuverable than a conventionally configured firearm. Where it is desirable for troops to be issued a more compact weapon, the use of a bullpup configuration allows for barrel length to be retained, thus preserving muzzle velocity, range and ballistic effectiveness. The bullpup concept was first tested militarily in 1901 with the British Thorneycroft carbine, but it was not until the Cold War that more successful designs and improvements led to wider adoption. In 1977, the Austrian Army became the first military force in the world to adopt a bullpup rifle, the Steyr AUG, as a principal combat weapon. Since then the militaries in many countries have followed suit with other bullpup designs, such as the Chinese QBZ- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifles Of Israel
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with both hands and braced firmly against the shooter's shoulder via a buttstock for stability during shooting. Rifles are used extensively in warfare, law enforcement, hunting, shooting sports, and crime. The term was originally ''rifled gun'', with the verb ''rifle'' referring to the early modern machining process of creating groovings with cutting tools. By the 20th century, the weapon had become so common that the modern noun ''rifle'' is now often used for any long-shaped handheld ranged weapon designed for well-aimed discharge activated by a trigger (e.g., personnel halting and stimulation response rifle, which is actually a laser dazzler). Like all typical firearms, a rifle's projectile (bullet) is propelled by the contained defla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IWI Tavor TS12
The IWI Tavor TS12 is an Israeli semi-automatic bullpup shotgun, based on the IWI Tavor assault rifle. The Tavor TS12 is designed and produced by Israel Weapon Industries (IWI). The TS12 was the best selling semi-automatic shotgun on GunBroker.com in 2020. History In January 2018, the TS12, which was the first bullpup shotgun developed by IWI, was revealed at SHOT Show The SHOT Show , which is an acronym for "Shooting, Hunting and Outdoor Trade Show", is an American annual trade show for the shooting sports, hunting, outdoor recreations and firearm manufacturing industries. The show is owned and sponsored by ..., and released on the market the same year. Design The TS12 loads its shells into three magazine tubes, each of which contain a total of five shells, allowing for a maximum of 15 + 1 shells. The tubes can be rotated via a button on the pistol grip. The TS12 has a Picatinny rail, with receptacles on both the left and right. References External links Offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-automatic Rifle
A semi-automatic rifle is an autoloading rifle that fires a single cartridge with each pull of the trigger, and uses part of the fired cartridge's energy to eject the case and load another cartridge into the chamber. For comparison, a bolt-action rifle requires the user to cycle the bolt manually before they can fire a second time, and a fully automatic rifle fires continuously until the trigger is released. History The first design of a recoil-operated semi-automatic rifle is attributed to Ferdinand Mannlicher, who unveiled the design in 1885 based on work begun in 1883. Other non-gas operated semi-automatic models were the Model 85 and Mannlicher Models 91, 93 and 95 rifles. The designs were deeply flawed and never made past the conceptual/prototype stage due to issues inherent to the black powder used in their cartridges (based around the Austrian 11×58mmR M/77), such as insufficient velocity and excessive fouling; automatic firearms would only become feasible after s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designated Marksman Rifle
A designated marksman rifle (DMR) is a modern scoped high- precision rifle used by infantrymen in the designated marksman (DM) role. It generally fills the engagement range gap between a service rifle and a dedicated sniper rifle, at around . DMRs, unlike the often bolt-action sniper rifles, are semi-automatic as these have higher rates of fire and typically larger magazine capacities (10, 20, or 30 rounds depending on the firearm and operational requirements) to allow rapid engagement of multiple targets. These rifles have to be effective, in terms of hit rates and terminal ballistics, at application ranges exceeding those of ordinary assault rifles and battle rifles, but do not require the extended-range performance of a dedicated sniper rifle. DMRs need to function as part of squad (and possibly at close quarters) and often share some basic characteristics with sniper rifles when compared to other weapons carried in the DM's platoon. They typically have telescopi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heckler & Koch MP5
The Heckler & Koch MP5 (german: Maschinenpistole 5) is a 9x19mm Parabellum submachine gun, developed in the 1960s by a team of engineers from the German small arms manufacturer Heckler & Koch. There are over 100 variants and clones of the MP5, including some semi-automatic versions. The MP5 is one of the most widely used submachine guns in the world,Hogg, Ian (2002). ''Jane's Guns Recognition Guide''. Jane's Information Group. . having been adopted by over forty nations and numerous military, law enforcement, intelligence, and security organizations. In 1999, Heckler & Koch developed the UMP, the MP5's successor. Despite its higher cost, the MP5 remained the more successful of the two options. History Heckler & Koch, encouraged by the success of the G3 automatic rifle, developed a family of small arms consisting of four types of firearms all based on a common G3 design layout and operating principle. The first type was chambered for 7.62×51mm NATO, the second for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
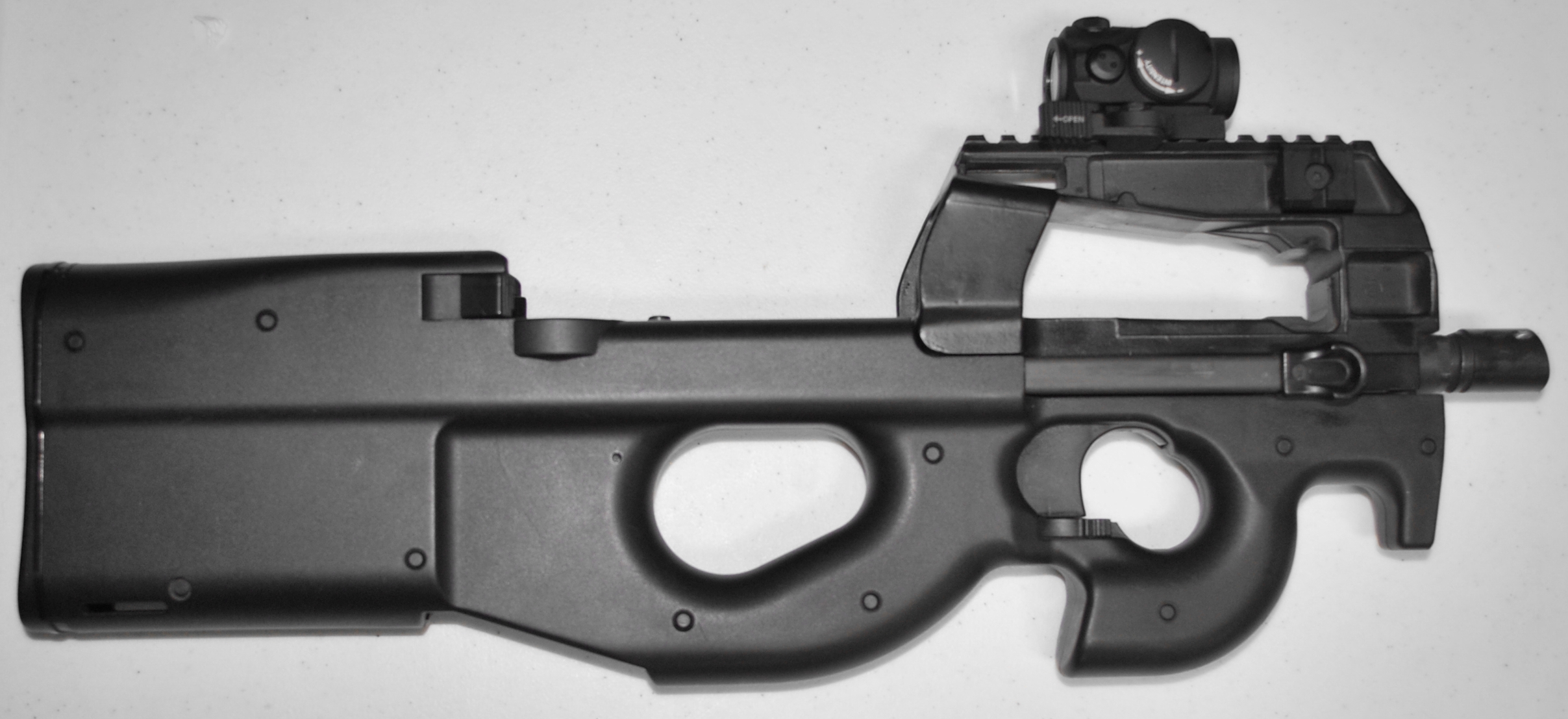
IWI Tavor X95
The IWI X95 (formerly known as the Micro-Tavor, MTAR or MTAR-21) is an Israeli bullpup assault rifle designed and produced by Israel Weapon Industries (IWI) as part of the Tavor rifle family, along with the TAR-21 and the Tavor 7. IWI US offers the rifle in semi-automatic only configuration as the 'Tavor X95'. In November 2009, the X95 was selected as the future standard issue weapon of the Israeli infantry.מיקרו–תבור לכל לוחם חי"ר . Dover.idf.il. Retrieved on 2010-08-31. Design The X95 can be easily distinguished from the TAR-21 (as well as from the CTAR-21, STAR-21, and GTAR-21) by the location of its |
Kalashnikov Rifle
A Kalashnikov (Калашников) rifle is any one of a series of automatic rifles based on the original design of Mikhail Kalashnikov. They are officially known in Russian as "Avtomát Kaláshnikova" ( rus, Автома́т Кала́шникова, t=Kalashnikov's Automatic Gun), but are widely known as Kalashnikovs, AKs, or in Russian slang, a "Kalash". They were originally manufactured in the Soviet Union, primarily by Kalashnikov Concern, formerly Izhmash, but these rifles and their variants are now manufactured in many other countries. The Kalashnikov is one of the most widely used guns in the world, with an estimated 72 million rifles in global circulation. Types The original Kalashnikov rifles and their derivatives, as produced in the Soviet Union and later the Russian Federation. Variants Original AK variants ( 7.62×39mm) * Issue of 1948/49 – The very earliest models, with the Type 1 stamped sheet metal receiver, are now very rare. * Issue of 1951 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMI Galil
The IMI Galil ( he, גליל) is a family of Israeli-made automatic rifles chambered for the 5.56×45mm NATO and 7.62×51mm NATO cartridges. Originally designed by Yisrael Galili and Yakov Lior in the late 1960s, the Galil was first produced by the state-owned Israel Military Industries and is now exported by the privatized Israel Weapon Industries. The first Galil rifle was manufactured using RK 62 receivers.Knupp, Jeremiah (December 28, 2017"Galil ACE: IWI Brings the AK Into the Modern Era" '' American Rifleman''. Moreover, the Galil design is largely based on the Finnish rifle RK 62 (itself a derivative of the AK-47). The Galil family of weapons is used by both military and police forces across 25 countries. The Israeli Army initially deployed the 5.56×45mm NATO Galil in three basic configurations; the Automatic Rifle Machine-gun (ARM), the Automatic Rifle (AR), and the Short Automatic Rifle (SAR). A modern version of the Galil currently in production in multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavor
The IWI Tavor TAR-21 is an Israeli bullpup assault rifle chambered in 5.56×45mm NATO caliber with a selective fire system, selecting between semi-automatic mode and full automatic fire mode. The Tavor is designed and produced by Israel Weapon Industries (IWI). It is produced in two main variants: the TAR-21 and the CTAR-21. Built around a long-stroke piston system (as found in the M1 Garand and AK-47), the Tavor is designed to maximize reliability, durability, simplicity of design, and ease of maintenance, particularly under adverse or battlefield conditions. In 2009, the Tavor X95 (also known as the Micro Tavor or MTAR) was selected by the Israeli Defense Forces to gradually replace the M16 assault rifle and M4 carbine variants as the standard-issued weapon of the Israeli infantry by the end of 2018. The first X95 bullpup rifles were issued to infantry units in 2013. Both the TAR-21 and X95 are part of the Tavor family of rifles, along with the Tavor 7. In the beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |