|
IFR
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR). The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument Flying Handbook'' defines IFR as: "Rules and regulations established by the FAA to govern flight under conditions in which flight by outside visual reference is not safe. IFR flight depends upon flying by reference to instruments in the flight deck, and navigation is accomplished by reference to electronic signals." It is also a term used by pilots and controllers to indicate the type of flight plan an aircraft is flying, such as an IFR or VFR flight plan. Basic information Comparison to visual flight rules It is possible and fairly straightforward, in relatively clear weather conditions, to fly an aircraft solely by reference to outside visual cues, such as the horizon to maintain orientation, nearby buildings and terrain features for na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFR On Top
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR). The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument Flying Handbook'' defines IFR as: "Rules and regulations established by the FAA to govern flight under conditions in which flight by outside visual reference is not safe. IFR flight depends upon flying by reference to instruments in the flight deck, and navigation is accomplished by reference to electronic signals." It is also a term used by pilots and controllers to indicate the type of flight plan an aircraft is flying, such as an IFR or VFR flight plan. Basic information Comparison to visual flight rules It is possible and fairly straightforward, in relatively clear weather conditions, to fly an aircraft solely by reference to outside visual cues, such as the horizon to maintain orientation, nearby buildings and terrain features for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is the expanse or space outside the Earth and aerospace which is the general term for Earth's atmosphere and the outer space within the planet's vicinity. Horizontal boundary By international law, a state "has complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above its territory", which corresponds with the maritime definition of territorial waters as being 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) out from a nation's coastline. Airspace not within any country's territorial limit is considered international, analogous to the "high seas" in maritime law. However, a country may, by international agreement, assume responsibility for controlling parts of international airspace, such as those over the oceans. Such airspace in respect of which a countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Flight Rules
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) is a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e., in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft. If the weather is less than VMC, pilots are required to use instrument flight rules, and operation of the aircraft will be primarily through referencing the instruments rather than visual reference. In a control zone, a VFR flight may obtain a clearance from air traffic control to operate as Special VFR. Requirements VFR requires a pilot to be able to see outside the cockpit to control the aircraft's altitude, navigate, and avoid obstacles and other aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
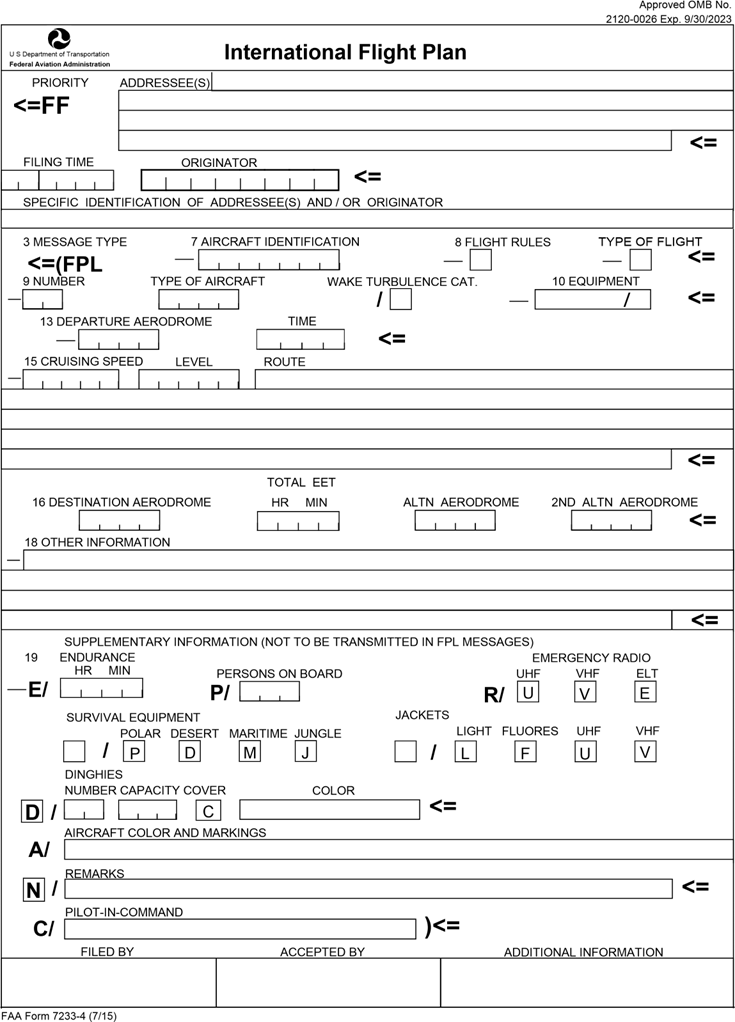
Flight Plan
Flight plans are documents filed by a aviator, pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider (e.g., the Federal Aviation Administration, FAA in the United States) prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is specified in ICAO Doc 4444. They generally include basic information such as departure and arrival points, estimated time en route, alternate airports in case of bad weather, type of flight (whether instrument flight rules [IFR] or visual flight rules [VFR]), the pilot's information, number of people on board, and information about the aircraft itself. In most countries, flight plans are required for flights under IFR, but may be optional for flying VFR unless crossing international borders. Flight plans are highly recommended, especially when flying over inhospitable areas such as water, as they provide a way of alerting rescuers if the flight is overdue. In the United States and Canada, when an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Meteorological Conditions
In aviation, instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) are weather conditions that require pilots to fly primarily by reference to flight instruments, and therefore under instrument flight rules (IFR), as opposed to flying by outside visual references under visual flight rules (VFR). Typically, this means flying in cloud or poor weather, where little or nothing can be seen or recognised when looking out of the window. Simulated IMC can be achieved for training purposes by wearing view-limiting devices, which restrict outside vision and force the trainee to rely on instrument indications only. Distinction from Visual Meteorological Conditions The weather conditions required for flight under VFR are known as visual meteorological conditions (VMC). The boundary criteria between VMC and IMC are known as ''VMC minima''. IMC and VMC are mutually exclusive. In fact, instrument meteorological conditions are defined as less than the minima specified for visual meteorological conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Approach
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point from which a landing may be made Visual approach, visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities, and in the United States by the Federal Aviation Administration, FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as "a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding (aviation), holding or ''en route'' obstacle clearance criteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Meteorological Conditions
In aviation, visual meteorological conditions (VMC) is an aviation flight category in which visual flight rules (VFR) flight is permitted—that is, conditions in which pilots have sufficient visibility to fly the aircraft maintaining visual separation from terrain and other aircraft. They are the opposite of instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). The boundary criteria between IMC and VMC are known as the VMC minima and are defined by: visibility, cloud ceilings (for takeoffs and landings), and cloud clearances. The exact requirements vary by type of airspace, whether it is day or night (for countries that permit night VFR), and from country to country. Typical visibility requirements vary from one statute mile to five statute miles (many countries define these in metric units as 1,500 m to 8 km). Typical cloud clearance requirements vary from merely remaining clear of clouds to remaining at least one mile away (1,500 m in some countries) from clouds horizontally and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Airspace
Controlled airspace is airspace of defined dimensions within which air traffic control (ATC) services are provided. The level of control varies with different airspace class, classes of airspace. Controlled airspace usually imposes higher weather minimums than are applicable in uncontrolled airspace. It is the opposite of uncontrolled airspace. Controlled airspace is established mainly for three different reasons: * high-volume air traffic areas, e.g. near airports * Instrument flight rules traffic under ATC guidance * security, e.g. within an air defense identification zone Controlled airspace usually exists in the immediate vicinity of busier airports, where aircraft used in commercial air transport flights are climbing out from or making an approach to the airport, or at higher Above Ground Level, levels where air transport flights would tend to cruise. Some countries also provide controlled airspace almost generally, however in most countries it is common to provide uncon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' include fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air aircraft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Clément Ader built the "Ader Éole" in France and made an uncontrolled, powered hop in 1890. This was the first powered aircraft, although it did not achieve controlled flight. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896. A major leap followed with the construction of the '' Wright Flyer'', the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet engine which enabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |